Google Apps Script|Fast Integration with Google APIs Using Firebase App Distribution API
Developers facing complex API integrations can streamline processes by leveraging Google Apps Script with Firebase App Distribution API, achieving faster deployment and simplified management in app distribution workflows.
点击这里查看本文章简体中文版本。
點擊這裡查看本文章正體中文版本。
This post was translated with AI assistance — let me know if anything sounds off!
Table of Contents
Quick Integration Method for Google Apps Script x Google APIs
Using Google Apps Script with Firebase App Distribution API as an example
Background
Previously, I wrote several articles about using Google Apps Script. Among them, “Using Google Apps Script to Automate Daily Data Report RPA” and “Simple 3 Steps — Build a Free GA4 Auto Data Notification Bot” introduced how to connect Google Analytics with Google Sheets, Web App, Slack, Telegram using Google Apps Script to quickly build a visual data platform and notification service. Additionally, last month’s article “Using Google Apps Script Web App Form to Connect Github Action CI/CD Workflow” directly used Google Apps Script Web App to connect with the Github API as a CI/CD GUI form service. In all these cases, whether using built-in Google Apps Script services or directly connecting to external services (Slack, Github…), there was no need to connect to Google APIs.
This time, when optimizing the CI/CD GUI form, I want to display the Firebase Distribution download link directly on the Web App after packaging the internal test version. This can only be achieved by integrating with Google APIs.
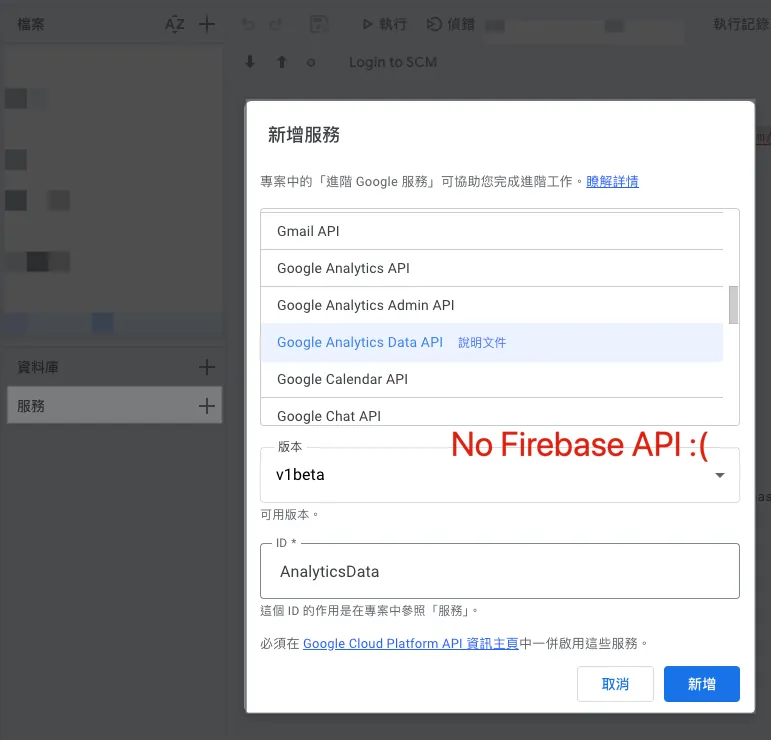
Google Apps Script x Firebase App Distribution API v1
As shown in the above image, unlike the built-in “AnalyticsData” service for connecting with Google Analytics, Firebase App Distribution does not offer a built-in integration service, so an advanced method is required for integration.
Originally thought I had to generate and exchange the Access Token using a Service Account myself (a bit complicated, you can refer to my previous Review Bot open-source project), but actually, it’s not that complicated.
Google Apps Script x Google APIs Advanced Service Integration
Integration Settings
Refer to the official documentation for details. We need to follow these steps for advanced setup:
You must enable Advanced Services in your script project.
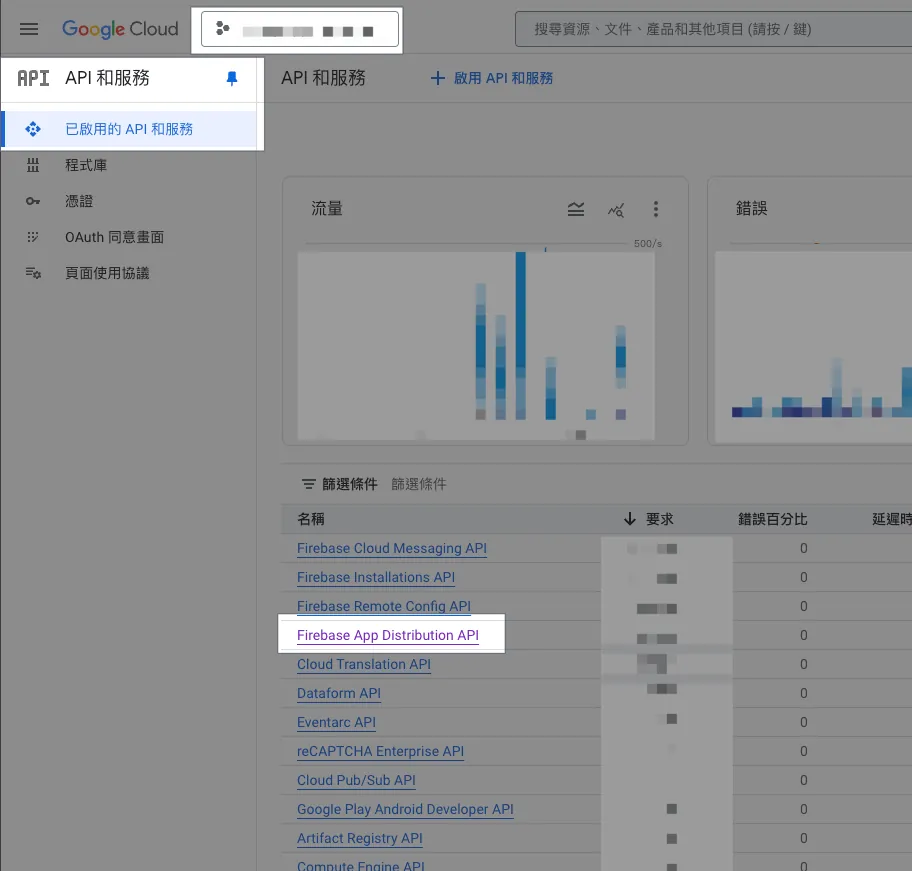
You must ensure that the API for the corresponding advanced service is enabled in the Cloud Platform (GCP) project used by the script.
If your script project uses the default GCP project created on or after April 8, 2019, the API will be automatically enabled once you enable advanced services and save the script project. If you have not yet agreed, the system may also prompt you to accept the Google Cloud and Google API terms of service.
If your script project uses a standard GCP project or an older default GCP project, you must manually enable the corresponding API for advanced services in the GCP project. You need edit permissions for the GCP project to make this change.
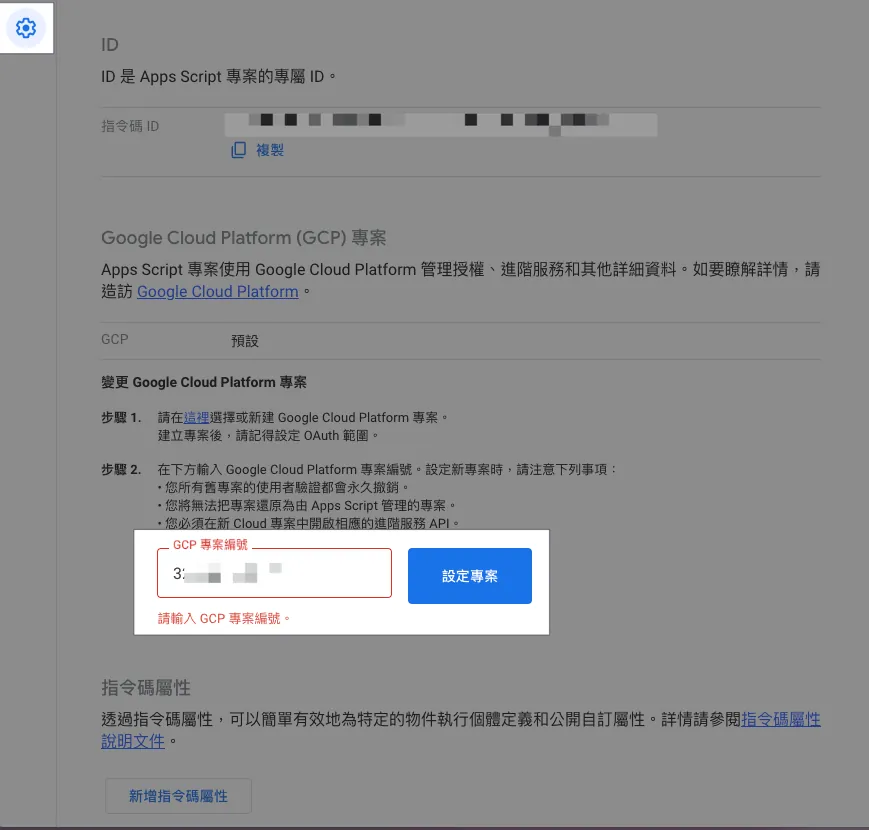
1. Project Setup — Configure the associated Google Cloud Platform (GCP) project
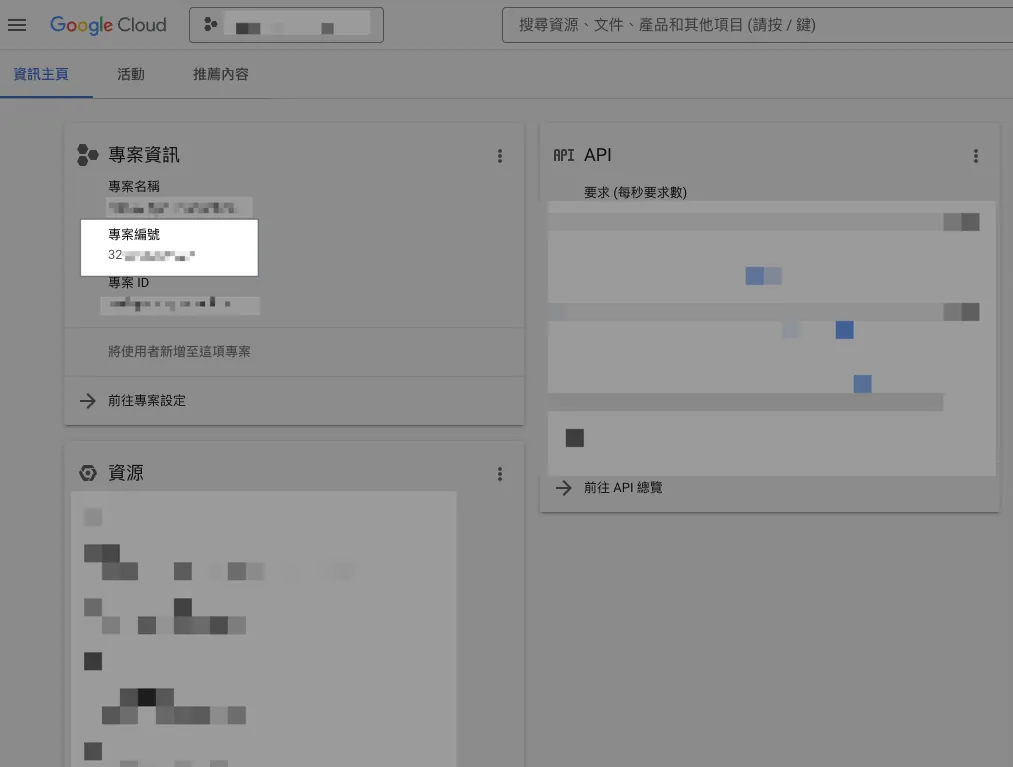
Google Apps Script x Google APIs advanced integration requires you to create a GCP project and link it to Google Apps Script. The usage permissions for Google APIs are based on the GCP settings.
Therefore, you need to create a GCP project (a Firebase GCP project is also acceptable), note the “Project Number” on the information homepage, and ensure that this GCP project has the Google APIs you want to use enabled, and that the currently logged-in account or the account you want to use has the necessary permissions for the GCP project and Google APIs.
This article uses the Firebase App Distribution API as an example.
Enter the Project Number into the Google Cloud Platform project number field under the Google Apps Script project settings. If the current logged-in account has permission for that GCP project, it will automatically bind and set successfully.
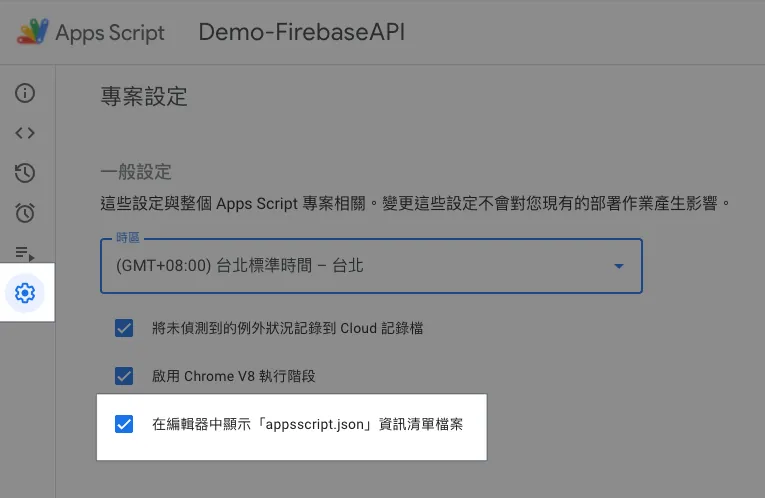
2. Project Setup — Enable Display of “appsscript.json” Manifest File in the Editor
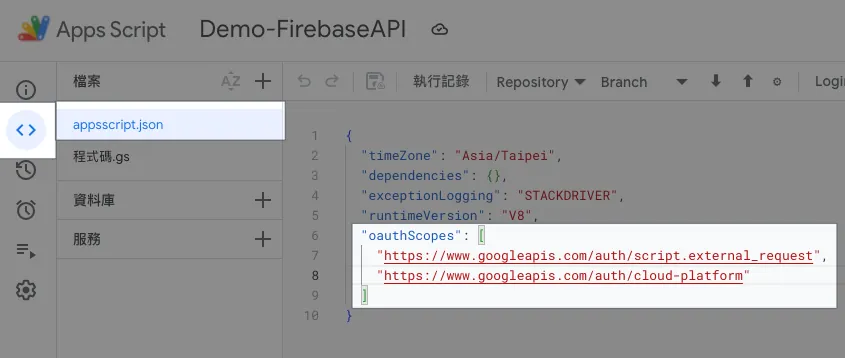
After enabling, return to the editor, and the file list will show the appsscript.json configuration file:
Make sure the oauthScopes include the following two descriptions:
1
2
3
4
"oauthScopes": [
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/script.external_request",
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform"
]
If not, please manually paste and save.
3. Writing Integration Code
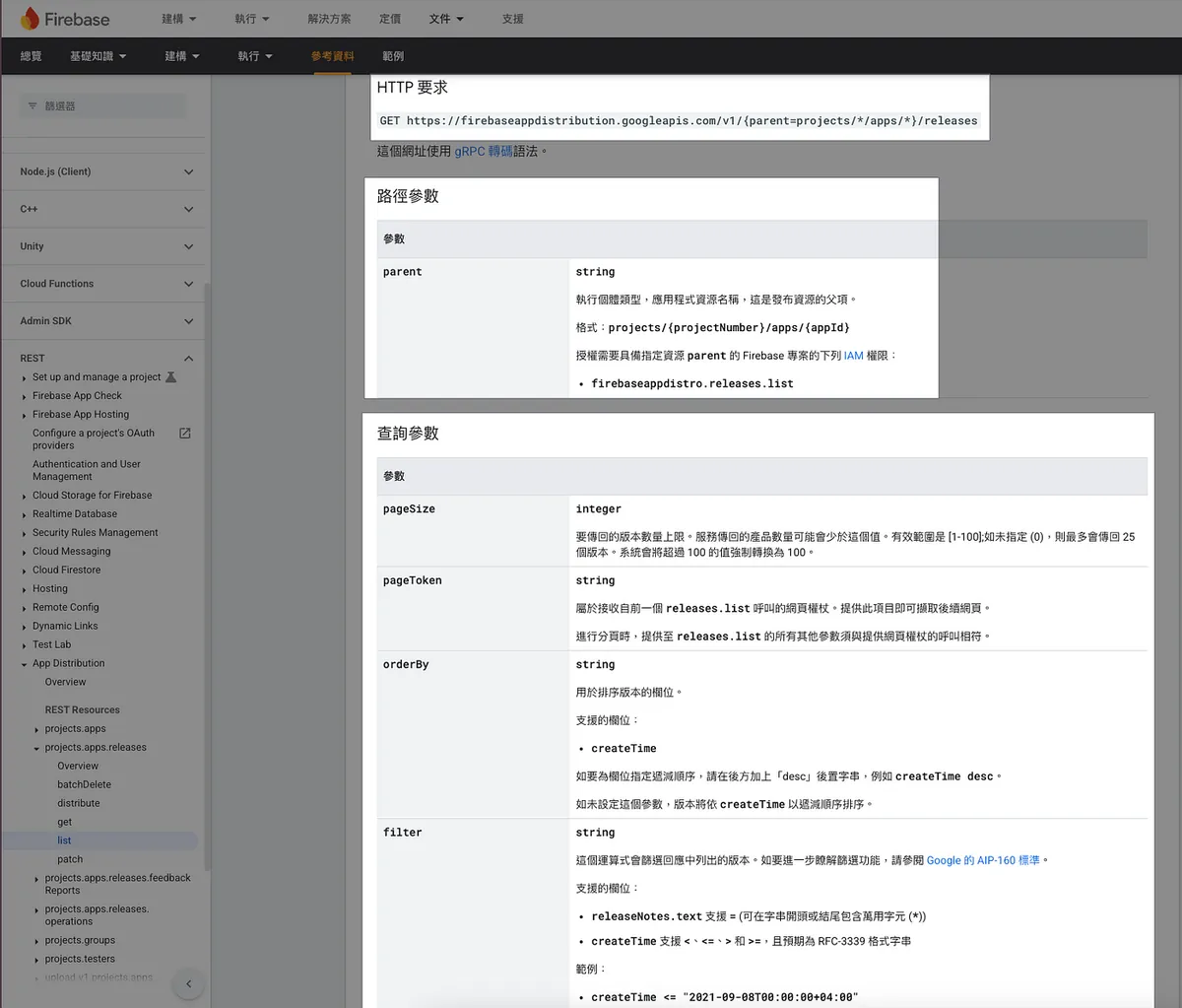
After setting up the GCP project, we can start writing the integration code by directly referring to the official documentation of the Google APIs we want to connect to, such as Firebase App Distribution API v1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
const project = "projects/[Firebase Project ID]/apps/[Firebase APP ID]"; // Please replace with your Project ID & App ID
function debug() {
const releases = firebaseDistribution("");
releases.forEach(function(release) {
// Release Object: https://firebase.google.com/docs/reference/app-distribution/rest/v1/projects.apps.releases?hl=zh-tw#Release
Logger.log(`${release.name} Download URL: ${release.testingUri}`);
});
}
function firebaseDistribution(releaseNote) {
const url = "https://firebaseappdistribution.googleapis.com/v1/"+project+"/releases?filter=releaseNotes.text%3D*"+releaseNote+"*";
// Filter: https://firebase.google.com/docs/reference/app-distribution/rest/v1/projects.apps.releases/list?hl=zh-tw
const headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8",
"Authorization": "Bearer " + ScriptApp.getOAuthToken(), // Use the current account to get the token directly
};
const options = {
"method": "get",
"headers": headers
};
const data = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
const result = JSON.parse(data.getContentText()).releases;
if (result == undefined) {
return [];
}
return result;
}
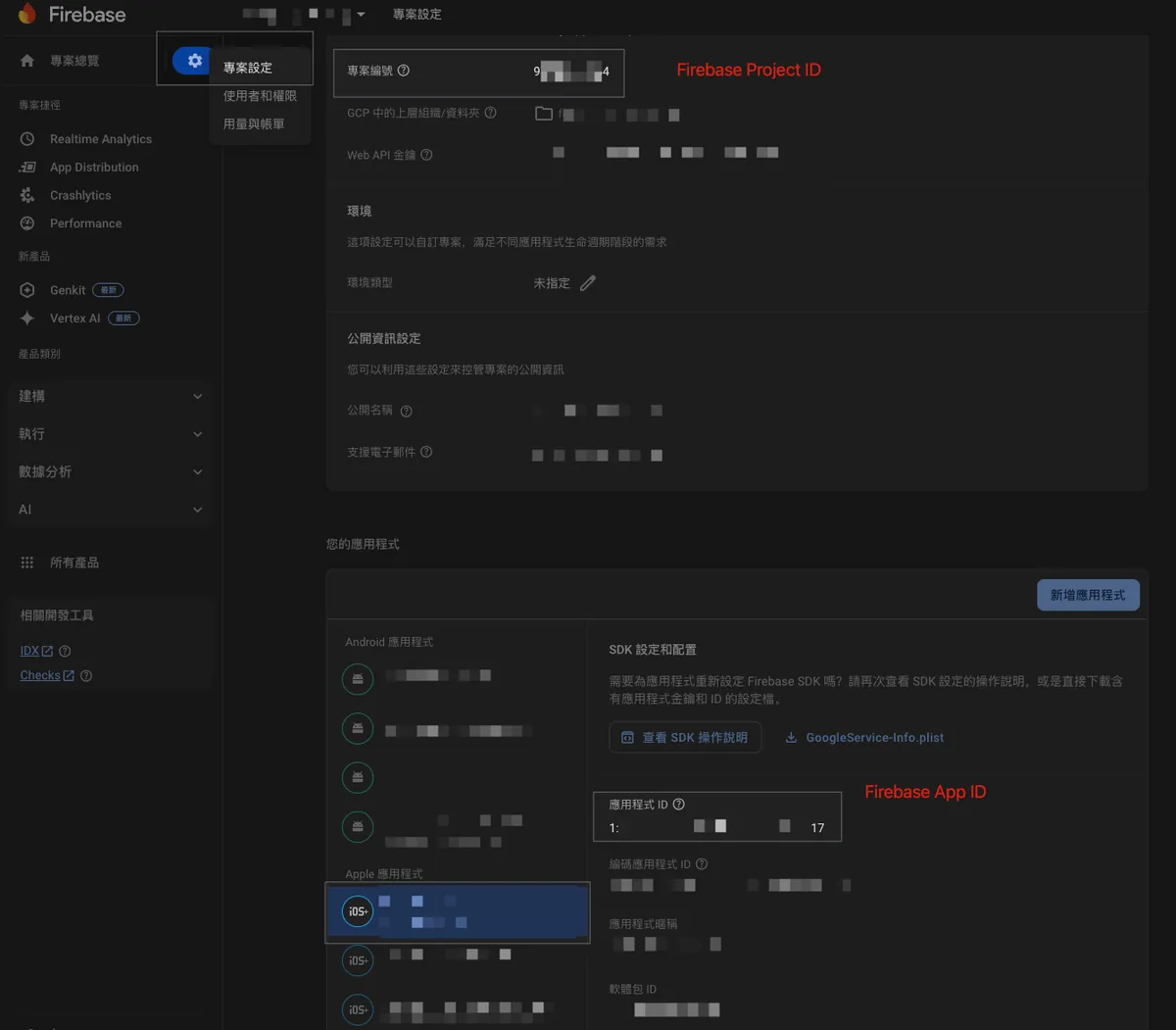
[Firebase Project ID] and [Firebase APP ID] can be found in the Firebase project settings:
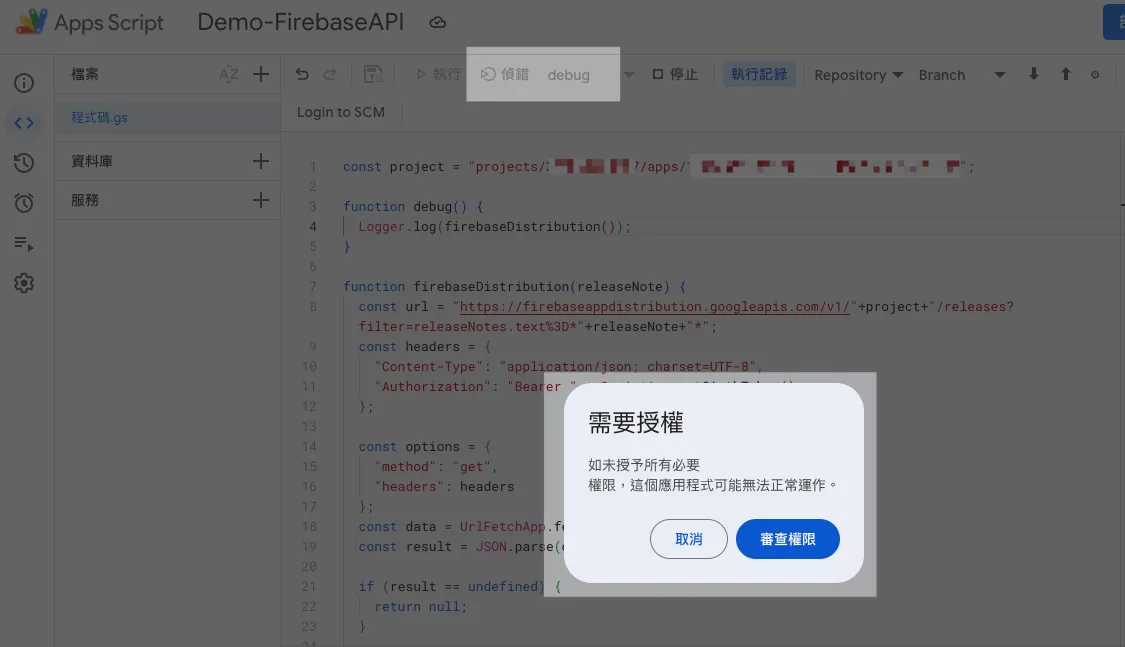
After pasting the code, the first execution requires permission authorization.
Click “Review Permissions”
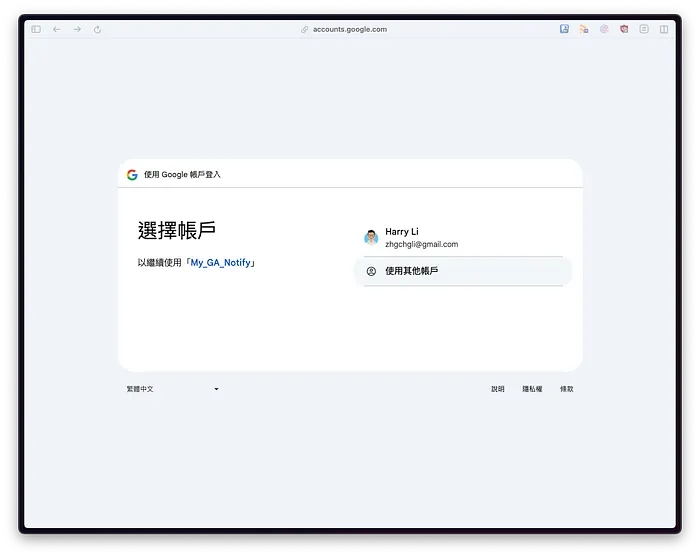
Select the account to execute, usually the current Google Apps Script account
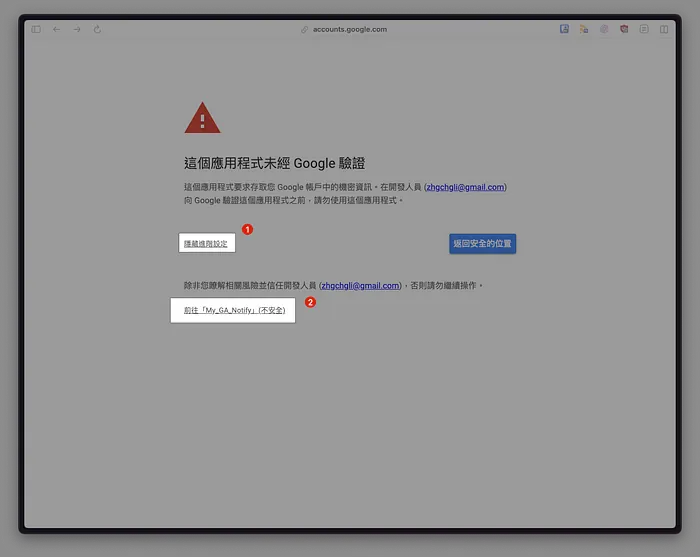
Select “Advanced” to expand -> Click “Go to XXX”
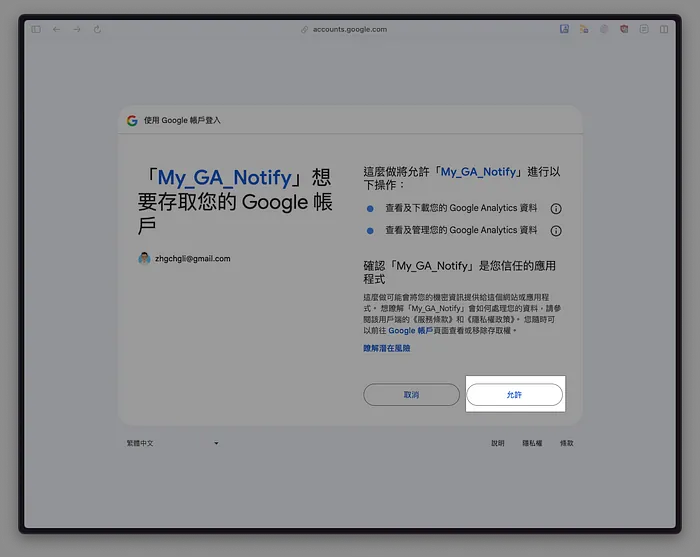
This is an app we created for our own use, so it does not require Google verification.Click “Allow”
The above screen may not appear and can be ignored if absent.
Allow then click “Debug” or “Run” later to execute the program:
If an error occurs:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Exception: Request failed for https://firebaseappdistribution.googleapis.com returned code 403. Truncated server response: {
"error": {
"code": 403,
"message": "Request had insufficient authentication scopes.",
"status": "PERMISSION_DENIED",
"details":... (use muteHttpExceptions option to examine full response)
...
or
1
Exception: Specified permissions are not sufficient to call UrlFetchApp.fetch. Required permissions: https://www.googleapis.com/auth/script.external_request
Please ensure that the oauthScopes in appsscript.json includes the following two descriptions (refer to step 2):
1
2
3
4
"oauthScopes": [
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/script.external_request",
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/cloud-platform"
]
If an error occurs:
1
2
3
4
Exception: Request failed for https://firebaseappdistribution.googleapis.com returned code 401. Truncated server response: {
"error": {
"code": 401,
"message": "Request had invalid authentication credentials. Expected OAuth 2 access token, login cookie or othe... (use muteHttpExceptions option to examine full response)
Represents a GCP project that has not been bound yet (refer to Step 1), or the GCP project has not enabled the desired Google APIs, or the current account lacks permission to use the GCP/Google APIs or the Firebase App. Please check the settings.
If an error occurs:
1
Exception: Request failed for https://firebaseappdistribution.googleapis.com returned code 404. Truncated server response:
or
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Exception: Request failed for https://firebaseappdistribution.googleapis.com returned code 400. Truncated server response: {
"error": {
"code": 400,
"message": "Request contains an invalid argument.",
"status": "INVALID_ARGUMENT"
}
}
Please verify if the Google APIs request path is correct.
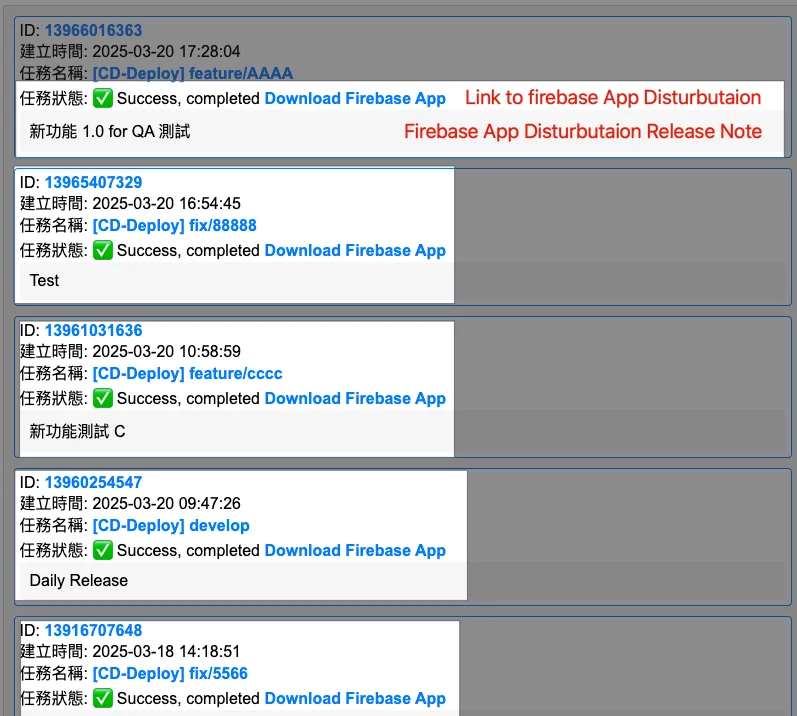
Integration Successful 🎉🎉🎉
You can see that in less than 10 lines of code, you can seamlessly connect to Google APIs, which is very convenient. For those interested, you can compare it with implementing it yourself, where the authentication token exchange steps for connecting to Google APIs are quite complicated.
Next Steps:
Combined with the previous article “Using Google Apps Script Web App Form to Connect Github Action CI/CD Workflow”, this integrates the CI/CD tasks and displays the Firebase App Distribution download link on the Web App for colleagues to download directly.
Demo Result
Other Google APIs can also be connected in the same way.
2025/07 Update:
This feature has been integrated into the actual packaging tool. You can refer to the latest article case: “CI/CD Practical Guide (Part 4): Using Google Apps Script Web App to Connect GitHub Actions for Building a Free and Easy Packaging Tool Platform”
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to contact me.
This post was originally published on Medium (View original post), and automatically converted and synced by ZMediumToMarkdown.