iOS Vision Framework|Explore Swift API Enhancements from WWDC 24 Session
Discover how iOS 18's Vision framework Swift APIs simplify image analysis and improve development efficiency. Learn key updates and practical usage to boost your app's computer vision capabilities seamlessly.
点击这里查看本文章简体中文版本。
點擊這裡查看本文章正體中文版本。
This post was translated with AI assistance — let me know if anything sounds off!
Table of Contents
iOS Vision framework x WWDC 24 Discover Swift enhancements in the Vision framework Session
Vision framework Feature Review & iOS 18 New Swift API Hands-on
Photo by BoliviaInteligente
Topic
The relationship with Vision Pro is like that between a hot dog and a dog—completely unrelated.
Vision framework
Vision framework is Apple’s integrated machine learning image recognition framework, allowing developers to easily and quickly implement common image recognition features. The Vision framework was first introduced in iOS 11.0+ (2017/iPhone 8) and has been continuously improved and optimized. It has enhanced integration with Swift Concurrency to boost performance, and starting from iOS 18.0, it offers a new Swift Vision framework API to fully leverage Swift Concurrency.
Features of the Vision Framework
Built-in Numerous Image Recognition and Motion Tracking Methods (A Total of 31 Types up to iOS 18)
On-Device uses only the phone’s chip for computation. The recognition process does not rely on cloud services, making it fast and secure.
API is simple and easy to use
Apple platforms all support iOS 11.0+, iPadOS 11.0+, Mac Catalyst 13.0+, macOS 10.13+, tvOS 11.0+, visionOS 1.0+
Published for many years (2017~present) and continuously updated
Integrating Swift Language Features to Enhance Computational Performance
Played around 6 years ago: Vision Introduction — APP Avatar Upload Automatic Face Recognition and Cropping (Swift)
This time, paired with WWDC 24 Discover Swift enhancements in the Vision framework Session, I reviewed and explored again with the new Swift features.
CoreML
Apple also has another framework called CoreML, which is an on-device chip-based machine learning framework. It allows you to train your own models for recognizing objects or documents and embed the models directly into your app. Interested users can try it out. (e.g. real-time article classification, real-time spam detection …)
p.s.
Vision : Mainly used for image analysis tasks like face recognition, barcode detection, and text recognition. It offers powerful APIs to process and analyze visual content in still images or videos.
VisionKit : Specifically designed for handling document scanning tasks. It provides a scanner view controller that can be used to scan documents and generate high-quality PDFs or images.
Vision framework cannot run on the simulator for M1 models and can only be tested on real devices; running in the simulator environment throws a Could not create Espresso context error. Checking the official forum discussion, no solution was found.
Since I do not have a physical iOS 18 device for testing, all the results in this article are based on the old (pre-iOS 18) methods; please leave a comment if there are errors with the new methods.
WWDC 2024 — Discover Swift enhancements in the Vision framework
Discover Swift enhancements in the Vision framework
This article summarizes WWDC 24 — Discover Swift enhancements in the Vision framework session, including some personal experimentation notes.
Introduction — Vision framework Features
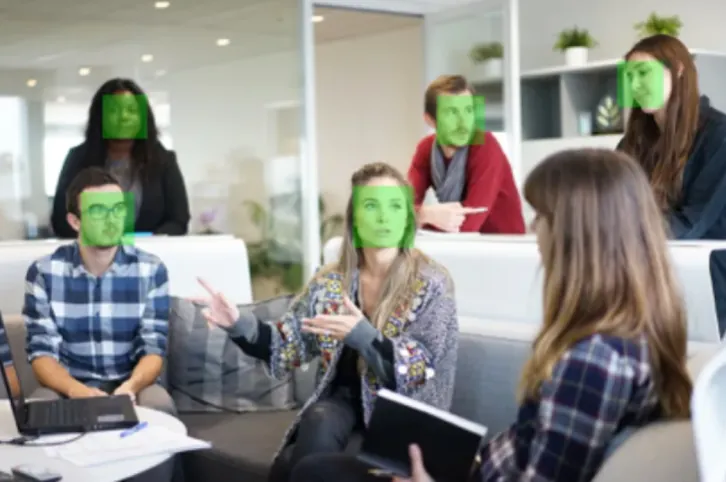
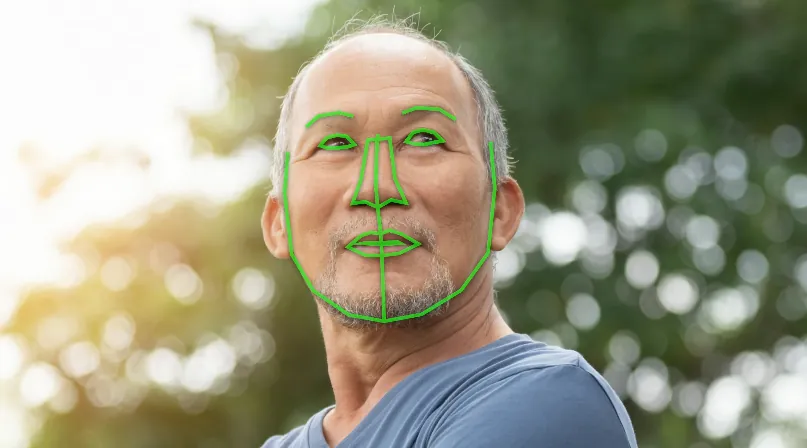
Facial Recognition and Contour Detection
Image Text Recognition
As of iOS 18, it supports 18 languages.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// List of supported languages
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
print(RecognizeTextRequest().supportedRecognitionLanguages.map { "\($0.languageCode!)-\(($0.region?.identifier ?? $0.script?.identifier)!)" })
} else {
print(try! VNRecognizeTextRequest().supportedRecognitionLanguages())
}
// The actual available recognition languages are based on this.
// Tested on iOS 18, the output is:
// ["en-US", "fr-FR", "it-IT", "de-DE", "es-ES", "pt-BR", "zh-Hans", "zh-Hant", "yue-Hans", "yue-Hant", "ko-KR", "ja-JP", "ru-RU", "uk-UA", "th-TH", "vi-VT", "ar-SA", "ars-SA"]
// Swedish mentioned at WWDC was not seen, unsure if it's not released yet or related to device region/language settings
Dynamic Motion Capture
Can achieve dynamic tracking of people and objects
Gesture capture enables air signature functionality
What’s new in Vision? (iOS 18)— Image rating feature (quality, memorability)
Can calculate a score for the input image, making it easy to filter high-quality photos.
The scoring method includes multiple dimensions, not only image quality but also lighting, angle, subject, whether it evokes memorable points, and more.
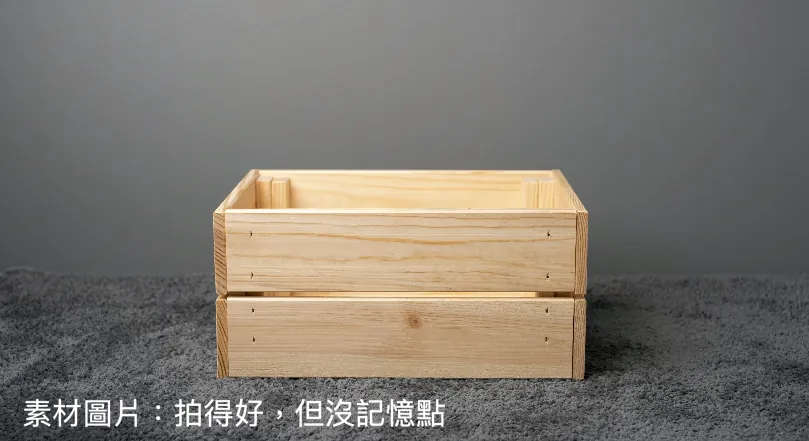
WWDC provided the above three images for illustration (under the same image quality), which are:
High-Quality Images: Composition, Lighting, and Memorable Elements
Low-Quality Images: No clear subject, appear to be taken casually or accidentally
Image Material: Technically well taken but lacks memorable elements, resembling stock photos used for material libraries.
iOS ≥ 18 New API: CalculateImageAestheticsScoresRequest
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
let request = CalculateImageAestheticsScoresRequest()
let result = try await request.perform(on: URL(string: "https://zhgchg.li/assets/cb65fd5ab770/1*yL3vI1ADzwlovctW5WQgJw.jpeg")!)
// Photo score
print(result.overallScore)
// Whether it is classified as a utility image
print(result.isUtility)
What’s new in Vision? (iOS 18) — Simultaneous Body and Hand Gesture Detection
Previously, only individual detection of body pose and hand pose was possible. This update allows developers to detect both body pose and hand pose simultaneously, combining them into a single request and result, making it easier to develop more application features.
iOS ≥ 18 New API: DetectHumanBodyPoseRequest
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
var request = DetectHumanBodyPoseRequest()
// Also detect hand poses
request.detectsHands = true
guard let bodyPose = try await request.perform(on: image).first else { return }
// Body pose joints
let bodyJoints = bodyPose.allJoints()
// Left hand pose joints
let leftHandJoints = bodyPose.leftHand.allJoints()
// Right hand pose joints
let rightHandJoints = bodyPose.rightHand.allJoints()
New Vision API
Apple has provided a new Swift Vision API wrapper for developers in this update. Besides supporting the original features, it mainly enhances Swift 6 and Swift Concurrency capabilities, offering better performance and a more Swift-friendly API usage.
Get started with Vision
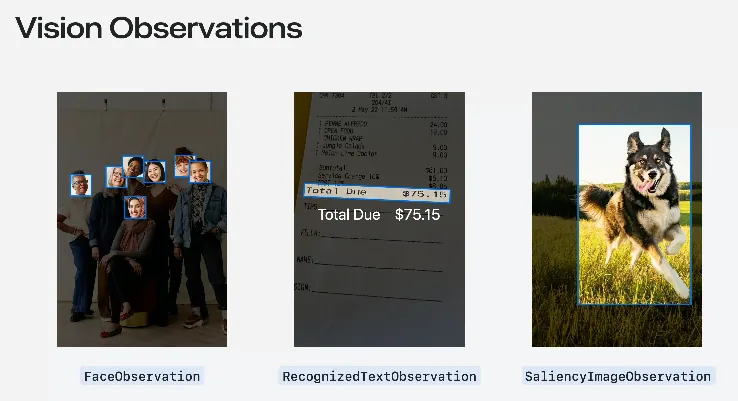
Here, the speaker reintroduced the basic usage of the Vision framework. Apple has already packaged 31 types (as of iOS 18) of common image recognition requests called “Request” and their corresponding returned “Observation” objects.
Request: DetectFaceRectanglesRequest Face region detection request
Result: FaceObservation
The previous article “Vision Introduction — APP Profile Picture Upload Automatic Face Crop Recognition (Swift)” used this pair of requests.Request: RecognizeTextRequest text recognition request
Result: RecognizedTextObservationRequest: GenerateObjectnessBasedSaliencyImageRequest Main Object Recognition Request
Result: SaliencyImageObservation
All 31 Types of Requests: Request:
\| Request Purpose \| Observation Description \| \|———————————————–\|——————————————————————\| \| CalculateImageAestheticsScoresRequest
Calculate the aesthetic score of an image. \| AestheticsObservation
Returns the aesthetic scores of the image, such as composition and color. \| \| ClassifyImageRequest
Classify image content. \| ClassificationObservation
Returns classification labels and confidence for objects or scenes in the image. \| \| CoreMLRequest
Analyze image using a Core ML model. \| CoreMLFeatureValueObservation
Generates observations based on the Core ML model output. \| \| DetectAnimalBodyPoseRequest
Detect animal poses in the image. \| RecognizedPointsObservation
Returns the animal’s skeleton points and their positions. \| \| DetectBarcodesRequest
Detect barcodes in the image. \| BarcodeObservation
Returns barcode data and type (e.g., QR code). \| \| DetectContoursRequest
Detect contours in the image. \| ContoursObservation
Returns detected contour lines in the image. \| \| DetectDocumentSegmentationRequest
Detect and segment documents in the image. \| RectangleObservation
Returns the rectangular boundary of the document. \| \| DetectFaceCaptureQualityRequest
Evaluate face capture quality. \| FaceObservation
Returns quality assessment scores of the face image. \| \| DetectFaceLandmarksRequest
Detect facial landmarks. \| FaceObservation
Returns detailed positions of facial landmarks (e.g., eyes, nose). \| \| DetectFaceRectanglesRequest
Detect faces in the image. \| FaceObservation
Returns bounding boxes of faces. \| \| DetectHorizonRequest
Detect horizon in the image. \| HorizonObservation
Returns the angle and position of the horizon. \| \| DetectHumanBodyPose3DRequest
Detect 3D human body poses in the image. \| RecognizedPointsObservation
Returns 3D human skeleton points and their spatial coordinates. \| \| DetectHumanBodyPoseRequest
Detect human body poses in the image. \| RecognizedPointsObservation
Returns human skeleton points and their coordinates. \| \| DetectHumanHandPoseRequest
Detect hand poses in the image. \| RecognizedPointsObservation
Returns hand skeleton points and their positions. \| \| DetectHumanRectanglesRequest
Detect humans in the image. \| HumanObservation
Returns bounding boxes of humans. \| \| DetectRectanglesRequest
Detect rectangles in the image. \| RectangleObservation
Returns coordinates of the four vertices of rectangles. \| \| DetectTextRectanglesRequest
Detect text regions in the image. \| TextObservation
Returns the position and bounding boxes of text areas. \| \| DetectTrajectoriesRequest
Detect and analyze object motion trajectories. \| TrajectoryObservation
Returns trajectory points and their time sequences. \| \| GenerateAttentionBasedSaliencyImageRequest
Generate attention-based saliency images. \| SaliencyImageObservation
Returns saliency maps of the most attractive areas in the image. \| \| GenerateForegroundInstanceMaskRequest
Generate foreground instance mask images. \| InstanceMaskObservation
Returns masks of foreground objects. \| \| GenerateImageFeaturePrintRequest
Generate image feature prints for comparison. \| FeaturePrintObservation
Returns feature print data of the image for similarity comparison. \| \| GenerateObjectnessBasedSaliencyImageRequest
Generate objectness-based saliency images. \| SaliencyImageObservation
Returns saliency maps of objectness areas. \| \| GeneratePersonInstanceMaskRequest
Generate person instance mask images. \| InstanceMaskObservation
Returns masks of person instances. \| \| GeneratePersonSegmentationRequest
Generate person segmentation images. \| SegmentationObservation
Returns binary masks for person segmentation. \| \| RecognizeAnimalsRequest
Detect and recognize animals in the image. \| RecognizedObjectObservation
Returns animal types and confidence levels. \| \| RecognizeTextRequest
Detect and recognize text in the image. \| RecognizedTextObservation
Returns detected text content and its region location. \| \| TrackHomographicImageRegistrationRequest
Track homographic image registration. \| ImageAlignmentObservation
Returns homography transformation matrices between images for registration. \| \| TrackObjectRequest
Track objects in the image. \| DetectedObjectObservation
Returns object positions and velocity information in the image. \| \| TrackOpticalFlowRequest
Track optical flow in the image. \| OpticalFlowObservation
Returns optical flow vector fields describing pixel movements. \| \| TrackRectangleRequest
Track rectangles in the image. \| RectangleObservation
Returns position, size, and rotation angle of rectangles in the image. \| \| TrackTranslationalImageRegistrationRequest
Track translational image registration. \| ImageAlignmentObservation
Returns translation transformation matrices between images for registration. \|
- Adding VN in front indicates the old API usage (versions before iOS 18).
The speaker mentioned several commonly used Requests, as follows.
ClassifyImageRequest
Identify the input image to obtain label categories and confidence levels.
[Travelogue] 2024 Second Visit to Kyushu: 9-Day Independent Trip, Entering via Busan → Hakata Cruise
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
let request = ClassifyImageRequest()
Task {
do {
let observations = try await request.perform(on: URL(string: "https://zhgchg.li/assets/cb65fd5ab770/1*yL3vI1ADzwlovctW5WQgJw.jpeg")!)
observations.forEach {
observation in
print("\(observation.identifier): \(observation.confidence)")
}
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
} else {
// Old approach
let completionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNClassificationObservation] else {
return
}
observations.forEach {
observation in
print("\(observation.identifier): \(observation.confidence)")
}
}
let request = VNClassifyImageRequest(completionHandler: completionHandler)
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(url: URL(string: "https://zhgchg.li/assets/cb65fd5ab770/1*3_jdrLurFuUfNdW4BJaRww.jpeg")!, options: [:])
do {
try handler.perform([request])
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
}
Analysis Results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
• outdoor: 0.75392926
• sky: 0.75392926
• blue_sky: 0.7519531
• machine: 0.6958008
• cloudy: 0.26538086
• structure: 0.15728651
• sign: 0.14224191
• fence: 0.118652344
• banner: 0.0793457
• material: 0.075975396
• plant: 0.054406323
• foliage: 0.05029297
• light: 0.048126098
• lamppost: 0.048095703
• billboards: 0.040039062
• art: 0.03977703
• branch: 0.03930664
• decoration: 0.036868922
• flag: 0.036865234
....omitted
RecognizeTextRequest
Recognize the text content in images. (a.k.a. Image to Text)
[Travelogue] 2023 Tokyo 5-Day Independent Trip
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
var request = RecognizeTextRequest()
request.recognitionLevel = .accurate
request.recognitionLanguages = [.init(identifier: "ja-JP"), .init(identifier: "en-US")] // Specify language code, e.g., Traditional Chinese
Task {
do {
let observations = try await request.perform(on: URL(string: "https://zhgchg.li/assets/9da2c51fa4f2/1*fBbNbDepYioQ-3-0XUkF6Q.jpeg")!)
observations.forEach {
observation in
let topCandidate = observation.topCandidates(1).first
print(topCandidate?.string ?? "No text recognized")
}
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
} else {
// Old approach
let completionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNRecognizedTextObservation] else {
return
}
observations.forEach {
observation in
let topCandidate = observation.topCandidates(1).first
print(topCandidate?.string ?? "No text recognized")
}
}
let request = VNRecognizeTextRequest(completionHandler: completionHandler)
request.recognitionLevel = .accurate
request.recognitionLanguages = ["ja-JP", "en-US"] // Specify language code, e.g., Traditional Chinese
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(url: URL(string: "https://zhgchg.li/assets/9da2c51fa4f2/1*fBbNbDepYioQ-3-0XUkF6Q.jpeg")!, options: [:])
do {
try handler.perform([request])
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
}
Analysis Results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
LE LABO Aoyama Store
TEL:03-6419-7167
*Thank you for your purchase*
No: 21347
Date: 2023/06/10 14:14:57
Staff:
1690370
Register: 008A 1
Product Name
Price Including Tax Quantity Total Including Tax
Kaiak 10 EDP FB 15ML
J1P7010000S
16,800
16,800
Another 13 EDP FB 15ML
J1PJ010000S
10,700
10,700
Lip Balm 15ML
JOWC010000S
2,000
1
Total Amount
(Tax Included)
CARD
2,000
3 items purchased
29,500
0
29,500
29,500
DetectBarcodesRequest
Detect barcode and QR code data in images.
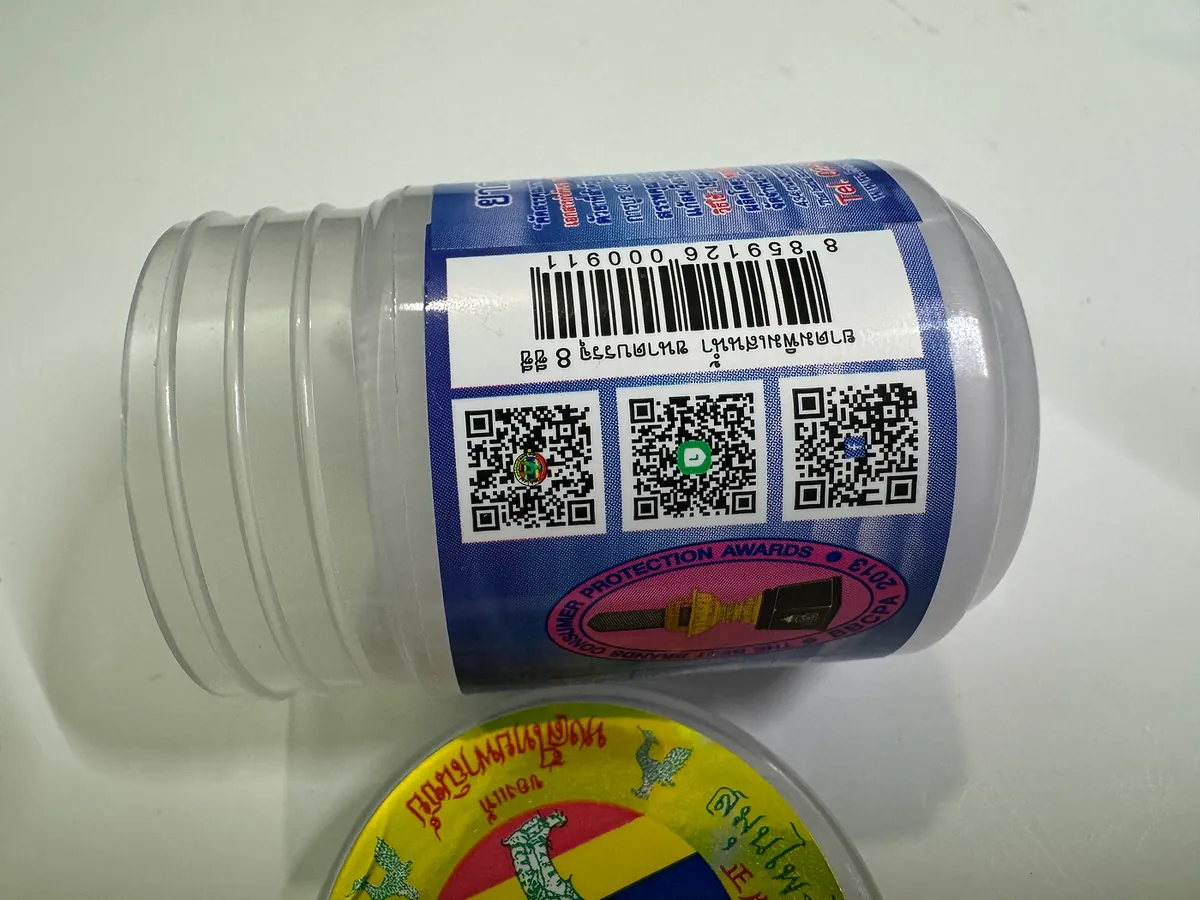
Locally Recommended White Flower Embrocation in Thailand
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
let filePath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "IMG_6777", ofType: "png")! // Local test image
let fileURL = URL(filePath: filePath)
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
let request = DetectBarcodesRequest()
Task {
do {
let observations = try await request.perform(on: fileURL)
observations.forEach {
observation in
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadString ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology)")
}
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
} else {
// Old approach
let completionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNBarcodeObservation] else {
return
}
observations.forEach {
observation in
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadStringValue ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology.rawValue)")
}
}
let request = VNDetectBarcodesRequest(completionHandler: completionHandler)
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(url: fileURL, options: [:])
do {
try handler.perform([request])
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
}
Analysis Results:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Payload: 8859126000911
Symbology: VNBarcodeSymbologyEAN13
Payload: https://lin.ee/hGynbVM
Symbology: VNBarcodeSymbologyQR
Payload: http://www.hongthaipanich.com/
Symbology: VNBarcodeSymbologyQR
Payload: https://www.facebook.com/qr?id=100063856061714
Symbology: VNBarcodeSymbologyQR
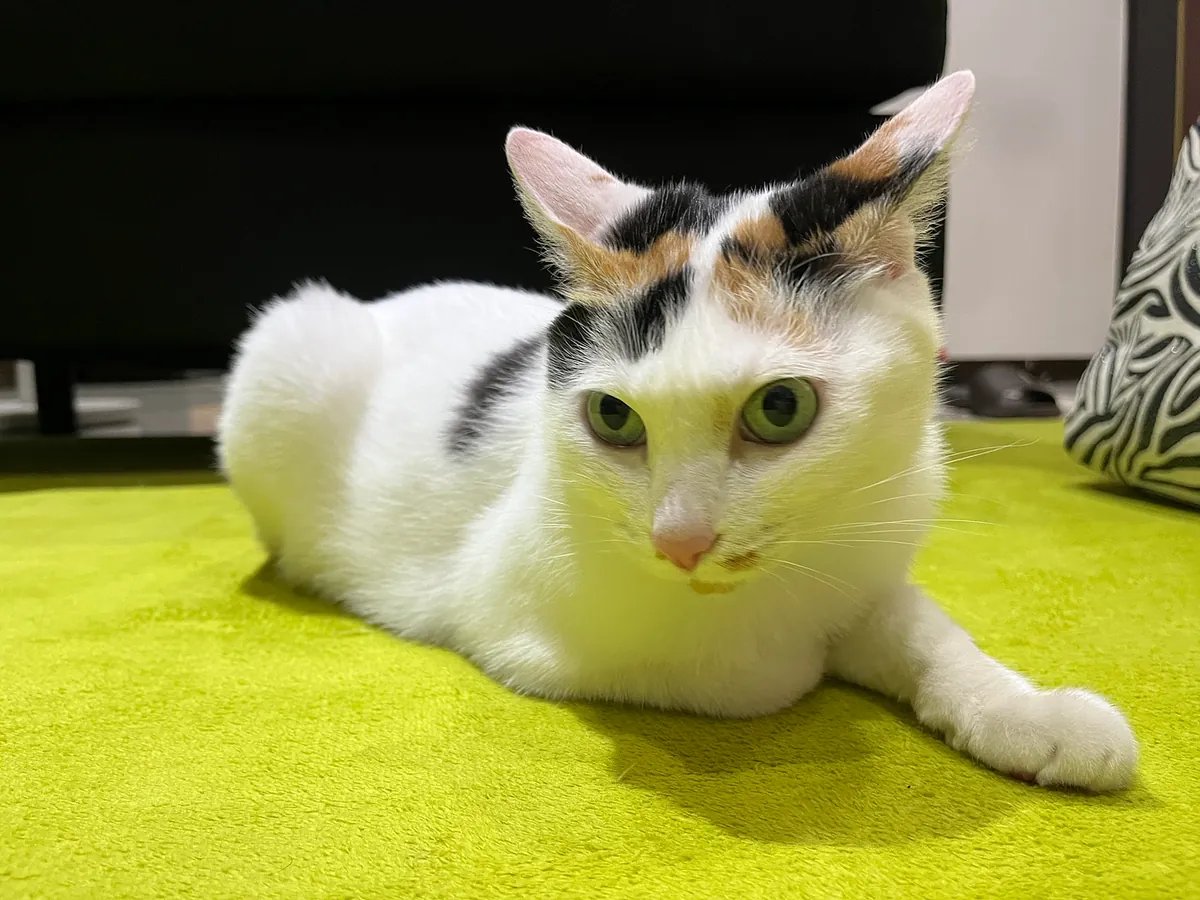
RecognizeAnimalsRequest
Identify the animal in the image and its confidence level.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
let filePath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "IMG_5026", ofType: "png")! // Local test image
let fileURL = URL(filePath: filePath)
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
let request = RecognizeAnimalsRequest()
Task {
do {
let observations = try await request.perform(on: fileURL)
observations.forEach {
observation in
let labels = observation.labels
labels.forEach {
label in
print("Detected animal: \(label.identifier) with confidence: \(label.confidence)")
}
}
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
} else {
// Old approach
let completionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNRecognizedObjectObservation] else {
return
}
observations.forEach {
observation in
let labels = observation.labels
labels.forEach {
label in
print("Detected animal: \(label.identifier) with confidence: \(label.confidence)")
}
}
}
let request = VNRecognizeAnimalsRequest(completionHandler: completionHandler)
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(url: fileURL, options: [:])
do {
try handler.perform([request])
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
}
Analysis Results:
1
Detected animal: Cat with confidence: 0.77245045
Others:
Detecting Human Figures in Images: DetectHumanRectanglesRequest
Detect poses of humans and animals (3D or 2D): DetectAnimalBodyPoseRequest, DetectHumanBodyPose3DRequest, DetectHumanBodyPoseRequest, DetectHumanHandPoseRequest
Detect and track the movement trajectory of objects (in different frames of videos or animations): DetectTrajectoriesRequest, TrackObjectRequest, TrackRectangleRequest
iOS ≥ 18 Update Highlight:
1
2
3
4
VN*Request -> *Request (e.g. VNDetectBarcodesRequest -> DetectBarcodesRequest)
VN*Observation -> *Observation (e.g. VNRecognizedObjectObservation -> RecognizedObjectObservation)
VNRequestCompletionHandler -> async/await
VNImageRequestHandler.perform([VN*Request]) -> *Request.perform()
WWDC Example
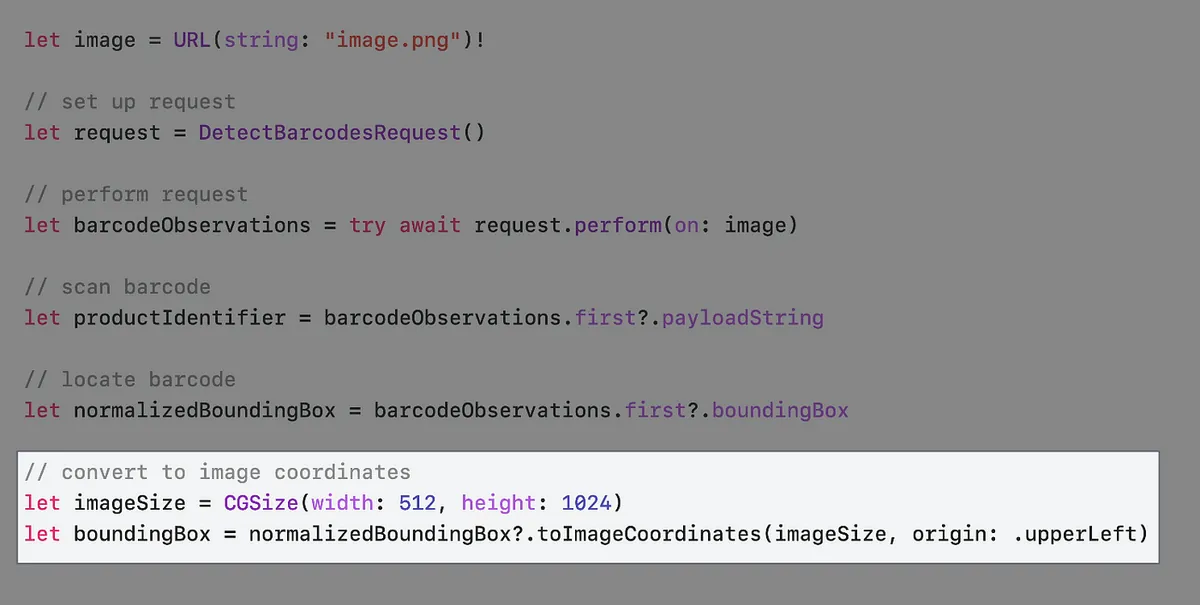
WWDC official video uses a supermarket barcode scanner as an example.
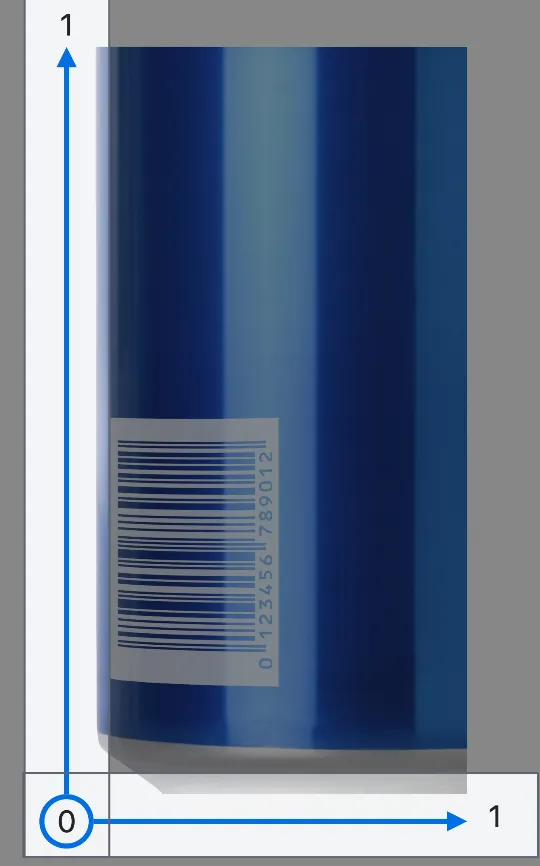
First, most products have barcodes available for scanning
We can get the barcode location from observation.boundingBox, but unlike the common UIView coordinate system, the origin of boundingBox is at the bottom-left corner, and its values range between 0 and 1.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
let filePath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "IMG_6785", ofType: "png")! // Local test image
let fileURL = URL(filePath: filePath)
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
var request = DetectBarcodesRequest()
request.symbologies = [.ean13] // Specify only EAN13 Barcode to scan for better performance
Task {
do {
let observations = try await request.perform(on: fileURL)
if let observation = observations.first {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.infoLabel.text = observation.payloadString
// Marking color Layer
let colorLayer = CALayer()
// iOS >=18 new coordinate conversion API toImageCoordinates
// Untested, may still need to calculate ContentMode = AspectFit offset:
colorLayer.frame = observation.boundingBox.toImageCoordinates(self.baseImageView.frame.size, origin: .upperLeft)
colorLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.red.withAlphaComponent(0.5).cgColor
self.baseImageView.layer.addSublayer(colorLayer)
}
print("BoundingBox: \(observation.boundingBox.cgRect)")
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadString ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology)")
}
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
} else {
// Old approach
let completionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNBarcodeObservation] else {
return
}
if let observation = observations.first {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.infoLabel.text = observation.payloadStringValue
// Marking color Layer
let colorLayer = CALayer()
colorLayer.frame = self.convertBoundingBox(observation.boundingBox, to: self.baseImageView)
colorLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.red.withAlphaComponent(0.5).cgColor
self.baseImageView.layer.addSublayer(colorLayer)
}
print("BoundingBox: \(observation.boundingBox)")
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadStringValue ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology.rawValue)")
}
}
let request = VNDetectBarcodesRequest(completionHandler: completionHandler)
request.symbologies = [.ean13] // Specify only EAN13 Barcode to scan for better performance
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(url: fileURL, options: [:])
do {
try handler.perform([request])
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
}
iOS ≥ 18 Update Highlight:
// iOS >=18 new coordinate conversion API toImageCoordinates
observation.boundingBox.toImageCoordinates(CGSize, origin: .upperLeft)
// https://developer.apple.com/documentation/vision/normalizedpoint/toimagecoordinates(from:imagesize:origin:)
Helper:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// Gen by ChatGPT 4o
// Because the photo's ImageView has ContentMode = AspectFit
// We need to calculate the vertical offset caused by the Fit's blank space
func convertBoundingBox(_ boundingBox: CGRect, to view: UIImageView) -> CGRect {
guard let image = view.image else {
return .zero
}
let imageSize = image.size
let viewSize = view.bounds.size
let imageRatio = imageSize.width / imageSize.height
let viewRatio = viewSize.width / viewSize.height
var scaleFactor: CGFloat
var offsetX: CGFloat = 0
var offsetY: CGFloat = 0
if imageRatio > viewRatio {
// Image fits by width
scaleFactor = viewSize.width / imageSize.width
offsetY = (viewSize.height - imageSize.height * scaleFactor) / 2
}
else {
// Image fits by height
scaleFactor = viewSize.height / imageSize.height
offsetX = (viewSize.width - imageSize.width * scaleFactor) / 2
}
let x = boundingBox.minX * imageSize.width * scaleFactor + offsetX
let y = (1 - boundingBox.maxY) * imageSize.height * scaleFactor + offsetY
let width = boundingBox.width * imageSize.width * scaleFactor
let height = boundingBox.height * imageSize.height * scaleFactor
return CGRect(x: x, y: y, width: width, height: height)
}
Output
1
2
3
BoundingBox: (0.5295758928571429, 0.21408638121589782, 0.0943080357142857, 0.21254415360708087)
Payload: 4710018183805
Symbology: VNBarcodeSymbologyEAN13
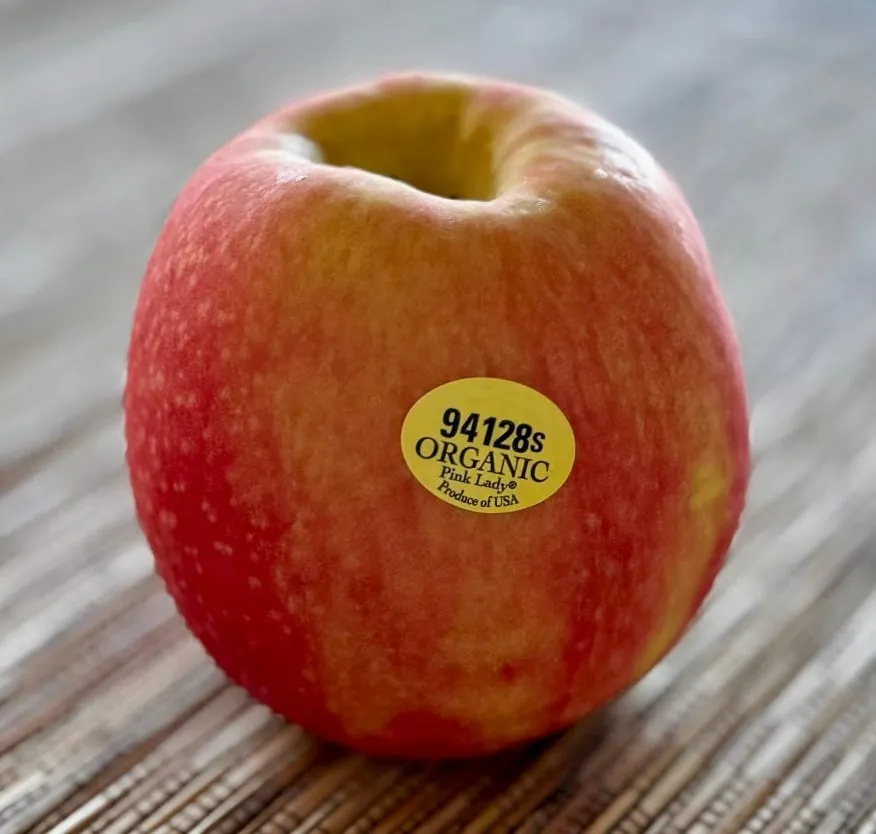
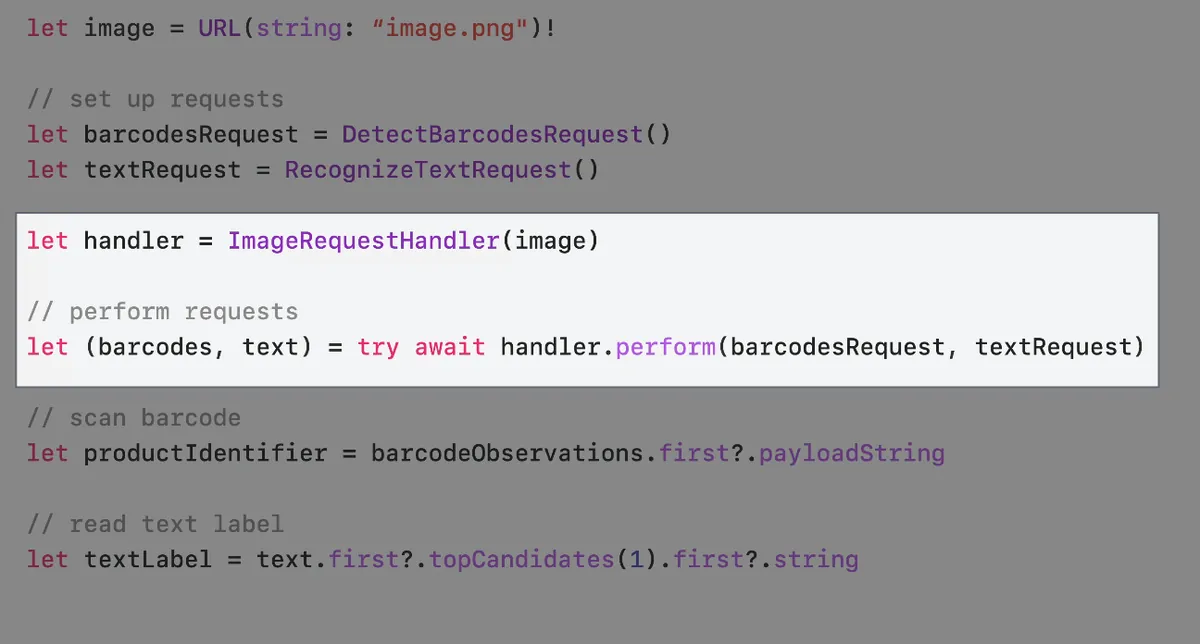
Some products have no Barcode, such as loose fruits with only product labels
Therefore, our scanner also needs to support scanning plain text labels.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
let filePath = Bundle.main.path(forResource: "apple", ofType: "jpg")! // Local test image
let fileURL = URL(filePath: filePath)
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
var barcodesRequest = DetectBarcodesRequest()
barcodesRequest.symbologies = [.ean13] // Specify EAN13 Barcode only to improve performance
var textRequest = RecognizeTextRequest()
textRequest.recognitionLanguages = [.init(identifier: "zh-Hnat"), .init(identifier: "en-US")]
Task {
do {
let handler = ImageRequestHandler(fileURL)
// parameter pack syntax and we must wait for all requests to finish before we can use their results.
// let (barcodesObservation, textObservation, ...) = try await handler.perform(barcodesRequest, textRequest, ...)
let (barcodesObservation, textObservation) = try await handler.perform(barcodesRequest, textRequest)
if let observation = barcodesObservation.first {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.infoLabel.text = observation.payloadString
// Highlight color layer
let colorLayer = CALayer()
// iOS >=18 new coordinate conversion API toImageCoordinates
// Untested, actual implementation may need to adjust for ContentMode = AspectFit offset:
colorLayer.frame = observation.boundingBox.toImageCoordinates(self.baseImageView.frame.size, origin: .upperLeft)
colorLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.red.withAlphaComponent(0.5).cgColor
self.baseImageView.layer.addSublayer(colorLayer)
}
print("BoundingBox: \(observation.boundingBox.cgRect)")
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadString ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology)")
}
textObservation.forEach {
observation in
let topCandidate = observation.topCandidates(1).first
print(topCandidate?.string ?? "No text recognized")
}
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
} else {
// Old implementation
let barcodesCompletionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNBarcodeObservation] else {
return
}
if let observation = observations.first {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.infoLabel.text = observation.payloadStringValue
// Highlight color layer
let colorLayer = CALayer()
colorLayer.frame = self.convertBoundingBox(observation.boundingBox, to: self.baseImageView)
colorLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.red.withAlphaComponent(0.5).cgColor
self.baseImageView.layer.addSublayer(colorLayer)
}
print("BoundingBox: \(observation.boundingBox)")
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadStringValue ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology.rawValue)")
}
}
let textCompletionHandler: VNRequestCompletionHandler = {
request, error in
guard error == nil else {
print("Request failed: \(String(describing: error))")
return
}
guard let observations = request.results as? [VNRecognizedTextObservation] else {
return
}
observations.forEach {
observation in
let topCandidate = observation.topCandidates(1).first
print(topCandidate?.string ?? "No text recognized")
}
}
let barcodesRequest = VNDetectBarcodesRequest(completionHandler: barcodesCompletionHandler)
barcodesRequest.symbologies = [.ean13] // Specify EAN13 Barcode only to improve performance
let textRequest = VNRecognizeTextRequest(completionHandler: textCompletionHandler)
textRequest.recognitionLevel = .accurate
textRequest.recognitionLanguages = ["en-US"]
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let handler = VNImageRequestHandler(url: fileURL, options: [:])
do {
try handler.perform([barcodesRequest, textRequest])
}
catch {
print("Request failed: \(error)")
}
}
}
Output:
1
2
3
4
94128s
ORGANIC
Pink Lady®
Produce of USh
iOS ≥ 18 Update Highlight:
1
2
3
4
let handler = ImageRequestHandler(fileURL)
// parameter pack syntax and we must wait for all requests to finish before we can use their results.
// let (barcodesObservation, textObservation, ...) = try await handler.perform(barcodesRequest, textRequest, ...)
let (barcodesObservation, textObservation) = try await handler.perform(barcodesRequest, textRequest)
iOS ≥ 18 performAll( )?changes=latest_minor){:target=”_blank”} method
The previous perform(barcodesRequest, textRequest) method requires both requests to complete before continuing; starting with iOS 18, a new performAll() method is provided, which changes the response to streaming, allowing handling as soon as one request returns a result, such as responding immediately when a barcode is scanned.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
if #available(iOS 18.0, *) {
// New API using Swift features
var barcodesRequest = DetectBarcodesRequest()
barcodesRequest.symbologies = [.ean13] // Specify EAN13 barcode only for better performance
var textRequest = RecognizeTextRequest()
textRequest.recognitionLanguages = [.init(identifier: "zh-Hnat"), .init(identifier: "en-US")]
Task {
let handler = ImageRequestHandler(fileURL)
let observation = handler.performAll([barcodesRequest, textRequest] as [any VisionRequest])
for try await result in observation {
switch result {
case .detectBarcodes(_, let barcodesObservation):
if let observation = barcodesObservation.first {
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.infoLabel.text = observation.payloadString
// Mark color Layer
let colorLayer = CALayer()
// iOS >=18 new coordinate conversion API toImageCoordinates
// Untested, may still need to calculate displacement for ContentMode = AspectFit:
colorLayer.frame = observation.boundingBox.toImageCoordinates(self.baseImageView.frame.size, origin: .upperLeft)
colorLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.red.withAlphaComponent(0.5).cgColor
self.baseImageView.layer.addSublayer(colorLayer)
}
print("BoundingBox: \(observation.boundingBox.cgRect)")
print("Payload: \(observation.payloadString ?? "No payload")")
print("Symbology: \(observation.symbology)")
}
case .recognizeText(_, let textObservation):
textObservation.forEach {
observation in
let topCandidate = observation.topCandidates(1).first
print(topCandidate?.string ?? "No text recognized")
}
default:
print("Unrecognized result: \(result)")
}
}
}
}
Optimize with Swift Concurrency
Assuming we have a photo wall list where each image needs automatic cropping to the main subject; in this case, Swift Concurrency can be used to improve loading efficiency.
Original Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
func generateThumbnail(url: URL) async throws -> UIImage {
let request = GenerateAttentionBasedSaliencyImageRequest()
let saliencyObservation = try await request.perform(on: url)
return cropImage(url, to: saliencyObservation.salientObjects)
}
func generateAllThumbnails() async throws {
for image in images {
image.thumbnail = try await generateThumbnail(url: image.url)
}
}
Execute only one at a time, resulting in slow efficiency and performance.
Optimization (1) — TaskGroup Concurrency
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
func generateAllThumbnails() async throws {
try await withThrowingDiscardingTaskGroup { taskGroup in
for image in images {
image.thumbnail = try await generateThumbnail(url: image.url)
}
}
}
Add each Task to a TaskGroup for concurrent execution.
Issue: Image recognition and screenshot operations consume a lot of memory and performance. Adding unlimited parallel tasks may cause user lag and OOM crashes.
Optimization (2) — TaskGroup Concurrency + Limiting Parallelism
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
func generateAllThumbnails() async throws {
try await withThrowingDiscardingTaskGroup {
taskGroup in
// Maximum number of concurrent tasks should not exceed 5
let maxImageTasks = min(5, images.count)
// Initially fill with 5 tasks
for index in 0..<maxImageTasks {
taskGroup.addTask {
image[index].thumbnail = try await generateThumbnail(url: image[index].url)
}
}
var nextIndex = maxImageTasks
for try await _ in taskGroup {
// When a task in the taskGroup completes...
// Check if index has reached the end
if nextIndex < images.count {
let image = images[nextIndex]
// Continue adding tasks one by one (keeping max at 5)
taskGroup.addTask {
image.thumbnail = try await generateThumbnail(url: image.url)
}
nextIndex += 1
}
}
}
}
Update an existing Vision app
Vision will remove CPU and GPU support for some requests on devices with a neural engine. On these devices, the neural engine offers the best performance.
You can check this using thesupportedComputeDevices()API.Remove all VN prefixes
VNXXRequest,VNXXXObservation->Request,ObservationUse async/await to replace the original VNRequestCompletionHandler
Use
*Request.perform()directly instead of the originalVNImageRequestHandler.perform([VN*Request])
Wrap-up
API Designed for Swift Language Features
New features and methods are Swift only, available for iOS ≥ 18
New Image Rating Feature, Body + Hand Motion Tracking
Thanks!
KKday Recruitment Advertisement
👉👉👉This book club sharing originates from the weekly technical sharing sessions within the KKday App Team. The team is currently enthusiastically recruiting a Senior iOS Engineer. Interested candidates are welcome to apply. 👈👈👈
References
Discover Swift enhancements in the Vision framework
The Vision Framework API has been redesigned to leverage modern Swift features like concurrency, making it easier and faster to integrate a wide array of Vision algorithms into your app. We’ll tour the updated API and share sample code, along with best practices, to help you get the benefits of this framework with less coding effort. We’ll also demonstrate two new features: image aesthetics and holistic body pose.
Chapters
0:00 — Introduction
1:07 — New Vision API
1:47 — Get started with Vision
11:05 — Update an existing Vision app
13:46 — What’s new in Vision?
Vision framework Apple Developer Documentation
-
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to contact me.
This post was originally published on Medium (View original post), and automatically converted and synced by ZMediumToMarkdown.


{:target="_blank"}](/assets/755509180ca8/1*8N5GtY1uqxP-4iAAAticOA.webp)









![[Travelogue] 2024 Second Visit to Kyushu 9-Day Free Travel, Entering via Busan→Hakata Cruise](/assets/755509180ca8/1*f1rNoOIQbE33M9F9NmoTXg.webp)
![[[Travelogue] Tokyo 5-Day Free Trip 2023](/posts/travel-journals/en/tokyo-5-day-travel-guide-top-tips-for-food-stay-transport-9da2c51fa4f2/)](/assets/755509180ca8/1*XL40lLT774PfO60rCIfnxA.webp)



{:target="_blank"}](/assets/755509180ca8/1*KZ7mdE8fobP-_oj7tJf_Ww.webp)