Crashlytics & Google Analytics|Automate Crash-Free User Rate Queries with Google Apps Script
Discover how to automate fetching Crashlytics crash-free user rates using Google Analytics and Google Apps Script, seamlessly populating your Google Sheets for real-time app performance insights.
点击这里查看本文章简体中文版本。
點擊這裡查看本文章正體中文版本。
This post was translated with AI assistance — let me know if anything sounds off!
Table of Contents
Crashlytics + Google Analytics Automated Query for App Crash-Free Users Rate
Using Google Apps Script to Query Crashlytics via Google Analytics and Auto-fill into Google Sheet
In the previous article “Crashlytics + Big Query: Building a More Real-Time and Convenient Crash Tracking Tool,” we exported raw crash data from Crashlytics to Big Query and used Google Apps Script to schedule queries for the Top 10 crashes and send notifications to a Slack channel.
This article continues from automating an important metric related to app crashes — Crash-Free Users Rate, the percentage of unaffected users. Many app teams continuously track and record this data. Traditionally, this was done manually. The goal here is to automate this repetitive task and avoid errors caused by manual data entry. As mentioned before, Firebase Crashlytics does not provide any API for querying data, so we need to connect Firebase data to other Google services and then use those services’ APIs to retrieve the relevant data.
At first, I thought this data could also be queried from Big Query; however, this approach was completely wrong because Big Query contains only raw crash data and does not include data for users without crashes. Therefore, it cannot calculate the Crash-Free Users Rate. There is little information about this requirement online, and after a long search, I found someone mentioning the keyword Google Analytics. I knew Firebase Analytics and Events could be linked to GA for queries, but I didn’t expect the Crash-Free Users Rate data to be included as well. After reviewing the GA API, Bingo!
Google Analytics Data API (GA4) offers two metrics:
crashAffectedUsers: Number of users affected by crashes
crashFreeUsersRate: Percentage of users not affected by crashes (expressed as a decimal)
Once you understand the routing, you can start implementing it!
Integrate Firebase -> Google Analytics
Refer to the official instructions for setup steps; omitted here for brevity.
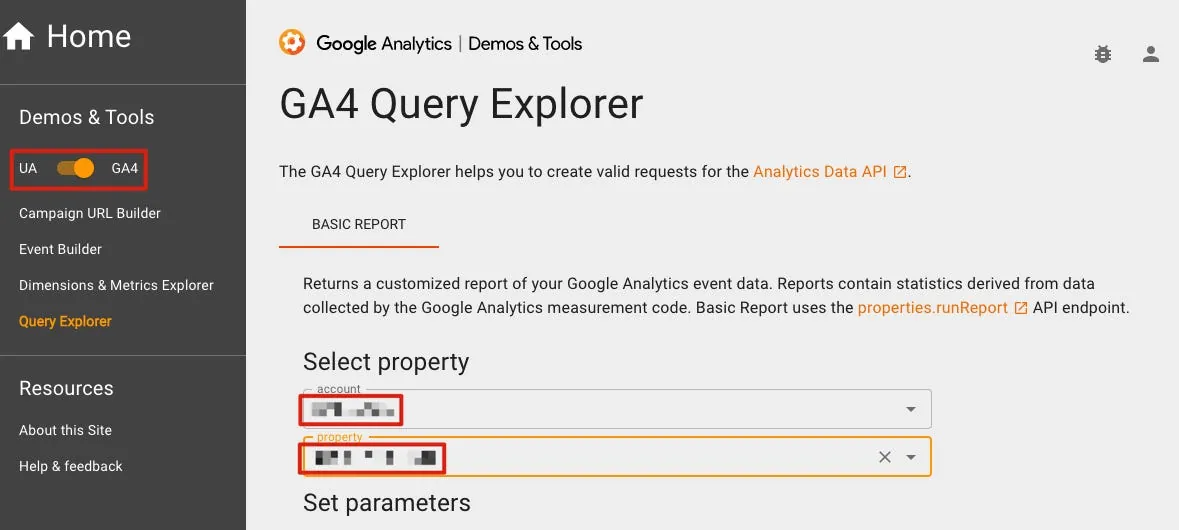
GA4 Query Explorer Tool
Before writing code, we can first use the official Web GUI Tool to quickly build query conditions and obtain query results; after confirming the results are what we want, we can then start coding.
Remember to select GA4 in the top left corner.
After logging in on the right, select the corresponding GA Account & Property.
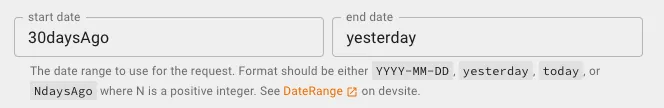
- Start Date, End Date: You can directly enter the date or use special variables to represent the date (
ysterday,today,30daysAgo,7daysAgo)
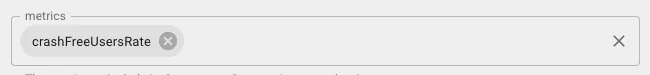
- metrics: Add
crashFreeUsersRate
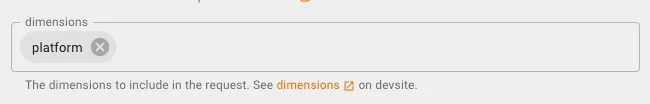
- dimensions: Add
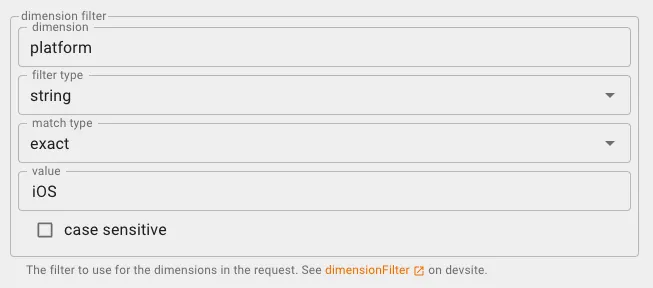
platform(device type iOS/Android/Desktop…)
- dimension filter: add
platform,string,exact,iOSorAndroid
Query the Crash Free Users Rate separately for both platforms.
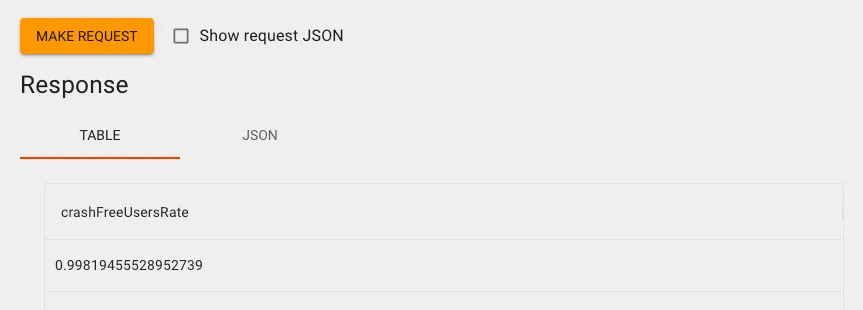
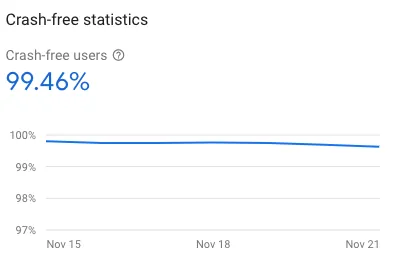
Scroll to the bottom and click “Make Request” to see the results. We can then get the Crash-Free Users Rate for the specified date range.
You can go back and open Firebase Crashlytics to compare if the data under the same conditions is identical.
There is a slight difference between the two numbers (one value differs by 0.0002), cause unknown, but within an acceptable margin of error; if we consistently use the GA Crash-Free Users Rate, it wouldn’t be considered an error.
Use Google Apps Script to Automatically Fill Data into Google Sheets
Next is the automation part. We will use Google Apps Script to query the GA Crash-Free Users Rate data and automatically fill it into our Google Sheet; achieving the goal of automatic entry and tracking.
Assuming our Google Sheet is as shown in the above image.
You can click Extensions -> Apps Script at the top of Google Sheets to create a Google Apps Script, or go to Google Apps Script -> click New Project at the top left.
After entering, you can first click the untitled project name at the top and give the project a name.
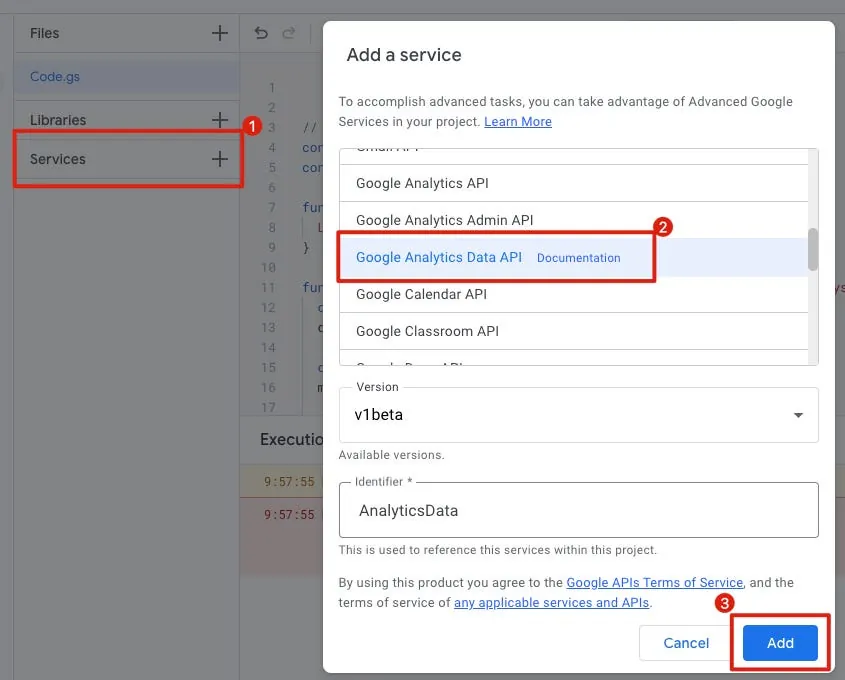
In the left menu under “Services,” click the “+” to add “Google Analytics Data API.”
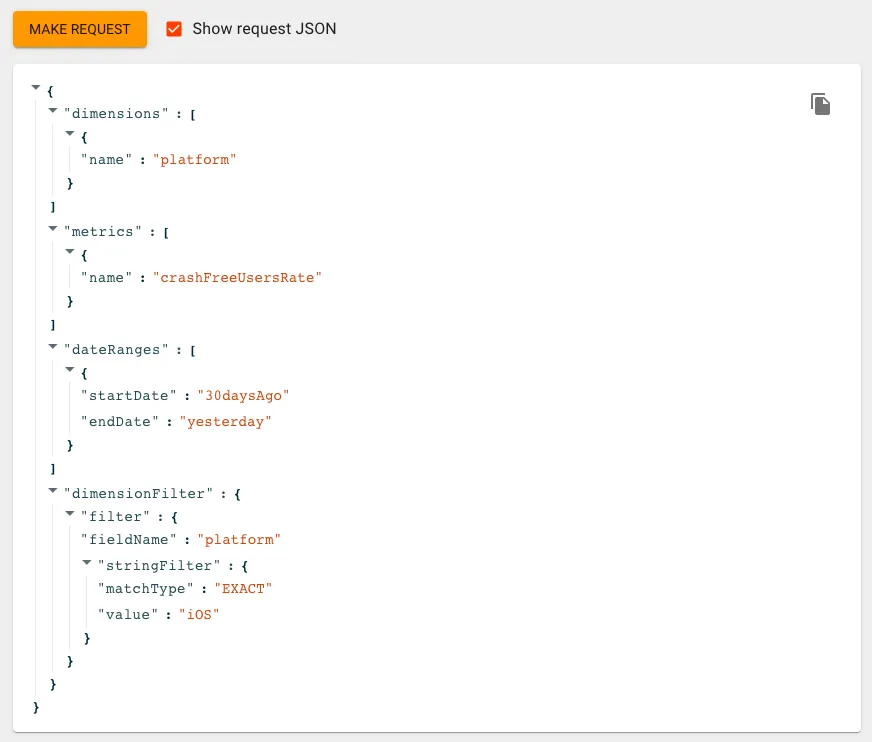
Back to the GA4 Query Explorer tool, you can check “Show Request JSON” next to the Make Request button to get the Request JSON for this condition.
The converted Request JSON to Google Apps Script is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
// Remember to add Google Analytics Data API to Services, or you'll see this error: ReferenceError: AnalyticsData is not defined
// https://ga-dev-tools.web.app/ga4/query-explorer/ -> property id
const propertyId = "";
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/googleSheetID/
const googleSheetID = "";
// Google Sheet name
const googleSheetName = "App Crash-Free Users Rate";
function execute() {
Logger.log(fetchCrashFreeUsersRate())
}
function fetchCrashFreeUsersRate(platform = "iOS", startDate = "30daysAgo", endDate = "today") {
const dimensionPlatform = AnalyticsData.newDimension();
dimensionPlatform.name = "platform";
const metric = AnalyticsData.newMetric();
metric.name = "crashFreeUsersRate";
const dateRange = AnalyticsData.newDateRange();
dateRange.startDate = startDate;
dateRange.endDate = endDate;
const filterExpression = AnalyticsData.newFilterExpression();
const filter = AnalyticsData.newFilter();
filter.fieldName = "platform";
const stringFilter = AnalyticsData.newStringFilter()
stringFilter.value = platform;
stringFilter.matchType = "EXACT";
filter.stringFilter = stringFilter;
filterExpression.filter = filter;
const request = AnalyticsData.newRunReportRequest();
request.dimensions = [dimensionPlatform];
request.metrics = [metric];
request.dateRanges = dateRange;
request.dimensionFilter = filterExpression;
const report = AnalyticsData.Properties.runReport(request, "properties/" + propertyId);
return parseFloat(report.rows[0].metricValues[0].value) * 100;
}
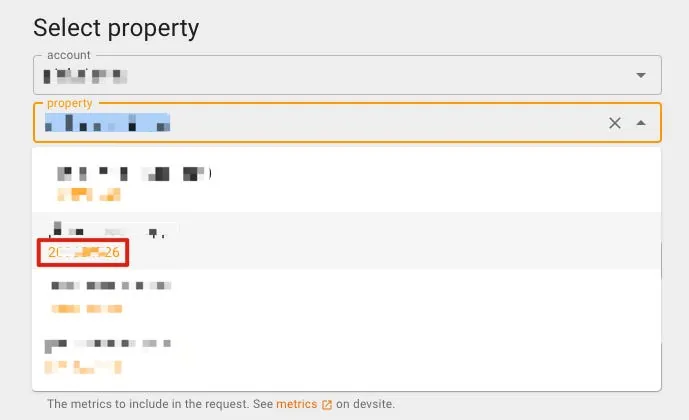
- GA Property ID: You can also get it from the GA4 Query Explorer tool mentioned earlier:
In the initial Property selection menu, the number below the chosen Property is the propertyId.
googleSheetID: Can be obtained from the Google Sheet URL https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/
googleSheetID/editgoogleSheetName: The name of the sheet in Google Sheets that records crash logs
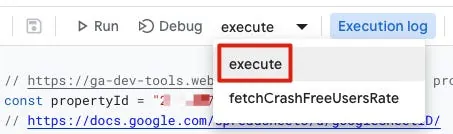
Paste the above code into the right code editor in Google Apps Script, then select the “execute” function from the method dropdown above. You can click Debug to test if the data can be retrieved correctly:
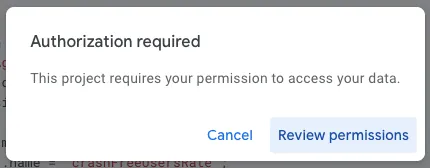
The first time you run it, an authorization prompt will appear:
Complete the account authorization by following the steps.
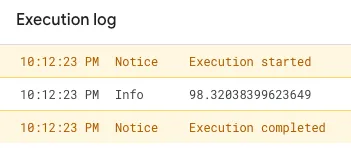
If the execution is successful, the Crash-Free Users Rate will be printed in the log below, indicating a successful query.
Next, we just need to add automatic input into Google Sheets, and we’re all set!
Complete Code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
// Remember to add Google Analytics Data API to Services, or you'll see this error: ReferenceError: AnalyticsData is not defined
// https://ga-dev-tools.web.app/ga4/query-explorer/ -> property id
const propertyId = "";
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/googleSheetID/
const googleSheetID = "";
// Google Sheet name
const googleSheetName = "";
function execute() {
const today = new Date();
const daysAgo7 = new Date(new Date().setDate(today.getDate() - 6)); // Today not included, so -6
const spreadsheet = SpreadsheetApp.openById(googleSheetID);
const sheet = spreadsheet.getSheetByName(googleSheetName);
var rows = [];
rows[0] = Utilities.formatDate(daysAgo7, "GMT+8", "MM/dd")+"~"+Utilities.formatDate(today, "GMT+8", "MM/dd");
rows[1] = fetchCrashFreeUsersRate("iOS", Utilities.formatDate(daysAgo7, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM-dd"), Utilities.formatDate(today, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM-dd"));
rows[2] = fetchCrashFreeUsersRate("android", Utilities.formatDate(daysAgo7, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM-dd"), Utilities.formatDate(today, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM-dd"));
sheet.appendRow(rows);
}
function fetchCrashFreeUsersRate(platform = "iOS", startDate = "30daysAgo", endDate = "today") {
const dimensionPlatform = AnalyticsData.newDimension();
dimensionPlatform.name = "platform";
const metric = AnalyticsData.newMetric();
metric.name = "crashFreeUsersRate";
const dateRange = AnalyticsData.newDateRange();
dateRange.startDate = startDate;
dateRange.endDate = endDate;
const filterExpression = AnalyticsData.newFilterExpression();
const filter = AnalyticsData.newFilter();
filter.fieldName = "platform";
const stringFilter = AnalyticsData.newStringFilter()
stringFilter.value = platform;
stringFilter.matchType = "EXACT";
filter.stringFilter = stringFilter;
filterExpression.filter = filter;
const request = AnalyticsData.newRunReportRequest();
request.dimensions = [dimensionPlatform];
request.metrics = [metric];
request.dateRanges = dateRange;
request.dimensionFilter = filterExpression;
const report = AnalyticsData.Properties.runReport(request, "properties/" + propertyId);
return parseFloat(report.rows[0].metricValues[0].value) * 100;
}
Click “Run or Debug” above again to execute.
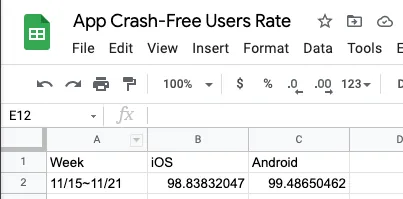
Back to Google Sheet, data added successfully!
Add Trigger for Scheduled Automation Execution
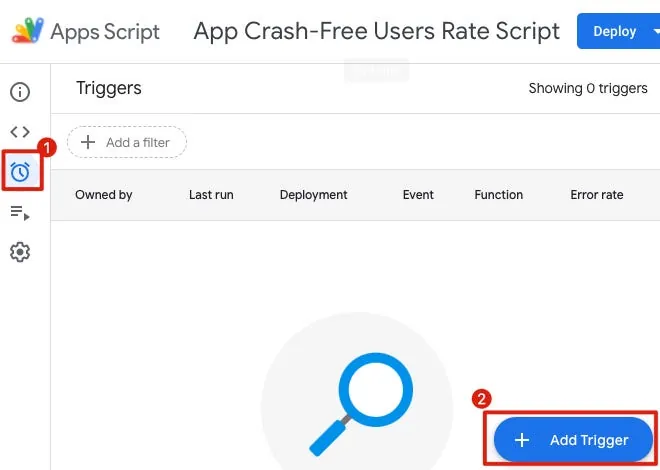
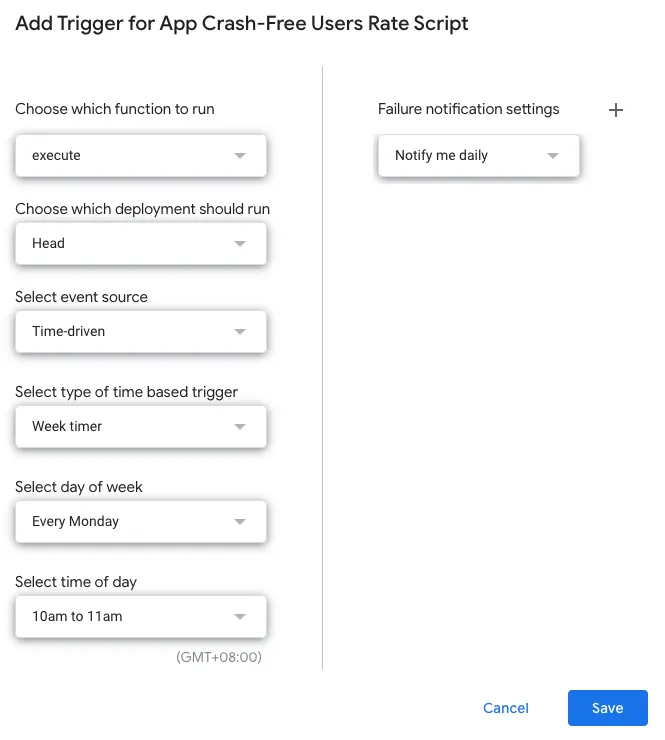
Select the clock button on the left -> “+ Add Trigger” at the bottom right.
The first function selects “execute”
The time-based trigger allows selecting a weekly timer to track and add data once every week
After setting, just click Save.
Completed
Starting now, fully automate the tracking of App Crash-Free Users Rate data; no manual queries or entries needed; let the machine handle everything automatically!
We only need to focus on solving the App Crash issue!
p.s. Unlike the previous article using Big Query which requires payment for data queries, this article’s queries on Crash-Free Users Rate and Google Apps Script are completely free to use.
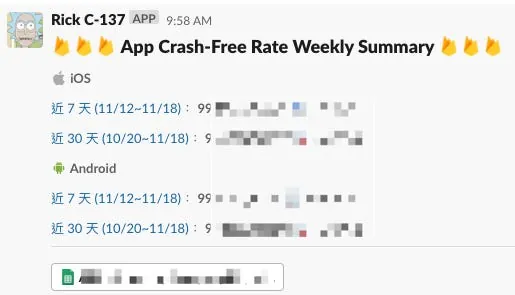
If you want to send the results to a Slack Channel simultaneously, refer to the previous article:
Further Reading
Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Google Analytics 4 (NEW 2023 Interface) (Thanks to Emma for providing the information)
Crashlytics + Big Query Build a More Real-Time and Convenient Crash Tracking Tool
Automate Routine Tasks Using Python + Google Cloud Platform + Line Bot
Slack Builds Fully Automated WFH Employee Health Reporting System
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to contact me.
This post was originally published on Medium (View original post), and automatically converted and synced by ZMediumToMarkdown.

{:target="_blank"}](/assets/793cb8f89b72/1*4BVf-FMVcY1UbVuLwfKOQg.webp)