iOS NSAttributedString HTML Render 自行实现|解决闪退与效能瓶颈
针对 iOS NSAttributedString HTML 解析闪退与效能差问题,提供纯 Swift XMLParser 自行实现 HTML Render 技术,避免主线程阻塞,提升渲染速度达 5~20 倍,并支援自订标签样式与扩充,确保稳定且可维护的文字渲染体验。
Click here to view the English version of this article.
點擊這裡查看本文章正體中文版本。
基于 SEO 考量,本文标题与描述经 AI 调整,原始版本请参考内文。
文章目录
自行实现 iOS NSAttributedString HTML Render
iOS NSAttributedString DocumentType.html 的替代方案
Photo by Florian Olivo
[TL;DR] 2023/03/12
重新使用其他方式开发了 「 ZMarkupParser HTML String 转换 NSAttributedString 工具 」 ,技术细节及开发故事请前往「 手工打造 HTML 解析器的那些事 」
起源
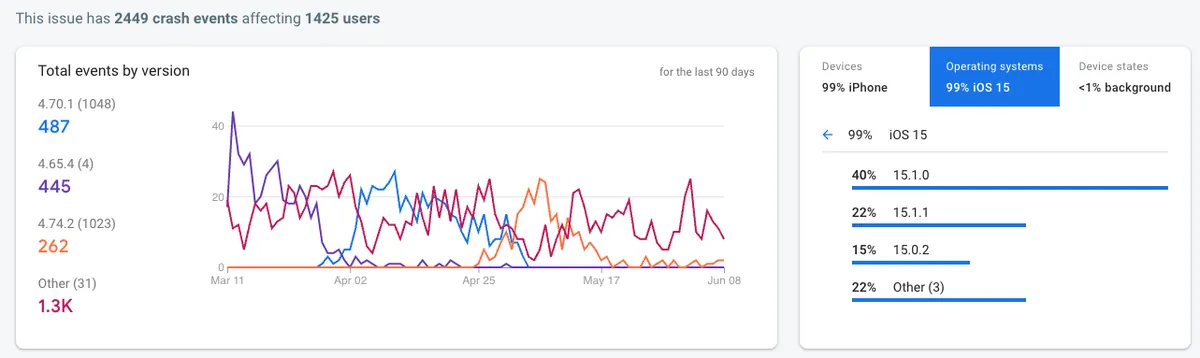
从去年 iOS 15 发布以来,App 始终被一项 Crash 问题长年霸榜,从数据来看,近 90 天 (2022/03/11~2022/06/08) 一共造成 2.4K+ 次闪退、影响 1.4K+ 位使用者。
此大量闪退问题从数据上看,官方应该已在 iOS ≥ 15.2 后续的版本修复(或减少发生机率),数据已呈现趋势下降。
最大宗受影响版本: iOS 15.0.X ~ iOS 15.X.X
另外有发现 iOS 12、iOS 13 也有零星闪退数,所以此问题应该已存在许久,只是 iOS 15 前几版发生的机率几乎是 100%。
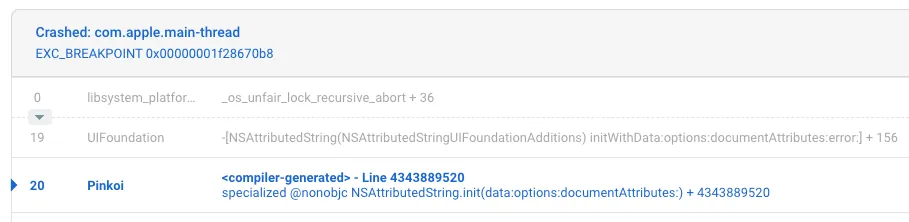
闪退原因:
1
<compiler-generated> line 2147483647 specialized @nonobjc NSAttributedString.init(data:options:documentAttributes:)
NSAttributedString 在 init 时发生 Crashed: com.apple.main-thread EXC_BREAKPOINT 0x00000001de9d4e44 闪退问题。
亦有可能是操作的地方不在 Main Thread.
重现方式:
此问题大量横空出世时,让开发团队想破脑袋;复测 Crash Log 上的点都没问题,不清楚使用者是在什么情况下发生的;直到有一次因缘巧合下我刚好切换成「省电模式」然后就触发问题了! ! WTF ! ! !
解答
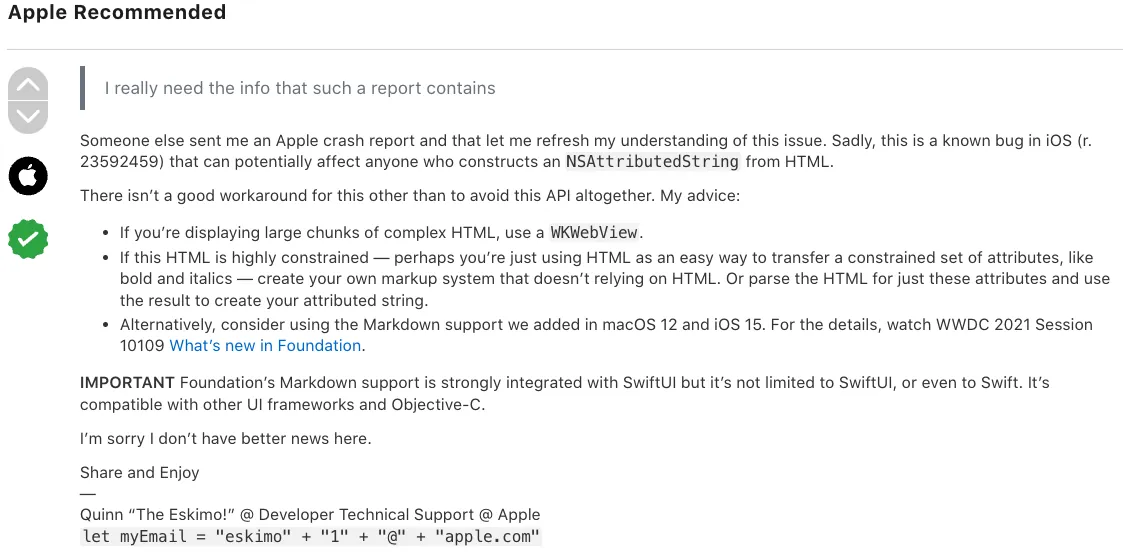
经过一番搜索发现网路上有许多相同案例,也从 App Developer Forums 找到最早的相同 闪退问题提问 ,并获得来自 官方 的回答:
这是已知的 iOS Foundation Bug:自 iOS 12 就已存在
如要渲染复杂的、无使用上约束的 HTML:请使用 WKWebView
有渲染约束:可自行撰写 HTML Parser & Render
直接使用 Markdown 做为渲染约束:iOS ≥ 15 NSAttributedString 可 直接使用 Markdown 格式渲染文字
渲染约束 的意思是限定 App 端能支援的渲染格式,例如只支援 粗体 、斜体、 超连结 。
补充. 渲染复杂的 HTML — 想制作文饶图效果
可与后端共同协调ㄧ个介面:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
"content":[
{"type":"text","value":"第1段纯文字"},
{"type":"text","value":"第2段纯文字"},
{"type":"text","value":"第3段纯文字"},
{"type":"text","value":"第4段纯文字"},
{"type":"image","src":"https://zhgchg.li/logo.png","title":"ZhgChgLi"},
{"type":"text","value":"第5段纯文字"}
]
}
可与 Markdown 组合加上支援文字渲染,或参考 Medium 做法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
"Paragraph": {
"text": "code in text, and link in text, and ZhgChgLi, and bold, and I, only i",
"markups": [
{
"type": "CODE",
"start": 5,
"end": 7
},
{
"start": 18,
"end": 22,
"href": "http://zhgchg.li",
"type": "LINK"
},
{
"type": "STRONG",
"start": 50,
"end": 63
},
{
"type": "EM",
"start": 55,
"end": 69
}
]
}
意思是 code in text, and link in text, and ZhgChgLi, and bold, and I, only i 这段文字的:
1
2
3
4
- 第 5 到第 7 字元要标示为 程式码 (用`Text`格式包装)
- 第 18 到第 22 字元要标示为 连结 (用[Text](URL)格式包装)
- 第 50 到第 63 字元要标示为 粗体(用*Text*格式包装)
- 第 55 到第 69 字元要标示为 斜体(用_Text_格式包装)
有规范&可描述的结构后,App 就能自行使用原生方式渲染,达到效能、使用体验最佳化。
UITextView 做文饶图的坑,可参考我之前的文章: iOS UITextView 文绕图编辑器 (Swift)
Why?
在实践解答之前我们先回归探究问题本身,个人认为这个问题主因并非来自 Apple,官方的 Bug 只是这个问题的引爆点。
问题主要来自 App 端被当成 Web 来进行渲染 ,优点是 Web 开发快速,同个 API Endpoint 可以不用区分 Client 都给 HTML、可以弹性渲染任何想呈现的内容;缺点是 HTML 并非 App 的常见接口、不能期望 App Engineer 懂 HTML、 效能极差 、只能在 Main Thread、开发阶段无法预期结果、无法确认支援规格。
再往上找问题,多半是原始需求无法确定、不能确定 App 需要支援哪些规格、为了求快,才导致直接使用 HTML 做为 App 与 Web 的接口。
效能极差
补充效能部分,实测直接使用 NSAttributedString DocumentType.html 与自行实现渲染的方式有 5~20 倍的速度差距。
Better
既然是 App 要用,更好的做法要以 App 开发方式为出发点,对 App 来说需求的调整成本比 Web 高很多;有效的 App 开发应该要基于有规格的迭代调整,当下需要确定能支援的规格,之后如果要改我们就安排时间扩充规格,无法快速的想改就改,可以减少沟通成本、增加工作效率。
确认需求范围
确认支援的规格
确认接口规范 (Markdown/BBCode/…要继续用 HTML 也行,但要是有约束的,例如只用
<b>/<i>/<a>/<u>,要在程式 明确告知 开发者)自行实现渲染机制
维护、迭代支援规格
[2023/02/27 Updated] [TL;DR]:
已更新做法,不使用 XMLParser,因容错率为 0 :
<br> / <Congratulation!> / <b>Bold<i>Bold+Italic</b>Italic</i> 以上三种有可能出现的情境 XMLParser 解析都会出错直接 Throw Error 显示空白。 使用 XMLParser,HTML 字串必须完全符合 XML 规则,无法像浏览器或 NSAttributedString.DocumentType.html 容错正常显示。
改使用纯 Swift 开发,透过 Regex 剖析出 HTML Tag 并经过 Tokenization,分析修正 Tag 正确性(修正没有 end 的 tag & 错位 tag),再转换成 abstract syntax tree,最终使用 Visitor Pattern 将 HTML Tag 与抽象样式对应,得到最终 NSAttributedString 结果;其中不依赖任何 Parser Lib。
— —
How?
木已成舟,回归正题,目前已用 HTML 在渲染 NSAttributedString 那我们该如何解决上述的闪退还有效能问题呢?
Inspired by
Strip HTML 去除 HTML
在谈 HTML Render 之前先谈 Strip HTML,还是再提一次前文 Why? 章节所说的,App 哪里会拿到 HTML、会拿到哪些 HTML 应该要在规格协定好;而不是 App 这边「 可能 」会拿到 HTML,需要 Strip 掉。
套句之前主管的名言:这样太疯了吧?
Option 1. NSAttributedString
1
2
3
let data = "<div>Text</div>".data(using: .unicode)!
let attributed = try NSAttributedString(data: data, options: [.documentType: NSAttributedString.DocumentType.html, .characterEncoding: String.Encoding.utf8.rawValue], documentAttributes: nil)
let string = attributed.string
使用 NSAttributedString Render HTML 然后再取 string 出来就会是干净的 String 了
问题同本章问题,iOS 15 容易闪退、效能不好、只能在 Main Thread 操作
Option 2. Regex
1
2
htmlString = "<div>Test</div>"
htmlString.replacingOccurrences(of: "<[^>]+>", with: "", options: .regularExpression, range: nil)
最简单有效的方式
Regex 并不能保证完全正确 e.g
<p foo=">now what?">Paragraph</p>是合法的 HTML 但会 Strip 错误
Option 3. XMLParser
参考 SwiftRichString 的做法,使用 Foundation 中的 XMLParser 将 HTML 做为 XML 解析自行实现 HTML Parser & Strip 功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
import UIKit
// Ref: https://github.com/malcommac/SwiftRichString
final class HTMLStripper: NSObject, XMLParserDelegate {
private static let topTag = "source"
private var xmlParser: XMLParser
private(set) var storedString: String
// The XML parser sometimes splits strings, which can break localization-sensitive
// string transforms. Work around this by using the currentString variable to
// accumulate partial strings, and then reading them back out as a single string
// when the current element ends, or when a new one is started.
private var currentString: String?
// MARK: - Initialization
init(string: String) throws {
let xmlString = HTMLStripper.escapeWithUnicodeEntities(string)
let xml = "<\(HTMLStripper.topTag)>\(xmlString)</\(HTMLStripper.topTag)>"
guard let data = xml.data(using: String.Encoding.utf8) else {
throw XMLParserInitError("Unable to convert to UTF8")
}
self.xmlParser = XMLParser(data: data)
self.storedString = ""
super.init()
xmlParser.shouldProcessNamespaces = false
xmlParser.shouldReportNamespacePrefixes = false
xmlParser.shouldResolveExternalEntities = false
xmlParser.delegate = self
}
/// Parse and generate attributed string.
func parse() throws -> String {
guard xmlParser.parse() else {
let line = xmlParser.lineNumber
let shiftColumn = (line == 1)
let shiftSize = HTMLStripper.topTag.lengthOfBytes(using: String.Encoding.utf8) + 2
let column = xmlParser.columnNumber - (shiftColumn ? shiftSize : 0)
throw XMLParserError(parserError: xmlParser.parserError, line: line, column: column)
}
return storedString
}
// MARK: XMLParserDelegate
@objc func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, didStartElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?, attributes attributeDict: [String: String]) {
foundNewString()
}
@objc func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, didEndElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?) {
foundNewString()
}
@objc func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, foundCharacters string: String) {
currentString = (currentString ?? "").appending(string)
}
// MARK: Support Private Methods
func foundNewString() {
if let currentString = currentString {
storedString.append(currentString)
self.currentString = nil
}
}
// handle html entity / html hex
// Perform string escaping to replace all characters which is not supported by NSXMLParser
// into the specified encoding with decimal entity.
// For example if your string contains '&' character parser will break the style.
// This option is active by default.
// ref: https://github.com/malcommac/SwiftRichString/blob/e0b72d5c96968d7802856d2be096202c9798e8d1/Sources/SwiftRichString/Support/XMLStringBuilder.swift
static func escapeWithUnicodeEntities(_ string: String) -> String {
guard let escapeAmpRegExp = try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "&(?!(#[0-9]{2,4}\\|[A-z]{2,6});)", options: NSRegularExpression.Options(rawValue: 0)) else {
return string
}
let range = NSRange(location: 0, length: string.count)
return escapeAmpRegExp.stringByReplacingMatches(in: string,
options: NSRegularExpression.MatchingOptions(rawValue: 0),
range: range,
withTemplate: "&")
}
}
let test = "我<br/><a href=\"http://google.com\">同意</a>提供<b><i>个</i>人</b>身分证字号/护照/居留<span style=\"color:#FF0000;font-size:20px;word-spacing:10px;line-height:10px\">证号码</span>,以供<i>跨境物流</i>方通关<span style=\"background-color:#00FF00;\">使用</span>,并已<img src=\"g.png\"/>了解跨境<br/>商品之物<p>流需</p>求"
let stripper = try HTMLStripper(string: test)
print(try! stripper.parse())
// 我同意提供个人身分证 字号/护照/居留证号码,以供跨境物流方通关使用,并已了解跨境商品之物流需求
使用 Foundation XML Parser 去处理 String,实现 XMLParserDelegate 用 currentString 存放 String,因 String 有时会拆成多个 String 所以 foundCharacters 是有机会被重复呼叫的, didStartElement 、 didEndElement 找到字串开始时、结束时,将当前结果存下并清空 currentString 。
优点是会连带转换 HTML Entity to 实际字元 e.g.
g -> g优点是实现复杂、遇到不合规格的 HTML 会 XMLParser 失败 e.g.
<br> 忘了写成 <br/>
个人认为单纯要 Strip HTML Option 2. 是比较好的方法 ,会介绍此方法是因为 Render HTML 也是使用相同原理,先用这个做为简单范例 :)
HTML Render w/XMLParser
使用 XMLParser 自行实现,同 Strip 原理,我们可以多加上剖析到什么 Tag 时要做对应的渲染方式。
需求规格:
支援扩充想剖析的 Tag
支援设定 Tag Default Style e.g <a> Tag 套用连结样式
支援剖析
styleAttributed,因 HTML 会在style="color:red"上去明示要显示的样式样式支援更改文字粗细、大小、底线、行距、字距、背景颜色、字颜色
不支援 Image Tag、Table Tag…等较复杂 TAG
大家可依照自己的规格需求去删减功能,例如不需支援背景颜色调整,则不需要开出可设定背景颜色的口。
本文只是概念实现, 并非架构上的 Best Practice ;如有明确规格、使用方式,可考虑套用些 Design Pattern 来实现,达成好维护好扩充。
⚠️⚠️⚠️ Attention ⚠️⚠️⚠️
再次提醒, 如果你的 App 是全新的或有机会直接全改成 Markdown 格式,建议还是采用以上方式,本篇自行撰写 Render 太复杂且效能不会比 Markdown 好 。
即使你是 iOS < 15 不支援原生 Markdown,还是可以在 Github 上找到 大神做好的 Markdown Parser 方案 。
HTMLTagParser
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
protocol HTMLTagParser {
static var tag: String { get } // 宣告想解析的 Tag Name, e.g. a
var storedHTMLAttributes: [String: String]? { get set } // Attributed 解析结果将存放于此, e.g. href,style
var style: AttributedStringStyle? { get } // 此 Tag 想套用的样式
func render(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString) // 实现渲染 HTML to attributedString 的逻辑
}
宣告可剖析的 HTML Tag 实体,方便扩充管理。
AttributedStringStyle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
protocol AttributedStringStyle {
var font: UIFont? { get set }
var color: UIColor? { get set }
var backgroundColor: UIColor? { get set }
var wordSpacing: CGFloat? { get set }
var paragraphStyle: NSParagraphStyle? { get set }
var customs: [NSAttributedString.Key: Any]? { get set } // 万能设定口,建议确定可支援规格后将其抽象出来,并关闭此开口
func render(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString)
}
// abstract implement
extension AttributedStringStyle {
func render(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString) {
let range = NSMakeRange(0, attributedString.length)
if let font = font {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.font, value: font, range: range)
}
if let color = color {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.foregroundColor, value: color, range: range)
}
if let backgroundColor = backgroundColor {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.backgroundColor, value: backgroundColor, range: range)
}
if let wordSpacing = wordSpacing {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.kern, value: wordSpacing as Any, range: range)
}
if let paragraphStyle = paragraphStyle {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.paragraphStyle, value: paragraphStyle, range: range)
}
if let customAttributes = customs {
attributedString.addAttributes(customAttributes, range: range)
}
}
}
宣告 Tag 可供设定的样式。
HTMLStyleAttributedParser
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
// only support tag attributed down below
// can set color,font seize,line height,word spacing,background color
enum HTMLStyleAttributedParser: String {
case color = "color"
case fontSize = "font-size"
case lineHeight = "line-height"
case wordSpacing = "word-spacing"
case backgroundColor = "background-color"
func render(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString, value: String) -> Bool {
let range = NSMakeRange(0, attributedString.length)
switch self {
case .color:
if let color = convertToiOSColor(value) {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.foregroundColor, value: color, range: range)
return true
}
case .backgroundColor:
if let color = convertToiOSColor(value) {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.backgroundColor, value: color, range: range)
return true
}
case .fontSize:
if let size = convertToiOSSize(value) {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.font, value: UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: CGFloat(size)), range: range)
return true
}
case .lineHeight:
if let size = convertToiOSSize(value) {
let paragraphStyle = NSMutableParagraphStyle()
paragraphStyle.lineSpacing = size
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.paragraphStyle, value: paragraphStyle, range: range)
return true
}
case .wordSpacing:
if let size = convertToiOSSize(value) {
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.kern, value: size, range: range)
return true
}
}
return false
}
// convert 36px -> 36
private func convertToiOSSize(_ string: String) -> CGFloat? {
guard let regex = try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "^([0-9]+)"),
let firstMatch = regex.firstMatch(in: string, options: [], range: NSRange(location: 0, length: string.utf16.count)),
let range = Range(firstMatch.range, in: string),
let size = Float(String(string[range])) else {
return nil
}
return CGFloat(size)
}
// convert html hex color #ffffff to UIKit Color
private func convertToiOSColor(_ hexString: String) -> UIColor? {
var cString: String = hexString.trimmingCharacters(in: .whitespacesAndNewlines).uppercased()
if cString.hasPrefix("#") {
cString.remove(at: cString.startIndex)
}
if (cString.count) != 6 {
return nil
}
var rgbValue: UInt64 = 0
Scanner(string: cString).scanHexInt64(&rgbValue)
return UIColor(
red: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0xFF0000) >> 16) / 255.0,
green: CGFloat((rgbValue & 0x00FF00) >> 8) / 255.0,
blue: CGFloat(rgbValue & 0x0000FF) / 255.0,
alpha: CGFloat(1.0)
)
}
}
实现 Style Attributed Parser 解析 style="color:red;font-size:16px" 但 CSS Style 有非常多可设定样式,所以需要列举可支援范围。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
extension HTMLTagParser {
func render(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString) {
defaultStyleRender(attributedString: &attributedString)
}
func defaultStyleRender(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString) {
// setup default style to NSMutableAttributedString
style?.render(attributedString: &attributedString)
// setup & override HTML style (style="color:red;background-color:black") to NSMutableAttributedString if is exists
// any html tag can have style attribute
if let style = storedHTMLAttributes?["style"] {
let styles = style.split(separator: ";").map { $0.split(separator: ":") }.filter { $0.count == 2 }
for style in styles {
let key = String(style[0])
let value = String(style[1])
if let styleAttributed = HTMLStyleAttributedParser(rawValue: key), styleAttributed.render(attributedString: &attributedString, value: value) {
print("Unsupport style attributed or value[\(key):\(value)]")
}
}
}
}
}
套用 HTMLStyleAttributedParser & HTMLStyleAttributedParser 抽象实现。
一些 Tag Parser & AttributedStringStyle 的实现范例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
struct LinkStyle: AttributedStringStyle {
var font: UIFont? = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 14)
var color: UIColor? = UIColor.blue
var backgroundColor: UIColor? = nil
var wordSpacing: CGFloat? = nil
var paragraphStyle: NSParagraphStyle?
var customs: [NSAttributedString.Key: Any]? = [.underlineStyle: NSUnderlineStyle.single.rawValue]
}
struct ATagParser: HTMLTagParser {
// <a></a>
static let tag: String = "a"
var storedHTMLAttributes: [String: String]? = nil
let style: AttributedStringStyle? = LinkStyle()
func render(attributedString: inout NSMutableAttributedString) {
defaultStyleRender(attributedString: &attributedString)
if let href = storedHTMLAttributes?["href"], let url = URL(string: href) {
let range = NSMakeRange(0, attributedString.length)
attributedString.addAttribute(NSAttributedString.Key.link, value: url, range: range)
}
}
}
struct BoldStyle: AttributedStringStyle {
var font: UIFont? = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 14, weight: .bold)
var color: UIColor? = UIColor.black
var backgroundColor: UIColor? = nil
var wordSpacing: CGFloat? = nil
var paragraphStyle: NSParagraphStyle?
var customs: [NSAttributedString.Key: Any]? = [.underlineStyle: NSUnderlineStyle.single.rawValue]
}
struct BoldTagParser: HTMLTagParser {
// <b></b>
static let tag: String = "b"
var storedHTMLAttributes: [String: String]? = nil
let style: AttributedStringStyle? = BoldStyle()
}
HTMLToAttributedStringParser: XMLParserDelegate 核心实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
// Ref: https://github.com/malcommac/SwiftRichString
final class HTMLToAttributedStringParser: NSObject {
private static let topTag = "source"
private var xmlParser: XMLParser?
private(set) var attributedString: NSMutableAttributedString = NSMutableAttributedString()
private(set) var supportedTagRenders: [HTMLTagParser] = []
private let defaultStyle: AttributedStringStyle
/// Styles applied at each fragment.
private var renderingTagRenders: [HTMLTagParser] = []
// The XML parser sometimes splits strings, which can break localization-sensitive
// string transforms. Work around this by using the currentString variable to
// accumulate partial strings, and then reading them back out as a single string
// when the current element ends, or when a new one is started.
private var currentString: String?
// MARK: - Initialization
init(defaultStyle: AttributedStringStyle) {
self.defaultStyle = defaultStyle
super.init()
}
func register(_ tagRender: HTMLTagParser) {
if let index = supportedTagRenders.firstIndex(where: { type(of: $0).tag == type(of: tagRender).tag }) {
supportedTagRenders.remove(at: index)
}
supportedTagRenders.append(tagRender)
}
/// Parse and generate attributed string.
func parse(string: String) throws -> NSAttributedString {
var xmlString = HTMLToAttributedStringParser.escapeWithUnicodeEntities(string)
// make sure <br/> format is correct XML
// because Web may use <br> to present <br/>, but <br> is not a vaild XML
xmlString = xmlString.replacingOccurrences(of: "<br>", with: "<br/>")
let xml = "<\(HTMLToAttributedStringParser.topTag)>\(xmlString)</\(HTMLToAttributedStringParser.topTag)>"
guard let data = xml.data(using: String.Encoding.utf8) else {
throw XMLParserInitError("Unable to convert to UTF8")
}
let xmlParser = XMLParser(data: data)
xmlParser.shouldProcessNamespaces = false
xmlParser.shouldReportNamespacePrefixes = false
xmlParser.shouldResolveExternalEntities = false
xmlParser.delegate = self
self.xmlParser = xmlParser
attributedString = NSMutableAttributedString()
guard xmlParser.parse() else {
let line = xmlParser.lineNumber
let shiftColumn = (line == 1)
let shiftSize = HTMLToAttributedStringParser.topTag.lengthOfBytes(using: String.Encoding.utf8) + 2
let column = xmlParser.columnNumber - (shiftColumn ? shiftSize : 0)
throw XMLParserError(parserError: xmlParser.parserError, line: line, column: column)
}
return attributedString
}
}
// MARK: Private Method
private extension HTMLToAttributedStringParser {
func enter(element elementName: String, attributes: [String: String]) {
// elementName = tagName, EX: a,span,div...
guard elementName != HTMLToAttributedStringParser.topTag else {
return
}
if let index = supportedTagRenders.firstIndex(where: { type(of: $0).tag == elementName }) {
var tagRender = supportedTagRenders[index]
tagRender.storedHTMLAttributes = attributes
renderingTagRenders.append(tagRender)
}
}
func exit(element elementName: String) {
if !renderingTagRenders.isEmpty {
renderingTagRenders.removeLast()
}
}
func foundNewString() {
if let currentString = currentString {
// currentString != nil ,ex: <i>currentString</i>
var newAttributedString = NSMutableAttributedString(string: currentString)
if !renderingTagRenders.isEmpty {
for (key, tagRender) in renderingTagRenders.enumerated() {
// Render Style
tagRender.render(attributedString: &newAttributedString)
renderingTagRenders[key].storedHTMLAttributes = nil
}
} else {
defaultStyle.render(attributedString: &newAttributedString)
}
attributedString.append(newAttributedString)
self.currentString = nil
} else {
// currentString == nil ,ex: <br/>
var newAttributedString = NSMutableAttributedString()
for (key, tagRender) in renderingTagRenders.enumerated() {
// Render Style
tagRender.render(attributedString: &newAttributedString)
renderingTagRenders[key].storedHTMLAttributes = nil
}
attributedString.append(newAttributedString)
}
}
}
// MARK: Helper
extension HTMLToAttributedStringParser {
// handle html entity / html hex
// Perform string escaping to replace all characters which is not supported by NSXMLParser
// into the specified encoding with decimal entity.
// For example if your string contains '&' character parser will break the style.
// This option is active by default.
// ref: https://github.com/malcommac/SwiftRichString/blob/e0b72d5c96968d7802856d2be096202c9798e8d1/Sources/SwiftRichString/Support/XMLStringBuilder.swift
static func escapeWithUnicodeEntities(_ string: String) -> String {
guard let escapeAmpRegExp = try? NSRegularExpression(pattern: "&(?!(#[0-9]{2,4}\\|[A-z]{2,6});)", options: NSRegularExpression.Options(rawValue: 0)) else {
return string
}
let range = NSRange(location: 0, length: string.count)
return escapeAmpRegExp.stringByReplacingMatches(in: string,
options: NSRegularExpression.MatchingOptions(rawValue: 0),
range: range,
withTemplate: "&")
}
}
// MARK: XMLParserDelegate
extension HTMLToAttributedStringParser: XMLParserDelegate {
func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, didStartElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?, attributes attributeDict: [String: String]) {
foundNewString()
enter(element: elementName, attributes: attributeDict)
}
func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, didEndElement elementName: String, namespaceURI: String?, qualifiedName qName: String?) {
foundNewString()
guard elementName != HTMLToAttributedStringParser.topTag else {
return
}
exit(element: elementName)
}
func parser(_ parser: XMLParser, foundCharacters string: String) {
currentString = (currentString ?? "").appending(string)
}
}
套用 Strip 的逻辑,我们可以帮拆好的架构在其中进行组合从 elementName 知道当前的 Tag 并套用相应的 Tag Parser 及套上定义好的 Style。
Test Result
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
let test = "我<br/><a href=\"http://google.com\">同意</a>提供<b><i>个</i>人</b>身分证字号/护照/居留<span style=\"color:#FF0000;font-size:20px;word-spacing:10px;line-height:10px\">证号码</span>,以供<i>跨境物流</i>方通关<span style=\"background-color:#00FF00;\">使用</span>,并已<img src=\"g.png\"/>了解跨境<br/>商品之物<p>流需</p>求"
let render = HTMLToAttributedStringParser(defaultStyle: DefaultTextStyle())
render.register(ATagParser())
render.register(BoldTagParser())
render.register(SpanTagParser())
//...
print(try! render.parse(string: test))
// Result:
// 我{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 3, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// }同意{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedSRGBColorSpace 0 0 1 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSLink = "http://google.com";
// NSUnderline = 1;
// }提供{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 3, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// }个{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Bold 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a013870) fobj=0x13a013870, spc=3.46\"";
// NSUnderline = 1;
// }人身分证字号/护照/居留{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 3, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// }证号码{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedSRGBColorSpace 1 0 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 20.00 pt. P [] (0x13a015fa0) fobj=0x13a015fa0, spc=4.82\"";
// NSKern = 10;
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 10, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// },以供跨境物流方通关{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 3, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// }使用{
// NSBackgroundColor = "UIExtendedSRGBColorSpace 0 1 0 1";
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 3, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// },并已了解跨境商品之物流需求{
// NSColor = "UIExtendedGrayColorSpace 0 1";
// NSFont = "\".SFNS-Regular 14.00 pt. P [] (0x13a012970) fobj=0x13a012970, spc=3.79\"";
// NSParagraphStyle = "Alignment 4, LineSpacing 3, ParagraphSpacing 0, ParagraphSpacingBefore 0, HeadIndent 0, TailIndent 0, FirstLineHeadIndent 0, LineHeight 0/0, LineHeightMultiple 0, LineBreakMode 0, Tabs (\n 28L,\n 56L,\n 84L,\n 112L,\n 140L,\n 168L,\n 196L,\n 224L,\n 252L,\n 280L,\n 308L,\n 336L\n), DefaultTabInterval 0, Blocks (\n), Lists (\n), BaseWritingDirection -1, HyphenationFactor 0, TighteningForTruncation NO, HeaderLevel 0 LineBreakStrategy 0 PresentationIntents (\n) ListIntentOrdinal 0 CodeBlockIntentLanguageHint ''";
// }
显示结果:
Done!
这样我们就完成了透过 XMLParser 自行实现 HTML Render 功能,并且保留扩充性跟规格性,可以从 Code 上管理、了解到目前 App 能支援的字串渲染类型。
完整 Github Repo 如下
本文同步发表于个人 Blog: [点我前往] 。
有任何问题及指教欢迎 与我联络 。
本文首次发表于 Medium (点击查看原始版本),由 ZMediumToMarkdown 提供自动转换与同步技术。