AVPlayer 本地 Cache 實作攻略|使用 AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate 節省 iOS 音樂串流流量
針對 iOS 音樂串流播放需求,實現 AVPlayer 本地 Cache 功能,避免重複下載同一檔案,降低流量成本;透過自訂 Resource Loader 與 PINCache 管理快取,支援分段 Range 請求與播放不中斷,提升使用體驗與效能。
基於 SEO 考量,本文標題與描述經 AI 調整,原始版本請參考內文。
文章目錄
AVPlayer 實踐本地 Cache 功能大全
AVPlayer/AVQueuePlayer with AVURLAsset 實作 AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate
Photo by Tyler Lastovich
[2023/03/12] Update
我將之前的實作開源了,有需求的朋友可直接使用。
- 客製化 Cache 策略,可以用 PINCache or 其他…
- 外部只需呼叫 make AVAsset 工廠,帶入 URL,則 AVAsset 就能支援 Caching
- 使用 Combine 實現 Data Flow 策略
- 寫了一些測試
前言
既上一篇「 iOS HLS Cache 實踐方法探究之旅 」後已過了大半年,團隊還是一直想要實現邊播邊 Cache 功能因為對成本的影響極大;我們是音樂串流平台,如果每次播放同樣的歌曲都要重新拿整個檔案,對我們或對非吃到飽的使用者來說都很傷流量,雖然音樂檔案頂多幾 MB,但積沙成塔都是錢!
另外因為 Android 那邊已經有實作邊播邊 Cache 的功能了,之前有比較過花費,Android 端上線後明顯節省了許多流量;相對更多使用者的 iOS 應該能有更好的節流體現。
根據 上一篇 的經驗,如果我們要繼續使用 HLS ( .m3u8/.ts) 來達成目的;事情將會變得非常複雜甚至無法達成;我們退而求其次退回去使用 mp3 檔,這樣就能直接使用 AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate 進行實作。
目標
- 播放過的音樂會在本地產生 Cache 備份
- 播放音樂時先檢查本地有無 Cache 讀取,有則不再重伺服器要檔案
- 可設 Cache 策略;上限總容量,超過時開始刪除最舊的 Cache 檔案
- 不干涉原本 AVPlayer 播放機制 (不然最快的方法就是自己先用 URLSession 把 mp3 載下來塞給 AVPlayer,但這樣就失去原本能播到哪載到哪的功能,使用者需要等待更長時間&更消耗流量)
前導知識 (1)— HTTP/1.1 Range 範圍請求、Connection Keep-Alive
HTTP/1.1 Range 範圍請求
首先我們要先了解在播放影片、音樂時是怎麼跟伺服器要求資料的;一般來說影片、音樂檔案都很大,不可能等到全部拿完才開始播放常見的是播到哪拿到了,只要有正在播放區段的資料就能運作。
要達到這個功能的方法就是透過 HTTP/1.1 Range 只返回指定資料字節範圍的資料,例如指定 0–100 就只返回 0–100 這 100 bytes 大小的資料;透過這個方法,可以依序分段取得資料,然後再彙整再一起成完整的檔案;這個方法也能運用在檔案下載續傳功能上。
如何應用?
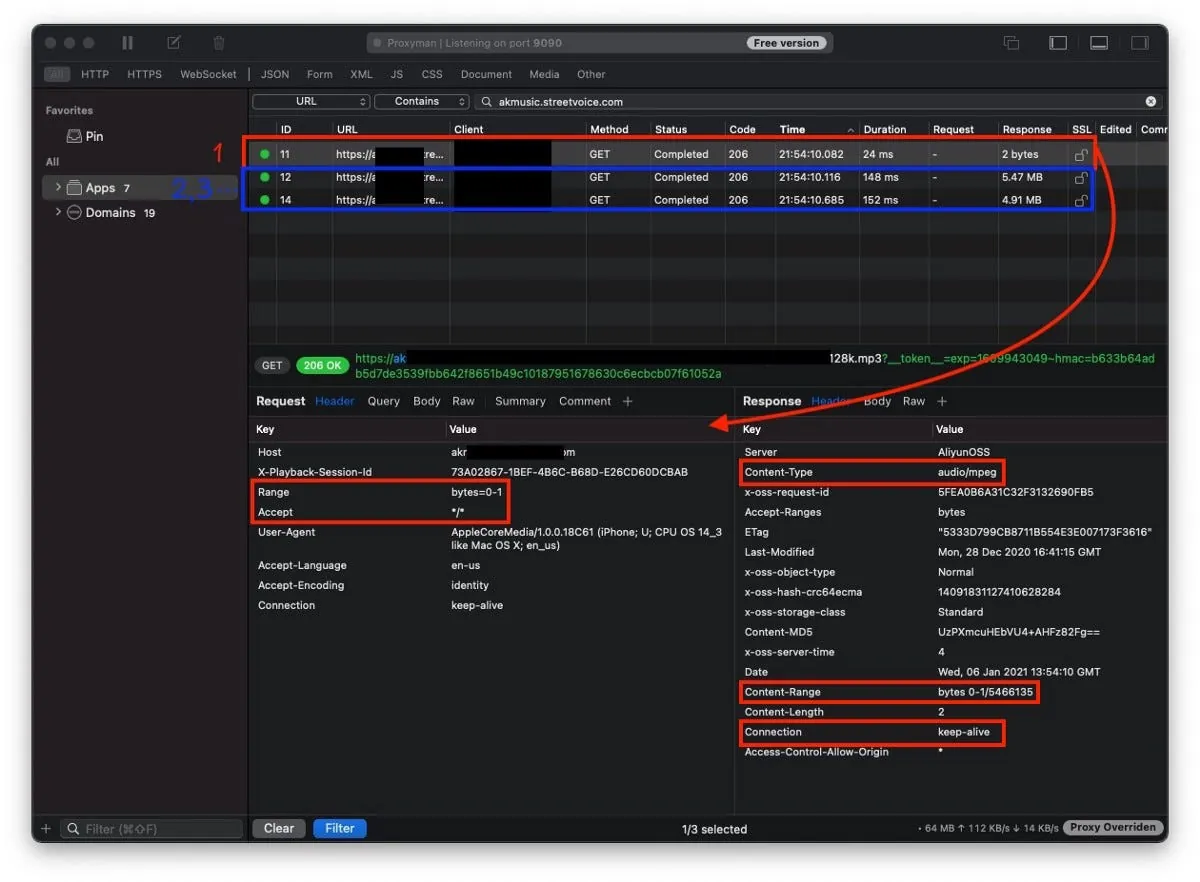
我們會先使用 HEAD 去看 Response Header 了解到伺服器是否支援 Range 範圍請求、資源總長度、檔案類型:
1
curl -i -X HEAD http://zhgchg.li/music.mp3
使用 HEAD 我們能從 Response Header 得到以下資訊:
- Accept-Ranges: bytes 代表伺服器支援 Range 範圍請求 如果沒有 Response 這個值或是是 Accept-Ranges: none 都代表不支援
- Content-Length: 資源總長度,我們要知道總長度才能去分段要資料。
- Content-Type: 檔案類型,AVPlayer 播放時需要知道的資訊。
但有時我們也會使用 GET Range: bytes=0–1 ,意思是我要求 0–1 範圍的資料但實際我根本不 Care 0–1是什麼內容,我只是要看 Response Header 的資訊; 原生 AVPlayer 就是使用 GET 去看,所以本篇也照舊使用 。
但比較建議使用 HEAD 去看,一方法比較正確,另一方面萬一伺服器不支援 Range 功能;用 GET 去摸就會變強迫下載完整檔案。
1
curl -i -X GET http://zhgchg.li/music.mp3 -H "Range: bytes=0–1"
使用 GET 我們能從 Response Header 得到以下資訊:
- Accept-Ranges: bytes 代表伺服器支援 Range 範圍請求 如果沒有 Response 這個值或是是 Accept-Ranges: none 都代表不支援
- Content-Range: bytes 0–1/資源總長度 ,「/」後的數字及資源總長度,我們要知道總長度才能去分段要資料。
- Content-Type: 檔案類型,AVPlayer 播放時需要知道的資訊。
知道伺服器支援 Range 範圍請求後,就能分段發起範圍請求:
1
curl -i -X GET http://zhgchg.li/music.mp3 -H "Range: bytes=0–100"
伺服器會返回 206 Partial Content:
1
2
3
4
Content-Range: bytes 0-100/總長度
Content-Length: 100
...
(binary content)
這時我們就得到 Range 0–100 的 Data,可再繼續發新請求拿 Range 100–200. .200–300…到結束。
如果拿的 Range 超過資源總長度會返回 416 Range Not Satisfiable。
另外,想拿完整檔案資料除了可以請求 Range 0-總長度,也可以使用 0- 方式即可:
1
curl -i -X GET http://zhgchg.li/music.mp3 -H "Range: bytes=0–"
其他還可以同個請求要求多個 Range 資料及下條件式子,但我們用不到,詳情可 參考這 。
Connection Keep-Alive
http 1.1 預設是開啟狀態, 此特性能實時取得已下載的資料 ,例如檔案 5 mb,能 16 kb、16 kb、16 kb… 的取得,不用等到 5mb 都好才給你。
1
Connection: Keey-Alive
如果發現伺服器不支援 Range、 Keep-Alive ?
那也不用搞這麼多了,直接自己用 URLSession 下載完 mp3 檔案塞給播放器就好….但這不是我們要的結果,可以請後端幫忙修改伺服器設定。
前導知識 (2) — AVPlayer 原生是如何處理 AVURLAsset 資源?
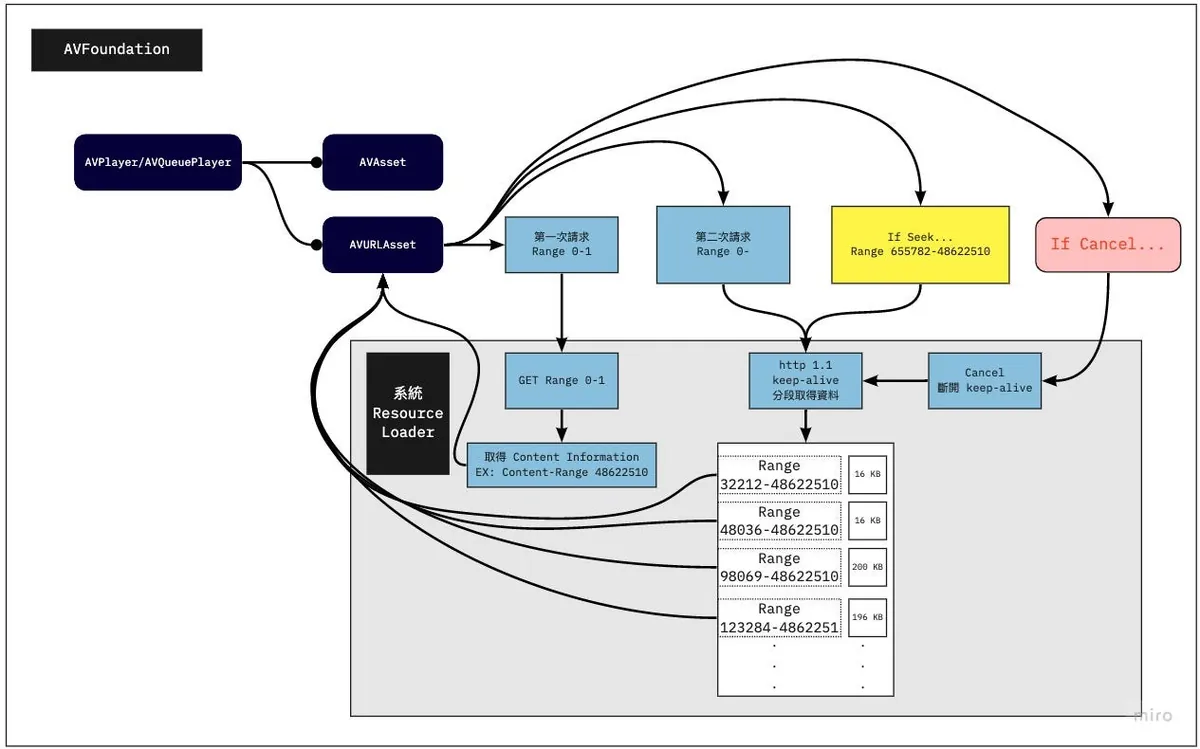
當我們使用 AVURLAsset init with URL 資源並賦予給 AVPlayer/AVQueuePlayer 開始播放之後,同上所述,首先會用 GET Range 0–1 去取得是否支援 Range 範圍請求、資源總長度、檔案類型這三個資訊。
有了檔案資訊後,會再發起第二次請求,請求從 0-總長度 的資料。
⚠️ AVPlayer 會請求從 0-總長度 的資料,並透過實時取得已下載的資料特性 ( 16 kb、16 kb、16 kb…) 取得到他覺得資料足夠後,會發起 Cancel 取消這個網路請求 (所以實際也不會拿完,除非檔案太小)。
繼續播放後才會透過 Range 往後請求資料。
(這部分跟我之前想的不一樣,我以為會是0–100、100–200. .這樣請求)
AVPlayer 請求範例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
1. GET Range 0-1 => Response: 總長度 150000 / public.mp3 / true
2. GET 0-150000...
3. 16 kb receive
4. 16 kb receive...
5. cancel() // current offset is 700
6. 繼續播放
7. GET 700-150000...
8. 16 kb receive
9. 16 kb receive...
10. cancel() // current offset is 1500
11. 繼續播放
12. GET 1500-150000...
13. 16 kb receive
14. 16 kb receive...
16. If seek to...5000
17. cancel(12.) // current offset is 2000
18. GET 5000-150000...
19. 16 kb receive
20. 16 kb receive...
...
⚠️ iOS ≤12 的情況下,會先發幾個較短的請求試著摸摸看(?然後才會發要求到總長度的請求; iOS ≥ 13 則會直接發要求到總長度的請求。
還有個題外的坑,就是在觀察怎麼拿資源的時候,我使用了 mitmproxy 工具嗅探,結果發現它顯示有錯,會等到 response 全部回來才會顯示,而不是顯示分段、使用持久連接接續下載;害我嚇了一大跳!以為 iOS 很笨居然每次都要整個檔案回來!下次要用工具時要有保持一點懷疑 Orz
Cancel 發起的時機
- 前面說到的第二次請求,請求從 0 開始 到總長度的資源,有足夠 Data 後會發起 Cancel 取消請求。
- Seek 時會先發起 Cancel 取消先前的請求。
⚠️ 在 AVQueuePlayer 中切換到下一個資源、AVPlayer 更換播放資源時並不會發起 Cancel 取消前一首的請求。
AVQueue Pre-buffering
其實也是同樣呼叫 Resource Loader 處理,只是他要求的資料範圍會比較小。
實現
有了以上前導知識後我們來看實現 AVPlayer 本地 Cache 功能的原理方式。
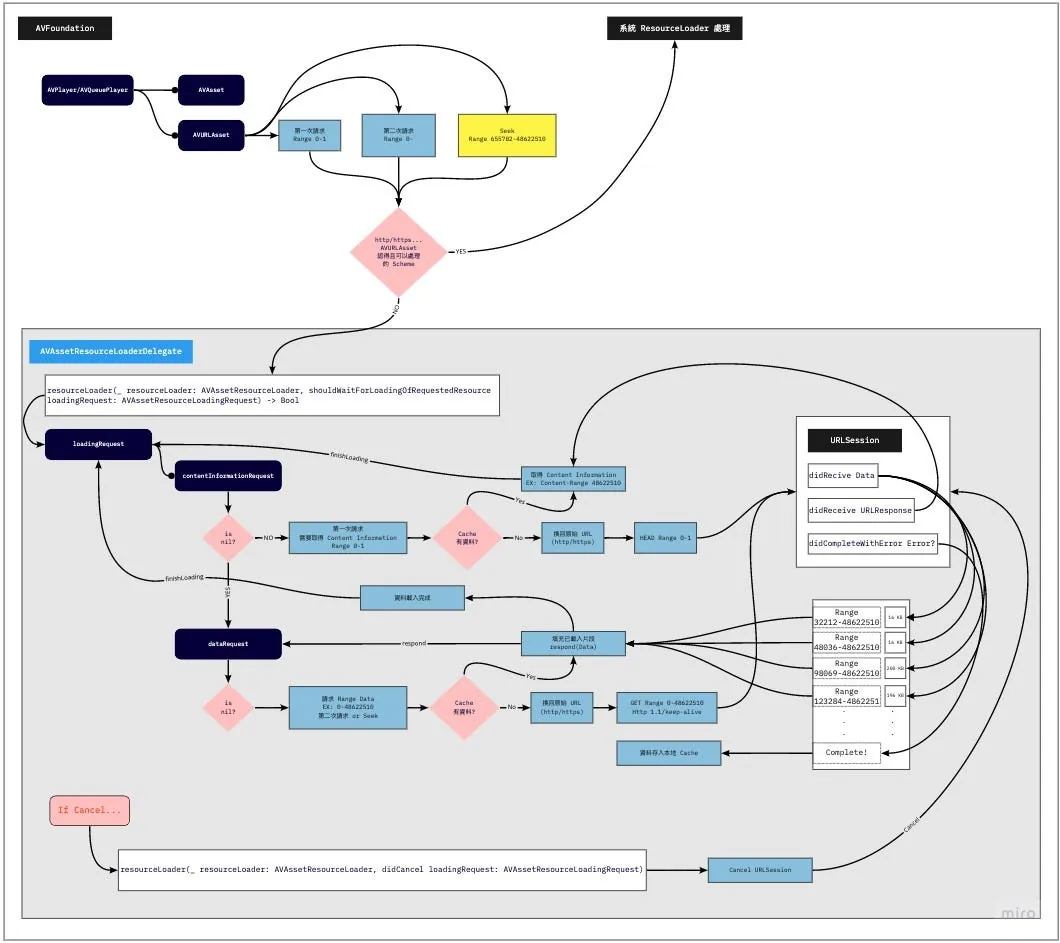
就是之前有提到的 AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate ,這個接口讓我們能 自行實踐 Resource Loader 給 Asset 用。
Resource Loader 實際就是個打工仔,播放器是要檔案資訊還是檔案資料,範圍哪裡都哪裡都是他告訴我們,我們去做就是。
看到有範例是一個 Resource Loader 服務所有 AVURLAsset ,我覺得是錯的,應該要一個 Resource Loader 服務一個 AVURLAsset,跟著 AVURLAsset 的生命週期,他本來就屬於 AVURLAsset。
一個 Resource Loader 服務所有 AVURLAsset 在 AVQueuePlayer 上會變得非常複雜且難以管理。
進入自訂的 Resource Loader 的時機點
要注意的是不是實踐了自己的 Resource Loader 他就會理你,只有當系統無法辨識處理這個資源的時候,才會走你的 Resource Loader。
所以我們在將 URL 資源給予 AVURLAsset 之前要先將 Scheme 換成我們自訂的 Scheme,不能是 http/https… 這些系統能處理的 Scheme。
1
http://zhgchg.li/music.mp3 => cacheable://zhgchg.li/music.mp3
AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate
只有兩個方法需要實現:
- func resourceLoader( _ resourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoader, shouldWaitForLoadingOfRequestedResource loadingRequest : AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) -> Bool :
此方法問我們能不能處理此資源,return true 能,return false 我們也不處理(unsupported url)。
我們能從 loadingRequest 取出要請求什麼(第一次請求檔案資訊還是請求資料,請求資料的話 Range 是多少到多少);知道請求後我們自行發起請求去拿資料, 在這我們就能決定要發起 URLSession 還是從本地返回 Data 。
另外也能在此做 Data 加解密操作,保護原始資料。
- func resourceLoader( _ resourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoader, didCancel loadingRequest : AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) :
前述說到的 Cancel 發起時機 發起 Cancel 時…
我們可以在這去取消正在請求的 URLSession。
本地 Cache 實現方式
Cache 的部分我直接使用 PINCache ,將 Cache 工作交由他處理,免去我們要處理 Cache 讀寫 DeadLock、清除 Cache LRU 策略 實作上的問題。
️️⚠️️️️️️️️️️️OOM警告!
因為這邊是針對音樂做 Cache 檔案大小頂多 10 MB 上下,所以才能使用 PINCache 作為本地 Cache 工具;如果是要服務影片就無法使用此方法(可能一次要載入好幾 GB 的資料到記憶體)
有這部分需求可參考大大的做法,用 FileHandle seek read/write 的特性進行處理。
開工!
不囉唆,先上完整專案:
AssetData
本地 Cache 資料物件映射實現 NSCoding,因 PINCache 是依賴 archivedData 方法 encode/decode。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
import Foundation
import CryptoKit
class AssetDataContentInformation: NSObject, NSCoding {
@objc var contentLength: Int64 = 0
@objc var contentType: String = ""
@objc var isByteRangeAccessSupported: Bool = false
func encode(with coder: NSCoder) {
coder.encode(self.contentLength, forKey: #keyPath(AssetDataContentInformation.contentLength))
coder.encode(self.contentType, forKey: #keyPath(AssetDataContentInformation.contentType))
coder.encode(self.isByteRangeAccessSupported, forKey: #keyPath(AssetDataContentInformation.isByteRangeAccessSupported))
}
override init() {
super.init()
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init()
self.contentLength = coder.decodeInt64(forKey: #keyPath(AssetDataContentInformation.contentLength))
self.contentType = coder.decodeObject(forKey: #keyPath(AssetDataContentInformation.contentType)) as? String ?? ""
self.isByteRangeAccessSupported = coder.decodeObject(forKey: #keyPath(AssetDataContentInformation.isByteRangeAccessSupported)) as? Bool ?? false
}
}
class AssetData: NSObject, NSCoding {
@objc var contentInformation: AssetDataContentInformation = AssetDataContentInformation()
@objc var mediaData: Data = Data()
override init() {
super.init()
}
func encode(with coder: NSCoder) {
coder.encode(self.contentInformation, forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.contentInformation))
coder.encode(self.mediaData, forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.mediaData))
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init()
self.contentInformation = coder.decodeObject(forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.contentInformation)) as? AssetDataContentInformation ?? AssetDataContentInformation()
self.mediaData = coder.decodeObject(forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.mediaData)) as? Data ?? Data()
}
}
AssetData 存放:
contentInformation: AssetDataContentInformationAssetDataContentInformation: 存放 是否支援 Range 範圍請求(isByteRangeAccessSupported)、資源總長度(contentLength)、檔案類型(contentType)mediaData: 原始音訊 Data (這邊檔案太大會 OOM)
PINCacheAssetDataManager
封裝 Data 存入、取出 PINCache 邏輯。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
import PINCache
import Foundation
protocol AssetDataManager: NSObject {
func retrieveAssetData() -> AssetData?
func saveContentInformation(_ contentInformation: AssetDataContentInformation)
func saveDownloadedData(_ data: Data, offset: Int)
func mergeDownloadedDataIfIsContinuted(from: Data, with: Data, offset: Int) -> Data?
}
extension AssetDataManager {
func mergeDownloadedDataIfIsContinuted(from: Data, with: Data, offset: Int) -> Data? {
if offset <= from.count && (offset + with.count) > from.count {
let start = from.count - offset
var data = from
data.append(with.subdata(in: start..<with.count))
return data
}
return nil
}
}
//
class PINCacheAssetDataManager: NSObject, AssetDataManager {
static let Cache: PINCache = PINCache(name: "ResourceLoader")
let cacheKey: String
init(cacheKey: String) {
self.cacheKey = cacheKey
super.init()
}
func saveContentInformation(_ contentInformation: AssetDataContentInformation) {
let assetData = AssetData()
assetData.contentInformation = contentInformation
PINCacheAssetDataManager.Cache.setObjectAsync(assetData, forKey: cacheKey, completion: nil)
}
func saveDownloadedData(_ data: Data, offset: Int) {
guard let assetData = self.retrieveAssetData() else {
return
}
if let mediaData = self.mergeDownloadedDataIfIsContinuted(from: assetData.mediaData, with: data, offset: offset) {
assetData.mediaData = mediaData
PINCacheAssetDataManager.Cache.setObjectAsync(assetData, forKey: cacheKey, completion: nil)
}
}
func retrieveAssetData() -> AssetData? {
guard let assetData = PINCacheAssetDataManager.Cache.object(forKey: cacheKey) as? AssetData else {
return nil
}
return assetData
}
}
這邊多抽出 Protocol 因為未來可能使用其他儲存方式替代 PINCache,所以其他程式在使用時是依賴 Protocol 而非 Class 實體。
⚠️
mergeDownloadedDataIfIsContinuted這個方法極其重要。
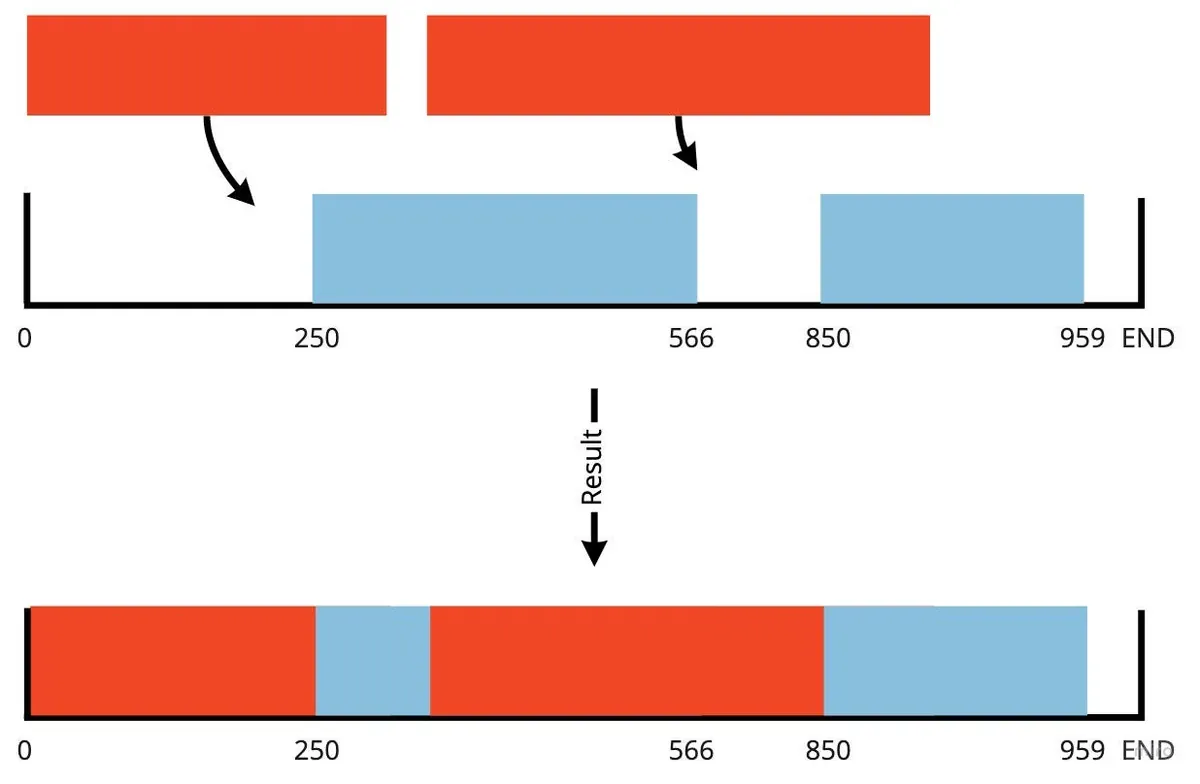
照線性播放只要一直 append 新 Data 到 Cache Data 中即可,但現實情況複雜得多,使用者可能播了 Range 0~100,直接 Seek 到 Range 200–500 播放;如何將已有的 0-100 Data 與新的 200–500 Data 合併就是一個很大的問題。
⚠️Data 合併有問題會出現可怕的播放鬼畜問題….
這邊的答案是, 我們不處理非連續資料 ;因為敝專案僅為音訊,檔案也就幾 MB (≤ 10MB) 以考量開發成本就沒做了,我只處理合併連續的資料(例如目前已有 0~100,新資料是 75~200,合併之後變0~200;如果新資料是 150~200,我則會忽略不合併處理)
如果要考慮非連續合併,除了在儲存上要使用其他方法(要有辦法辨識空缺部分);在 Request 時也要能 Query 出哪段需要發網路請求去拿、哪段是從本地拿;要考量到這情況實作會非常複雜。
圖片取自: iOS AVPlayer 视频缓存的设计与实现
CachingAVURLAsset
AVURLAsset 是 weak 持有 ResourceLoader Delegate,所以這邊建議自己建立一個 AVURLAsset Class 繼承自 AVURLAsset,在內部建立、賦予、持有 ResourceLoader ,讓他跟著 AVURLAsset 的生命週期;另外也可以儲存原始 URL、CacheKey 等資訊…。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
class CachingAVURLAsset: AVURLAsset {
static let customScheme = "cacheable"
let originalURL: URL
private var _resourceLoader: ResourceLoader?
var cacheKey: String {
return self.url.lastPathComponent
}
static func isSchemeSupport(_ url: URL) -> Bool {
guard let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: false) else {
return false
}
return ["http", "https"].contains(components.scheme)
}
override init(url URL: URL, options: [String: Any]? = nil) {
self.originalURL = URL
guard var components = URLComponents(url: URL, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: false) else {
super.init(url: URL, options: options)
return
}
components.scheme = CachingAVURLAsset.customScheme
guard let url = components.url else {
super.init(url: URL, options: options)
return
}
super.init(url: url, options: options)
let resourceLoader = ResourceLoader(asset: self)
self.resourceLoader.setDelegate(resourceLoader, queue: resourceLoader.loaderQueue)
self._resourceLoader = resourceLoader
}
}
使用:
1
2
3
4
5
if CachingAVURLAsset.isSchemeSupport(url) {
let asset = CachingAVURLAsset(url: url)
let avplayer = AVPlayer(asset)
avplayer.play()
}
其中 isSchemeSupport() 是用來判斷 URL 是否支援掛我們的 Resource Loader(排除 file:// )。
originalURL 存放原始資源 URL。
cacheKey 存放這個資源的 Cache Key,這邊直接用檔案名稱當 Cache Key。
cacheKey 請依照現實場景做調整,如果檔案名稱未 hash 可能重複就建議先 hash 後當 key 避免碰撞;如果要 hash 整個 URL 當 key 也要注意 URL 是否會變動 (例如有用 CDN)。
Hash 可使用 md5…sha. .,iOS ≥ 13 可直接使用 Apple 的 CryptoKit ,其他就上 Github 找吧!
ResourceLoaderRequest
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
import Foundation
import CoreServices
protocol ResourceLoaderRequestDelegate: AnyObject {
func dataRequestDidReceive(_ resourceLoaderRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest, _ data: Data)
func dataRequestDidComplete(_ resourceLoaderRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest, _ error: Error?, _ downloadedData: Data)
func contentInformationDidComplete(_ resourceLoaderRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest, _ result: Result<AssetDataContentInformation, Error>)
}
class ResourceLoaderRequest: NSObject, URLSessionDataDelegate {
struct RequestRange {
var start: Int64
var end: RequestRangeEnd
enum RequestRangeEnd {
case requestTo(Int64)
case requestToEnd
}
}
enum RequestType {
case contentInformation
case dataRequest
}
struct ResponseUnExpectedError: Error { }
private let loaderQueue: DispatchQueue
let originalURL: URL
let type: RequestType
private var session: URLSession?
private var dataTask: URLSessionDataTask?
private var assetDataManager: AssetDataManager?
private(set) var requestRange: RequestRange?
private(set) var response: URLResponse?
private(set) var downloadedData: Data = Data()
private(set) var isCancelled: Bool = false {
didSet {
if isCancelled {
self.dataTask?.cancel()
self.session?.invalidateAndCancel()
}
}
}
private(set) var isFinished: Bool = false {
didSet {
if isFinished {
self.session?.finishTasksAndInvalidate()
}
}
}
weak var delegate: ResourceLoaderRequestDelegate?
init(originalURL: URL, type: RequestType, loaderQueue: DispatchQueue, assetDataManager: AssetDataManager?) {
self.originalURL = originalURL
self.type = type
self.loaderQueue = loaderQueue
self.assetDataManager = assetDataManager
super.init()
}
func start(requestRange: RequestRange) {
guard isCancelled == false, isFinished == false else {
return
}
self.loaderQueue.async { [weak self] in
guard let self = self else {
return
}
var request = URLRequest(url: self.originalURL)
self.requestRange = requestRange
let start = String(requestRange.start)
let end: String
switch requestRange.end {
case .requestTo(let rangeEnd):
end = String(rangeEnd)
case .requestToEnd:
end = ""
}
let rangeHeader = "bytes=\(start)-\(end)"
request.setValue(rangeHeader, forHTTPHeaderField: "Range")
let session = URLSession(configuration: .default, delegate: self, delegateQueue: nil)
self.session = session
let dataTask = session.dataTask(with: request)
self.dataTask = dataTask
dataTask.resume()
}
}
func cancel() {
self.isCancelled = true
}
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, dataTask: URLSessionDataTask, didReceive data: Data) {
guard self.type == .dataRequest else {
return
}
self.loaderQueue.async {
self.delegate?.dataRequestDidReceive(self, data)
self.downloadedData.append(data)
}
}
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, dataTask: URLSessionDataTask, didReceive response: URLResponse, completionHandler: @escaping (URLSession.ResponseDisposition) -> Void) {
self.response = response
completionHandler(.allow)
}
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, task: URLSessionTask, didCompleteWithError error: Error?) {
self.isFinished = true
self.loaderQueue.async {
if self.type == .contentInformation {
guard error == nil,
let response = self.response as? HTTPURLResponse else {
let responseError = error ?? ResponseUnExpectedError()
self.delegate?.contentInformationDidComplete(self, .failure(responseError))
return
}
let contentInformation = AssetDataContentInformation()
if let rangeString = response.allHeaderFields["Content-Range"] as? String,
let bytesString = rangeString.split(separator: "/").map({String($0)}).last,
let bytes = Int64(bytesString) {
contentInformation.contentLength = bytes
}
if let mimeType = response.mimeType,
let contentType = UTTypeCreatePreferredIdentifierForTag(kUTTagClassMIMEType, mimeType as CFString, nil)?.takeRetainedValue() {
contentInformation.contentType = contentType as String
}
if let value = response.allHeaderFields["Accept-Ranges"] as? String,
value == "bytes" {
contentInformation.isByteRangeAccessSupported = true
} else {
contentInformation.isByteRangeAccessSupported = false
}
self.assetDataManager?.saveContentInformation(contentInformation)
self.delegate?.contentInformationDidComplete(self, .success(contentInformation))
} else {
if let offset = self.requestRange?.start, self.downloadedData.count > 0 {
self.assetDataManager?.saveDownloadedData(self.downloadedData, offset: Int(offset))
}
self.delegate?.dataRequestDidComplete(self, error, self.downloadedData)
}
}
}
}
針對 Remote Request 的封裝,主要是服務 ResourceLoader 發起的資料請求。
RequestType :用來區分此 Request 是 第一次請求檔案資訊(contentInformation)、還是請求資料(dataRequest)
RequestRange :請求 Range 範圍,end 可指定到哪(requestTo(Int64) )或全部(requestToEnd)。
檔案資訊可由:
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, dataTask: URLSessionDataTask, didReceive response: URLResponse, completionHandler: @escaping (URLSession.ResponseDisposition) -> Void)
中取得 Response Header,另外要注意如果要改 HEAD 去摸,不會進這個要用其他方法接。
isByteRangeAccessSupported:看 Response Header 中的 Accept-Ranges == bytescontentType:播放器要的檔案類型資訊,格式是統一類識別符,不是 audio/mpeg ,而是寫作 public.mp3contentLength:看 Response Header 中的 Content-Range :bytes 0–1/ 資源總長度
⚠️這邊要注意伺服器給的格式大小寫,不一定是寫作 Accept-Ranges/Content-Range;有的伺服器的格式是小寫 accept-ranges、Accept-ranges…
補充:如果要考量大小寫可以寫 HTTPURLResponse Extension
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
import CoreServices
extension HTTPURLResponse {
func parseContentLengthFromContentRange() -> Int64? {
let contentRangeKeys: [String] = [
"Content-Range",
"content-range",
"Content-range",
"content-Range"
]
var rangeString: String?
for key in contentRangeKeys {
if let value = self.allHeaderFields[key] as? String {
rangeString = value
break
}
}
guard let rangeString = rangeString,
let contentLengthString = rangeString.split(separator: "/").map({String($0)}).last,
let contentLength = Int64(contentLengthString) else {
return nil
}
return contentLength
}
func parseAcceptRanges() -> Bool? {
let contentRangeKeys: [String] = [
"Accept-Ranges",
"accept-ranges",
"Accept-ranges",
"accept-Ranges"
]
var rangeString: String?
for key in contentRangeKeys {
if let value = self.allHeaderFields[key] as? String {
rangeString = value
break
}
}
guard let rangeString = rangeString else {
return nil
}
return rangeString == "bytes" || rangeString == "Bytes"
}
func mimeTypeUTI() -> String? {
guard let mimeType = self.mimeType,
let contentType = UTTypeCreatePreferredIdentifierForTag(kUTTagClassMIMEType, mimeType as CFString, nil)?.takeRetainedValue() else {
return nil
}
return contentType as String
}
}
使用:
- contentLength = response.parseContentLengthFromContentRange( )
- isByteRangeAccessSupported = response.parseAcceptRanges( )
- contentType = response.mimeTypeUTI( )
1
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, dataTask: URLSessionDataTask, didReceive data: Data)
同前導知識所述,會實時取得已下載的資料,所以這個方法會一直進,片段片段的拿到 Data;我們將他 append 進 downloadedData 存放。
1
func urlSession(_ session: URLSession, task: URLSessionTask, didCompleteWithError error: Error?)
任務取消或結束時都會進這個方法,在這將已下載的資料保存下來。
如前導知識中提到的 Cancel 機制,因播放器在拿到足夠資料後就會發起 Cancel,Cancel Request;所以進到這個方法時實際會是 error = NSURLErrorCancelled ,因此不管 error 我們有拿到資料都會嘗試存下來。
⚠️ 因 URLSession 會用並行方式出去請求資料,所以請保持操作都在DispatchQueue裡,避免資料錯亂(資料錯亂一樣會出現可怕的播放鬼畜)。
️️⚠️URLSession 沒有呼叫
finishTasksAndInvalidate或invalidateAndCancel兩個方法都會強持有物件導致 Memory Leak;所以不管是取消或是完成我們都要呼叫,這樣才能在任務結束釋放 Request。
️️⚠️️️️️️️️️️️如果怕
downloadedDataOOM,可以在 didReceive Data 中就存入本地。
ResourceLoader
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
import AVFoundation
import Foundation
class ResourceLoader: NSObject {
let loaderQueue = DispatchQueue(label: "li.zhgchg.resourceLoader.queue")
private var requests: [AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest] = [:]
private let cacheKey: String
private let originalURL: URL
init(asset: CachingAVURLAsset) {
self.cacheKey = asset.cacheKey
self.originalURL = asset.originalURL
super.init()
}
deinit {
self.requests.forEach { (request) in
request.value.cancel()
}
}
}
extension ResourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate {
func resourceLoader(_ resourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoader, shouldWaitForLoadingOfRequestedResource loadingRequest: AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) -> Bool {
let type = ResourceLoader.resourceLoaderRequestType(loadingRequest)
let assetDataManager = PINCacheAssetDataManager(cacheKey: self.cacheKey)
if let assetData = assetDataManager.retrieveAssetData() {
if type == .contentInformation {
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.contentLength = assetData.contentInformation.contentLength
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.contentType = assetData.contentInformation.contentType
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.isByteRangeAccessSupported = assetData.contentInformation.isByteRangeAccessSupported
loadingRequest.finishLoading()
return true
} else {
let range = ResourceLoader.resourceLoaderRequestRange(type, loadingRequest)
if assetData.mediaData.count > 0 {
let end: Int64
switch range.end {
case .requestTo(let rangeEnd):
end = rangeEnd
case .requestToEnd:
end = assetData.contentInformation.contentLength
}
if assetData.mediaData.count >= end {
let subData = assetData.mediaData.subdata(in: Int(range.start)..<Int(end))
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.respond(with: subData)
loadingRequest.finishLoading()
return true
} else if range.start <= assetData.mediaData.count {
// has cache data...but not enough
let subEnd = (assetData.mediaData.count > end) ? Int((end)) : (assetData.mediaData.count)
let subData = assetData.mediaData.subdata(in: Int(range.start)..<subEnd)
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.respond(with: subData)
}
}
}
}
let range = ResourceLoader.resourceLoaderRequestRange(type, loadingRequest)
let resourceLoaderRequest = ResourceLoaderRequest(originalURL: self.originalURL, type: type, loaderQueue: self.loaderQueue, assetDataManager: assetDataManager)
resourceLoaderRequest.delegate = self
self.requests[loadingRequest]?.cancel()
self.requests[loadingRequest] = resourceLoaderRequest
resourceLoaderRequest.start(requestRange: range)
return true
}
func resourceLoader(_ resourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoader, didCancel loadingRequest: AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) {
guard let resourceLoaderRequest = self.requests[loadingRequest] else {
return
}
resourceLoaderRequest.cancel()
requests.removeValue(forKey: loadingRequest)
}
}
extension ResourceLoader: ResourceLoaderRequestDelegate {
func contentInformationDidComplete(_ resourceLoaderRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest, _ result: Result<AssetDataContentInformation, Error>) {
guard let loadingRequest = self.requests.first(where: { $0.value == resourceLoaderRequest })?.key else {
return
}
switch result {
case .success(let contentInformation):
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.contentType = contentInformation.contentType
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.contentLength = contentInformation.contentLength
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.isByteRangeAccessSupported = contentInformation.isByteRangeAccessSupported
loadingRequest.finishLoading()
case .failure(let error):
loadingRequest.finishLoading(with: error)
}
}
func dataRequestDidReceive(_ resourceLoaderRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest, _ data: Data) {
guard let loadingRequest = self.requests.first(where: { $0.value == resourceLoaderRequest })?.key else {
return
}
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.respond(with: data)
}
func dataRequestDidComplete(_ resourceLoaderRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest, _ error: Error?, _ downloadedData: Data) {
guard let loadingRequest = self.requests.first(where: { $0.value == resourceLoaderRequest })?.key else {
return
}
loadingRequest.finishLoading(with: error)
requests.removeValue(forKey: loadingRequest)
}
}
extension ResourceLoader {
static func resourceLoaderRequestType(_ loadingRequest: AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) -> ResourceLoaderRequest.RequestType {
if let _ = loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest {
return .contentInformation
} else {
return .dataRequest
}
}
static func resourceLoaderRequestRange(_ type: ResourceLoaderRequest.RequestType, _ loadingRequest: AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) -> ResourceLoaderRequest.RequestRange {
if type == .contentInformation {
return ResourceLoaderRequest.RequestRange(start: 0, end: .requestTo(1))
} else {
if loadingRequest.dataRequest?.requestsAllDataToEndOfResource == true {
let lowerBound = loadingRequest.dataRequest?.currentOffset ?? 0
return ResourceLoaderRequest.RequestRange(start: lowerBound, end: .requestToEnd)
} else {
let lowerBound = loadingRequest.dataRequest?.currentOffset ?? 0
let length = Int64(loadingRequest.dataRequest?.requestedLength ?? 1)
let upperBound = lowerBound + length
return ResourceLoaderRequest.RequestRange(start: lowerBound, end: .requestTo(upperBound))
}
}
}
}
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest != nil 則代表是第一次請求,播放器要求先給檔案資訊。
請求檔案資訊時我們需要賦予這三項資訊:
loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.isByteRangeAccessSupported:是否支援 Range 拿 DataloadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.contentType:統一類識別符loadingRequest.contentInformationRequest?.contentLength:檔案總長度 Int64
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.requestedOffset 可取得要求 Range 的起始 offset。
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.requestedLength 可取得要求 Range 的長度。
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.requestsAllDataToEndOfResource == true 則不管要求 Range 的長度,直接拿到底。
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.respond(with: Data) 返回已載入的 Data 給播放器。
loadingRequest.dataRequest?.currentOffset 可取得當前 data offset, dataRequest?.respond(with: Data) 後 currentOffset 會跟著推移。
loadingRequest.finishLoading() 資料都載完了,告知播放器。
1
func resourceLoader(_ resourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoader, shouldWaitForLoadingOfRequestedResource loadingRequest: AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest) -> Bool
播放器請求資料,我們先看本地 Cache 有無資料,有則返回;若只有部分資料則一樣返回部分,例如我本地有 0–100 ,播放器要求 0–200,則先返回 0–100。
若沒有本地 Cache、返回的資料不夠,則會發起 ResourceLoaderRequest 請求從網路拿資料。
1
func resourceLoader(_ resourceLoader: AVAssetResourceLoader, didCancel loadingRequest: AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest)
播放器取消請求,取消 ResourceLoaderRequest。
你可能有發現
resourceLoaderRequestRange的 offset 是看currentOffset,因為我們會先從本地dataRequest?.respond(with: Data)已下載 Data;所以直接看推移後的 offset 即可。
1
func private var requests: [AVAssetResourceLoadingRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest] = [:]
⚠️ requests 有的範例是只用
currentRequest: ResourceLoaderRequest來存放,這會有個問題,因為可能當前的 request 正在拿取,使用者又 seek 這時會取消舊的發起新的;但因不一定會照順序發生,可能先走發新請求再走取消;所以用 Dictionary 去存取操作還是比較安全!
⚠️讓所有操作都在同個 DispatchQueue 防止出現資料鬼畜。
deinit 時取消所有還在請求的 requests Resource Loader Deinit 即代表 AVURLAsset Deinit,代表播放器已經不需要這個資源了;所以我們可以 Cancel 還在取資料的 Request,已經載的一樣會寫入 Cache。
補充及鳴謝
感謝 Lex 汤 大大指點。
感謝 外孫女 提供開發上的意見及支持。
本篇只針對音樂小檔
影片大檔案可能會在 downloadedData、AssetData/PINCacheAssetDataManager 發生 Out Of Memory 問題。
同前述,如果要解決這個問題請使用 fileHandler seek read/wirte 去操作本地 Cache 讀取寫入(取代AssetData/PINCacheAssetDataManager);或找看看 Github 有沒有大 data write/read to file 的專案可用。
AVQueuePlayer 切換播放項目時取消正在下載的項目
同前導知識中所述,在更換播放目標時是不會發起 Cancel 的;如果是 AVPlayer 會走 AVURLAsset Deinit 所以下載也會中斷;但 AVQueuePlayer 不會,因為都還在 Queue 裡,只是播放目標換到下一首而已。
這邊唯一做法就只能接收變換播放目標通知,然後在收到通知後取消上一手的 AVURLAsset loading。
1
asset.cancelLoading()
音訊資料加解密
音訊加解密可在 ResourceLoaderRequest 中拿到 Data 進行、還有儲存時能在 AssetData 的 encode/decode 對存在本地的 Data進行加解密。
CryptoKit SHA 使用範本:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
class AssetData: NSObject, NSCoding {
static let encryptionKeyString = "encryptionKeyExzhgchgli"
...
func encode(with coder: NSCoder) {
coder.encode(self.contentInformation, forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.contentInformation))
if #available(iOS 13.0, *),
let encryptionData = try? ChaChaPoly.seal(self.mediaData, using: AssetData.encryptionKey).combined {
coder.encode(encryptionData, forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.mediaData))
} else {
//
}
}
required init?(coder: NSCoder) {
super.init()
...
if let mediaData = coder.decodeObject(forKey: #keyPath(AssetData.mediaData)) as? Data {
if #available(iOS 13.0, *),
let sealedBox = try? ChaChaPoly.SealedBox(combined: mediaData),
let decryptedData = try? ChaChaPoly.open(sealedBox, using: AssetData.encryptionKey) {
self.mediaData = decryptedData
} else {
//
}
} else {
//
}
}
}
PINCache 相關操作
PINCache 包含 PINMemoryCache 和 PINDiskCache,PINCache 會幫我們處理從檔案讀到 Memory 或從 Memory 寫入檔案的事,我們只需要對 PINCache 進行操作。
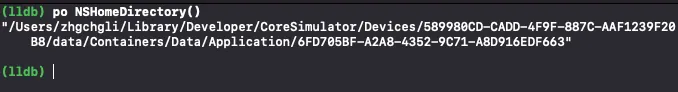
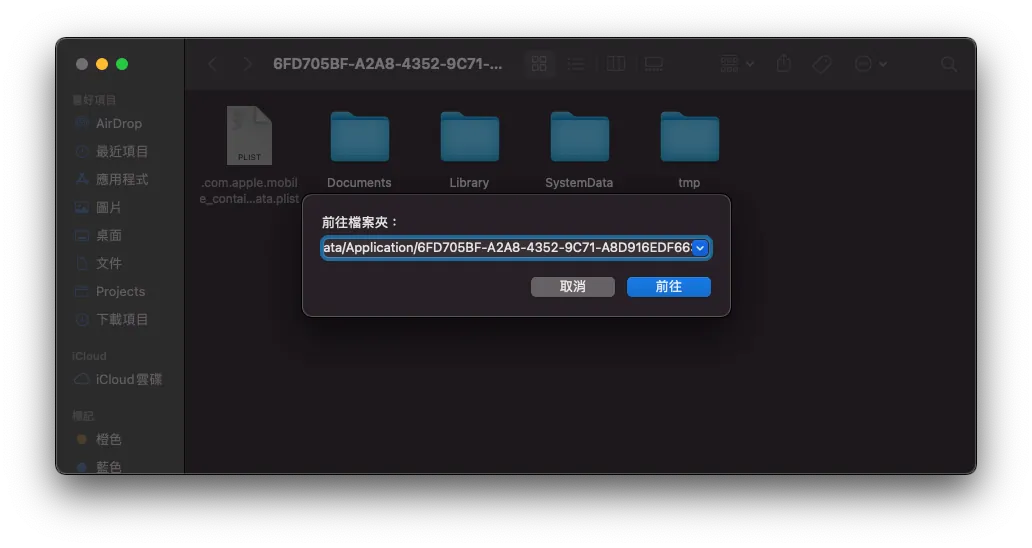
在模擬器中查找 Cache 檔案位置:
使用 NSHomeDirectory() 取得模擬器檔案路徑
Finder -> 前往 -> 貼上路徑
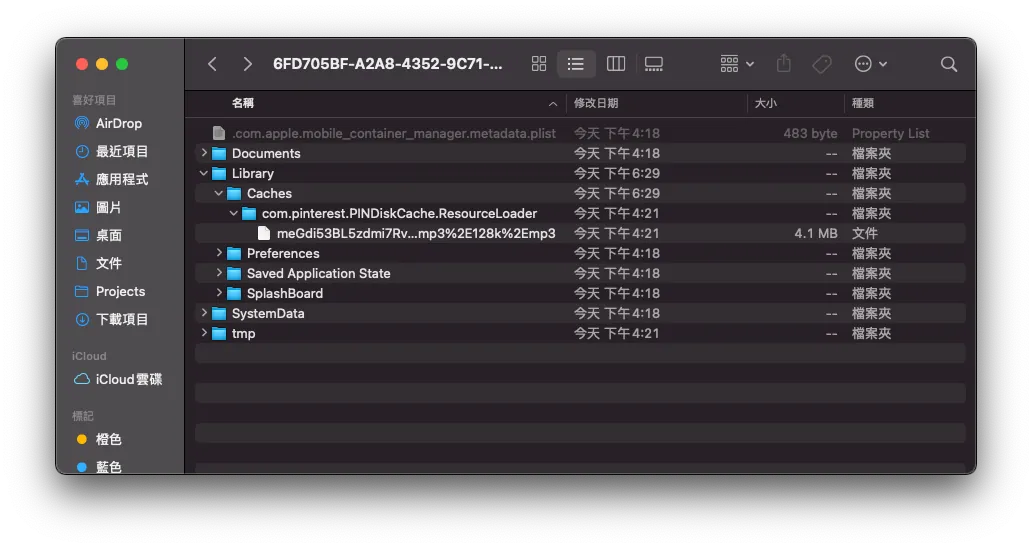
在 Library -> Caches -> com.pinterest.PINDiskCache.ResourceLoader 就是我們建的 Resource Loader Cache 目錄。
PINCache(name: “ResourceLoader”) 其中的 name 就是目錄名稱。
也可以指定 rootPath ,目錄就可以改到 Documents 底下(不怕被系統清掉)。
設定 PINCache 最大上限:
1
2
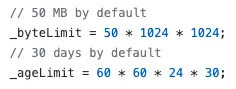
PINCacheAssetDataManager.Cache.diskCache.byteCount = 300 * 1024 * 1024 // max: 300mb
PINCacheAssetDataManager.Cache.diskCache.byteLimit = 90 * 60 * 60 * 24 // 90 days
系統預設上限
設 0 的話就不會主動刪除檔案。
後記
原先太小看這個功能的困難度,以為三兩下就能處理好;結果吃盡苦頭,大概又多花了兩週處理資料儲存的問題,不過也就此徹底了解整個 Resource Loader 運作機制、 GCD 、Data。
參考資料
最後附上研究如何實作的參考資料
- iOS AVPlayer 视频缓存的设计与实现 僅講原理
- 基于AVPlayer实现音视频播放和缓存,支持视频画面的同步输出 [ SZAVPlayer ] 有附程式(很完整,但很複雜)
- CachingPlayerItem (簡易實現,較好懂但不完整)
- 可能是目前最好的 AVPlayer 音视频缓存方案 AVAssetResourceLoaderDelegate
- 仿抖音 Swift 版 [ Github ](蠻有意思的專案,復刻抖音 APP;裡面也有用到 Resource Loader)
- iOS HLS Cache 實踐方法探究之旅
延伸
- DLCachePlayer (Objective-C 版)
有任何問題及指教歡迎 與我聯絡 。
本文首次發表於 Medium (點此查看原始版本),由 ZMediumToMarkdown 提供自動轉換與同步技術。
{:target="_blank"}](/assets/6ce488898003/1*XgMZGKMb-YNCFnS9MbiZhw.webp)