Google Apps Script|Automate Daily Data Reports with RPA for Google Workspace
Boost your productivity by automating daily data reports in Google Workspace using Google Apps Script RPA. Eliminate manual tasks, reduce errors, and generate accurate reports effortlessly every day.
点击这里查看本文章简体中文版本。
點擊這裡查看本文章正體中文版本。
This post was translated with AI assistance — let me know if anything sounds off!
Table of Contents
Implementing Daily Data Report RPA Automation with Google Apps Script
Using Google Apps Script for Robotic Process Automation of Google Workspace Services
Photo by Possessed Photography
Robotic Process Automation
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) translates to “Process Automation Robots” in Chinese. Looking back at human history, from gathering by hand to the Stone Age and then to agricultural civilization, from the Industrial Revolution last century to the rise of information technology in the past 20 years, human work efficiency and productivity have grown exponentially. Along this journey, RPA applications have been everywhere: water wheels in the agricultural era (automating threshing), textile machines in the Industrial Revolution (automating weaving), factory robotic arms (automating assembly), and finally, the focus of this article—automating information-related tasks such as automatic report queries and automatic notifications.
To be honest, I only recently learned this term. Since my first job (7 years ago), I have been working on RPA tasks such as writing web crawlers for data statistics, automating CI/CD processes, automating data queries, automating stability data alerts, and automating daily routine operations. However, I used to refer to all of these simply as “automation.” It’s time to give it a proper name — RPA (Robotic Process Automation).
Previous RPA work mostly focused on “manually writing code to automate a single problem,” lacking comprehensive early-stage evaluation and analysis, use of No/Low Code tools, compliance, operation monitoring, real data statistics, continuous improvement, and corporate culture promotion. These are all essential parts of complete RPA. However, as mentioned earlier, I only recently learned about this professional field, so please allow me to start with a practical implementation article first!
There are many platforms offering RPA services, such as Automation Anywhere, UiPath, Microsoft Power Automate, Blue Prism, as well as Zapier, IFTTT, Automate.io, and more.
Choose the right service based on the actual problem you want to solve and the platform.
Recommend a free and open-source browser-based RPA tool: Automa.
Broadly speaking, transforming active dependencies between people or between people and tasks into dependencies on platforms by people or tasks is also a form of RPA.
For example: Use Asana/Jira and other project management tools to manage tasks uniformly.
Based on the concept of shifting from active to passive, a service that originally required manual checking for new notifications can be automated with RPA to notify us automatically when there are updates.
For example: previously implemented Gmail to Slack to forward specific notification emails to the work group.
Benefits Assessment of Robotic Process Automation
Previously, in the “2021 Pinkoi Tech Career Talk — Secrets of High-Efficiency Engineering Teams,” I shared about the cost of cumulative small tasks and flow interruptions; assuming a routine repetitive task takes 15 minutes each time and occurs 10 times a week, nearly 130 hours are wasted annually; adding the “flow switching” cost, the total waste could reach nearly 200 hours per year.
2021 Pinkoi Tech Career Talk — Secrets to High-Efficiency Engineering Teams
Flow switching means the time it takes to pause from being fully focused and engaged in an important task, handle other matters, and then return to regain the same focused state.
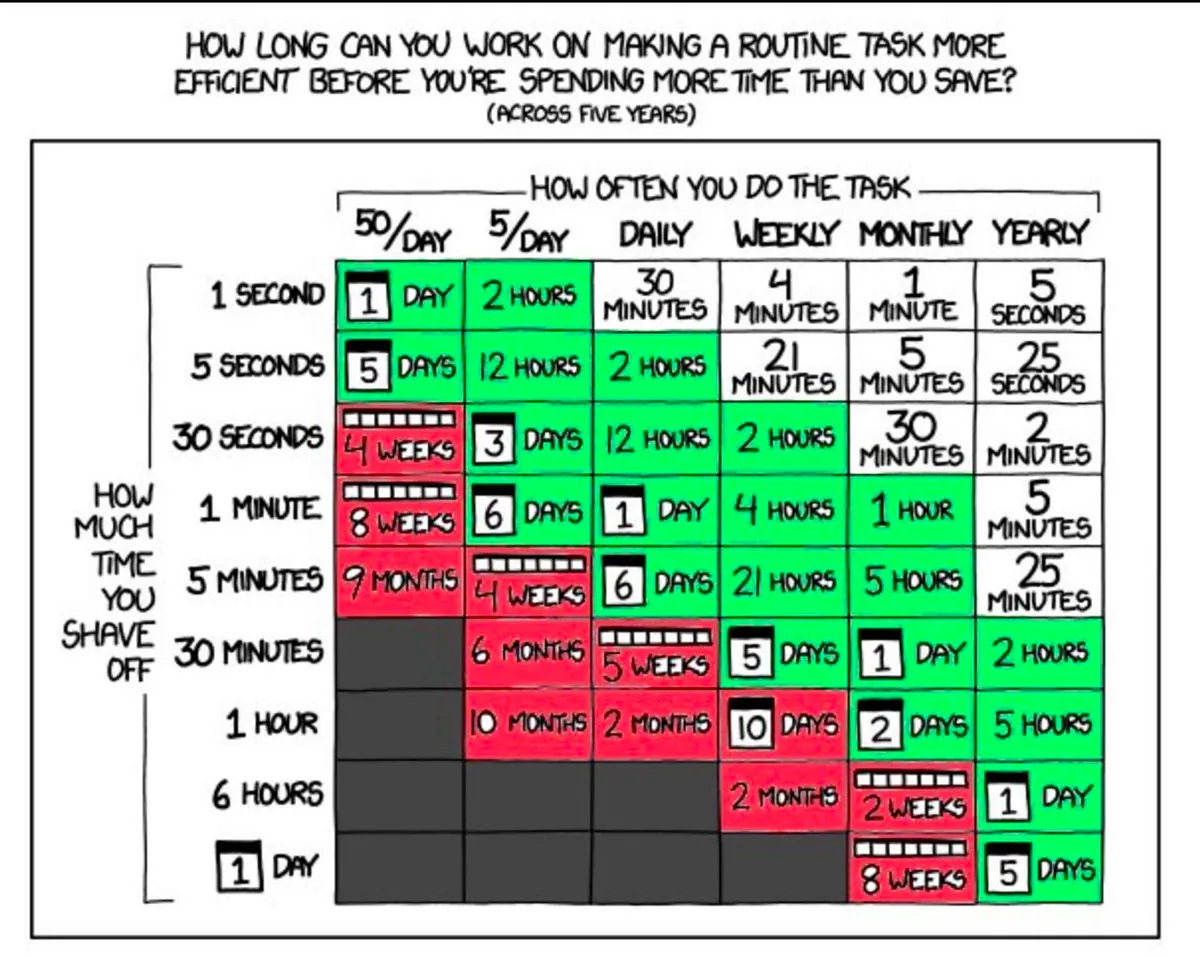
The benefits of developing RPA can be evaluated by the diagram below. As long as the development time and frequency of occurrence exceed the wasted time, it is worth investing resources to implement:
https://twitter.com/swyx/status/1196401158744502272
X-axis: Task occurrence frequency e.g., 50/Day (50 times per day)
Y-axis: How much manpower time is needed to complete each task
Time-consuming range calculated over 5 years; the middle of the table shows the labor cost of wasted time over 5 years
White indicates that the time cost of automation may exceed the benefits gained, making improvement not worthwhile.
Green indicates items worth automating
Red indicates a strong recommendation to automate.
Besides saving time, automated standardized processes also reduce human error and improve stability.
The Relationship Between Robotic Process Automation and AI
With the rise of AI, RPA is often mentioned; however, I believe RPA and AI are not directly related. RPA existed long before AI, and the benefits of implementing AI in businesses may not surpass those of improving RPA. RPA is more about corporate culture and work habits. Nonetheless, it is undeniable that AI can help RPA reach the next level. For example, RPA used to handle only precise, routine tasks, but with AI, it can perform fuzzy, more dynamic, and intelligent decision-making tasks.
Robotic Process Automation at Google Workspace
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) is a great partner for our daily office collaboration. We use Gmail for email hosting, Google Docs for documents, Google Sheets for reports, Google Forms for surveys, and more. Connecting these services or communicating with internal and external systems requires us to implement RPA.
But Google does not offer direct RPA services; however, you can achieve this through the following services:
No Code: App Sheet (paid service) allows non-developers to create service integration automation directly through a GUI.
Low Code: Google Apps Script (free service) enables quick and easy connection of Google services and external/internal systems with simple scripting.
Function as a Service: Cloud Functions (paid service with free tier) lets you write full code and services, deploy, and run directly on Google Cloud.
No Code platform App Sheet I haven’t used it before, but I have considerable experience with Cloud Functions and Google Apps Script. Below are some personal experiences and choices from my past use:
Cloud Functions
Deployment Required
Supports multiple programming languages: Node.js, Python, Java, Go, PHP, Ruby…
Supports third-party package dependency management, installation, and usage
Supports full authentication mechanism
Maximum execution time limit: 60 minutes
Pay as You Go: Charges Based on Usage Count, Execution Time, Different Processors, and Memory Used
Cold Start Limitation (If not called for a long time, the first call will have a longer response time)
Cannot directly connect to Google services; must go through Auth/API verification
Free Plan Details
Cloud Functions offers a permanent free plan for compute time resources, including allocations based on GB-seconds and GHz-seconds. Besides 2 million invocations, this free plan provides 400,000 GB-seconds and 200,000 GHz-seconds of compute time, along with 5 GB of internet data transfer per month. The free plan usage is calculated at the equivalent USD amount of the Tier 1 pricing mentioned above. Regardless of whether the function runs in a Tier 1 or Tier 2 pricing region, the system allocates the equivalent USD amount. However, when deducting from the free plan quota, the system uses the function execution region’s tier (Tier 1 or Tier 2) as the basis.
Please note, even if you use the free plan, you must have a valid billing account.
In summary, Cloud Functions are recommended when a more complete and complex RPA integration is needed or when there are multiple external API integration requirements.
Previous cases using Cloud Functions include:
I use it only when integrating with non-Google Workspace services and when bridging other external services is required.
Google Apps Script
Convenient, simple, and fast
Completely Free
No complicated Auth authentication needed for service integration
(Google Apps Script uses the currently logged-in account as the execution identity)Built-in scheduling and calendar trigger features
Uses Google Network to perform web requests
Development is only possible with Google Apps Script (based on JavaScript)
No support for package managers or version control features
Due to security concerns, customizing the Request User-Agent information is not possible
Execution time limit: the script must finish within 6 minutes or it will be terminated.
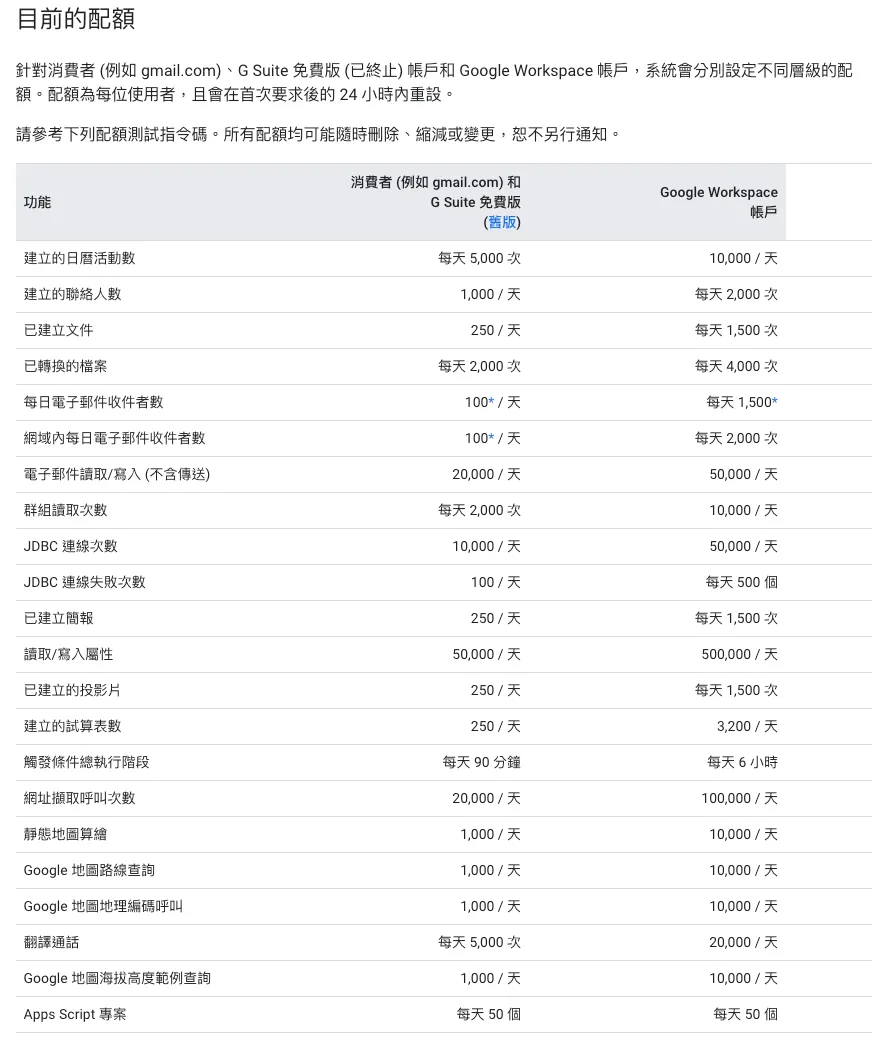
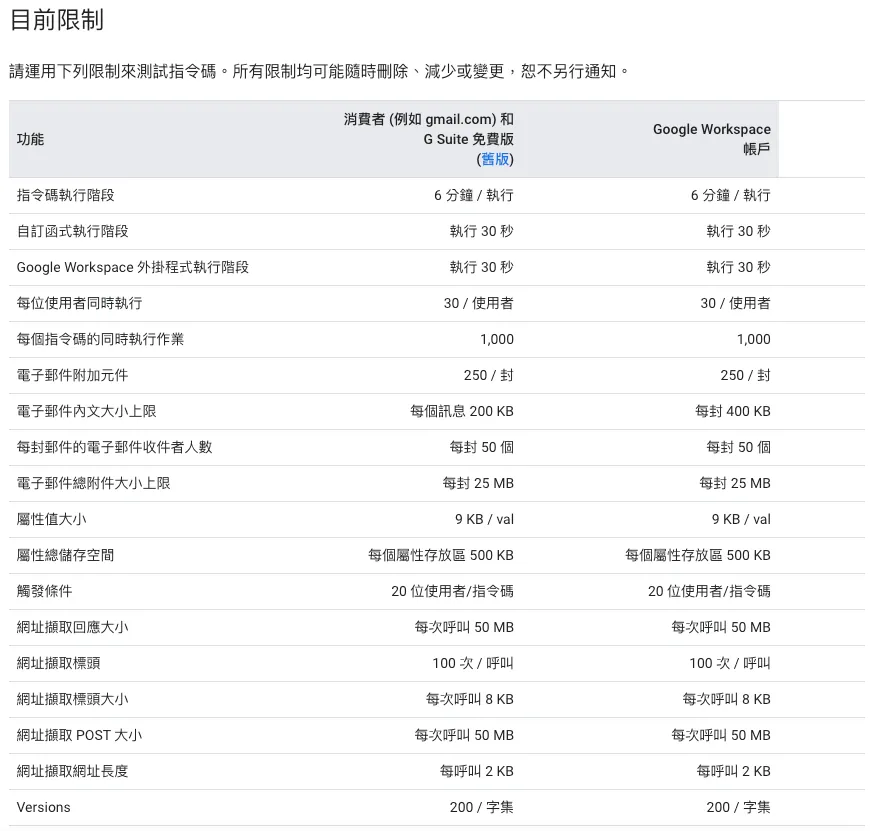
Other limits and quotas can be found in the official GAS Information:
Previous cases using Google Apps Script include:
Due to execution time limits and API request customization restrictions, I only use Google Apps Script for simple and quick services. For needs involving integration with Google services, I prioritize Google Apps Script (because implementing full Google service authentication in Cloud Functions requires more effort).
Robotic Process Automation with Google Apps Script — Workday Report (Google Sheet x Google Analytics)
Finally, we arrive at the main topic of this article: implementing Google service RPA automation using Google Apps Script.
Background
The product team needs to query Google Analytics data daily and fill it into a Google Sheet report for team trend analysis. The daily data should also be published on a Dashboard screen for all members to stay updated.
Colleagues spend about 30 minutes every day upon arriving at the office to complete this task; if there are other matters to handle, they must wait until this routine work is finished before starting or may delay sending the daily data message.
A Simple Estimate of RPA Benefits:
Annual consumption expenditure:
1 person x 30 mins x 365 days (including holidays) = 182 hoursAutomation Cost:
In this case, it takes about 1 person x 5 days = 40 hours
Therefore, we only need to invest one week of development time to handle the workload of the colleague responsible for data checking in the long term, enabling them to focus on more important tasks.
Goal
Our goal is to use Google Apps Script to build an RPA that automatically fetches daily data from Google Analytics and internal system report APIs, then fills it into Google Sheets, along with creating a Web UI Dashboard.
Final Result
- Google Sheet:
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit?usp=sharing
- Web GUI URL:
https://script.google.com/macros/s/AKfycbz2Vk-ikU8DSXjpnLq9r6HNAn3zlNAosvDoItG0cxy0bmItRDSVyEzTdwsL2HyFUz99/exec
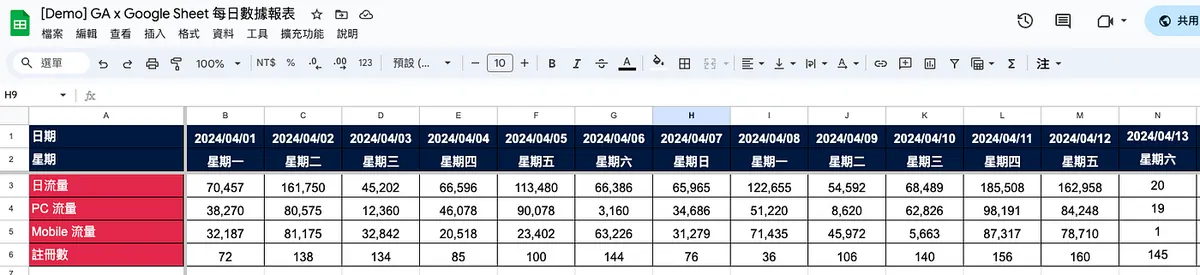
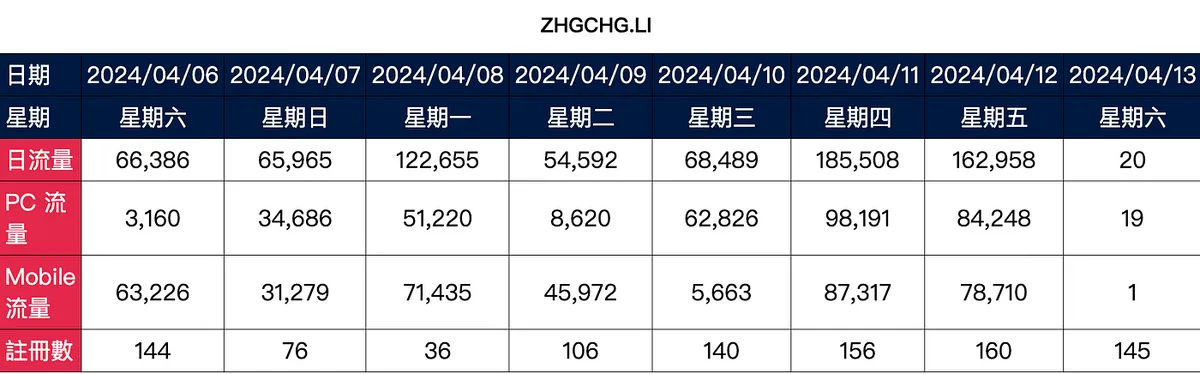
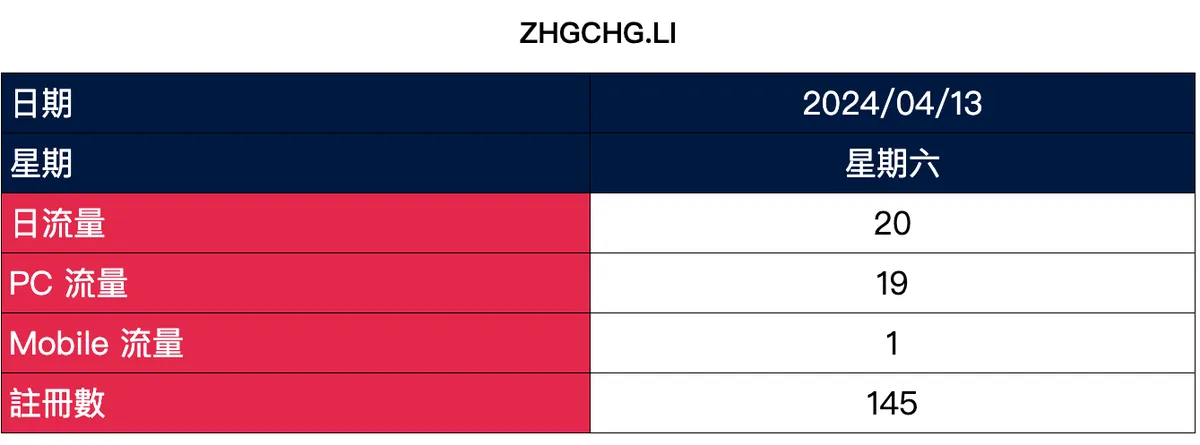
The data is fake and for demo use only; from 2024/04/13 onward, it will be especially low or remain at 0 because my zhgchg.li GA truly has “0” traffic Q_Q.
Tasks to Complete
Creating Google Apps Script and Getting Familiar with the Editor
Get/Create the Sheet for the Corresponding Date
Integrate Google Analytics to Retrieve Data
Fill in the data
Set Schedule for Daily Automatic Execution
Disclaimer
Due to the article’s explanation needs, the following code minimizes abstraction to enhance clarity. You can modify it according to your actual requirements.
At the end of the article, there is a complete public Google Sheet & Google Apps Script. If you don’t want to follow the steps one by one, you can directly modify the template attached at the end.
Step 1. Create Google Apps Script
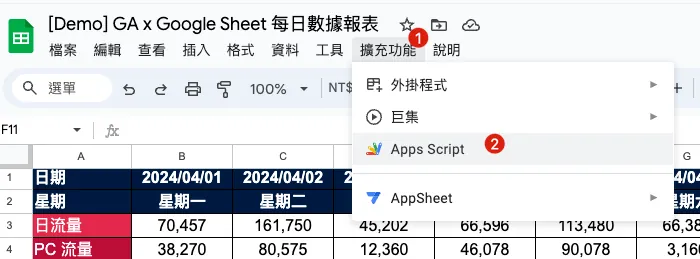
Simply select “Extensions” -> “Apps Script” on the report where we want to implement automation to automatically create a Google Apps Script linked to the Google Sheet report.
You can also create Google Apps Script directly from the Google Apps Script homepage, but this will not link it to Google Sheets.
Linking is not required to operate the corresponding Google Sheet. Both creation methods are possible. The difference is who owns the script: if linked to a report, the owner is the report owner; if created independently, the owner is the creator. Ownership matters because if the account is deactivated due to resignation, the script may become invalid or be deleted.
After creating the script, we can first rename our script project from the top.
Basic Knowledge of Google Apps Script
Before moving on to the next step of writing the program, let’s first cover some basic knowledge of Google Apps Script.
About the Editor
Default import of Google service SDKs (can be called without explicit import):
CalendarApp Calendar
DocumentApp Google Drive
FormApp Google Form
SpreadsheetApp Google Sheet
GmailApp Gmail
Files:
You can add multiple .gs files to store different object codes for better organization; all files run under the same namespace and lifecycle, so be careful as duplicate object or variable names may overwrite each other.
Besides .gs script files, you can also add .html HTML Template files for rendering the Web UI. (This will be explained later)Database:
Databases written by others (a.k.a Lib) can be imported and used via their Script ID. Of course, programs we write can also be deployed as databases for others to use.
There are also some powerful tools packaged by experts available. The downside is that Script IDs can only be found through Google search, as there is no official database list for reference.
e.g. HTML Parser Tool Cheer.io Script ID:1ReeQ6WO8kKNxoaA_O0XEQ589cIrRvEBA9qcWpNqdOP17i47u6N9M5Xh0Service:
The SDK for Google services allows you to add and use services that are not included by default.
e.g. Google Analytics DataRestore, Next Step Operation
Save or Control + s
Run or Control + r
If an error occurs, directly prompt in the Console and terminate the scriptDebugging
When the execution reaches a breakpoint (10), it will pause and open the Debug View on the right. You can then continue running the program.
If an error occurs, the execution will pause and open the Debug View on the right.Debugging and Running Target Method (Function Name)
Only methods within the currently selected file can be chosen.View Editor Execution Log
Another point is formatting: in some browsers, pressing “Control + [” to indent may trigger the back action. Be careful with this!
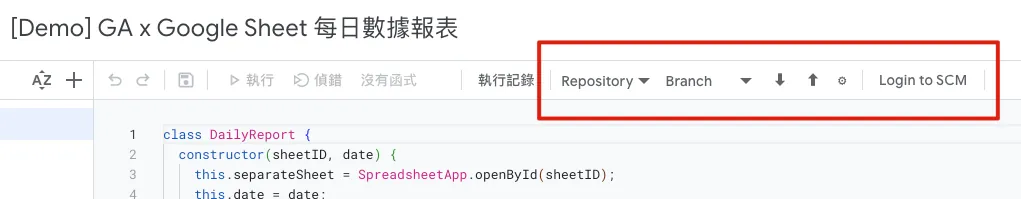
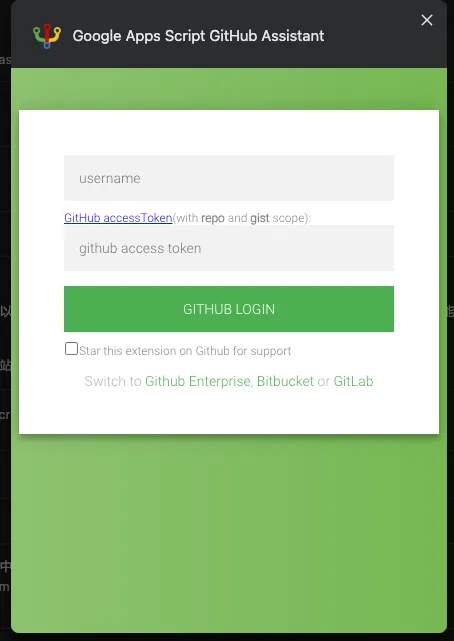
Google Apps Script GitHub Assistant Chrome Extension version control plugin
- It is recommended to install this extension to connect Google Apps Script with git, enabling version control to prevent accidental loss of work.
- If you encounter a Push/Pull Error or clicking has no response, please first follow the steps above: “Options” -> Connect to Github or re-verify Google authorization.
Logger Message
You can use the following script with Debug to print debug logs in the console below.
1
Logger.log("Hi")
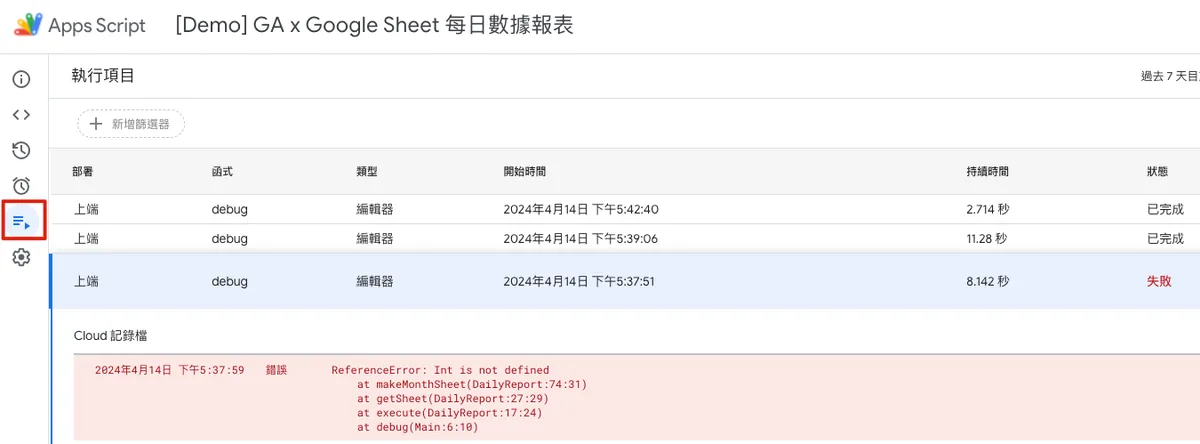
Execution Records and Error Information
If logs or errors occur while running in the editor, they will be displayed directly. To check execution records or errors that happen during automatic runs, go to the “Executions” tab.
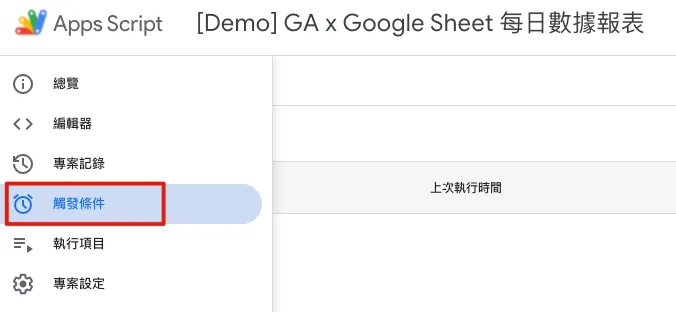
Automatic Trigger
The “Trigger Conditions” tab allows you to set how methods in the script are automatically triggered. The available automatic trigger conditions include:
When Google Sheet: opens, edits, content changes, or form is submitted
Scheduled cycle trigger: Execute once every X minutes, X hours, X days, X weeks, or X months
Trigger on specific date: Execute at YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM
When Calendar: Updated Trigger
Error notification settings allow you to configure how you are notified when a script execution fails.
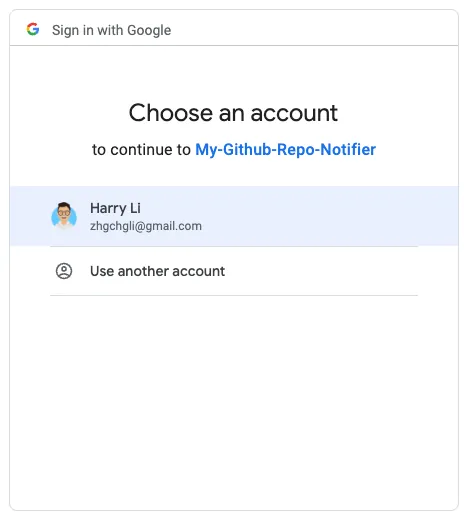
Grant Execution Permission Identity
The first time you run/deploy or add a new service or resource, you need to reauthorize your identity. After authorization, all executions will run under your authorized identity, so make sure the account you authorize (usually the current one) has permission for the resource or service (e.g., access to the Google Sheet).
After the account selection pop-up appears, choose the account to authorize execution (usually the current Google Apps Script account):
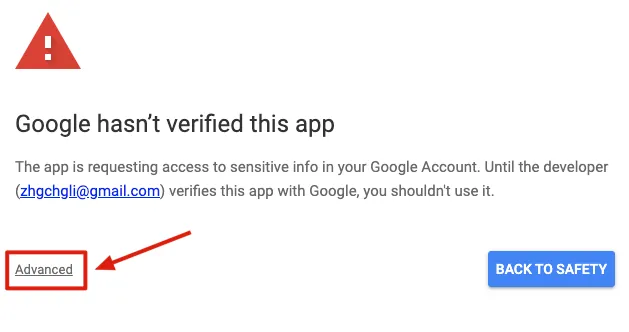
The message “Google hasn’t verified this app” appears because the app we are developing is for personal use and does not require Google verification.
Simply click “Advanced” -> “Go to XXX (unsafe)” -> “Allow”:
After completing the authorization, the script can run successfully. If the resources are unchanged, re-authorization is not required.
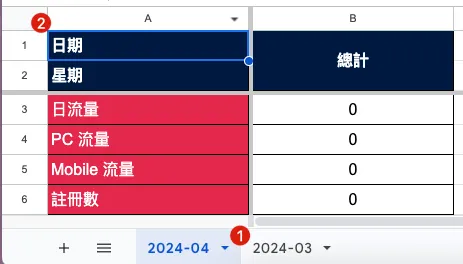
2. Get/Create the Sheet for the Corresponding Date
After understanding the basics, we can start writing the program for the first feature.
We create the following multiple files to conveniently store different objects.
DailyReportStyle.gs Column Style Object:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
class HeaderStyle {
constructor() {
this.color = "#ffffff";
this.backgroundColor = "#e3284b";
this.bold = false;
this.size = 12;
this.horizontalAlignment = "center";
this.verticalAlignment = "middle";
}
}
class ContentStyle {
constructor() {
this.color = "#000000";
this.backgroundColor = "#ffffff";
this.bold = false;
this.size = 12;
this.horizontalAlignment = "center";
this.verticalAlignment = "middle";
}
}
class HeaderDateStyle {
constructor() {
this.color = "#ffffff";
this.backgroundColor = "#001a40";
this.bold = true;
this.size = 12;
this.horizontalAlignment = "center";
this.verticalAlignment = "middle";
}
}
DailyReportField.gs field data object:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
class DailyReportField {
constructor(name, headerStyle, contentStyle, format = null, value = null) {
this.name = name;
this.headerStyle = headerStyle;
this.contentStyle = contentStyle;
this.format = format;
this.value = value;
}
}
DailyReport.gs main script logic for the report:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
class DailyReport {
constructor(sheetID, date) {
this.separateSheet = SpreadsheetApp.openById(sheetID);
this.date = date;
this.sheetFields = [
new DailyReportField("Date", new HeaderDateStyle(), new HeaderDateStyle()),
new DailyReportField("Day of Week", new HeaderDateStyle(), new HeaderDateStyle()),
new DailyReportField("Daily Traffic", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0", '=INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,COLUMN(),4),"1","")&4)+INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,COLUMN(),4),"1","")&5)'), // =4(PC Traffic) + 5(Mobile Traffic)
new DailyReportField("PC Traffic", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0"),
new DailyReportField("Mobile Traffic", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0"),
new DailyReportField("Registrations", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0")
]
// Explanation of the Daily Traffic formula:
// 1. The COLUMN() function returns the current cell's column number.
// 2. ADDRESS(1, COLUMN(), 4) generates a relative address without $ signs for row 1 and the current column. For example, in column 3, it returns "C1".
// 3. SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, COLUMN(), 4), "1", "") removes the "1" from the address, leaving just the column letter, e.g., "C".
// 4. INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, COLUMN(), 4), "1", "") & 4) concatenates the column letter with 4 to form a reference like "C4", which INDIRECT converts to a cell reference.
// 5. Similarly, INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, COLUMN(), 4), "1", "") & 5) references the cell in the same column but row 5.
// 6. Finally, the formula adds the values from these two INDIRECT references.
}
execute() {
const sheet = this.getSheet();
}
// Get the target sheet for the given date
getSheet() {
// Use month to identify the sheet, find the current month sheet
var thisMonthSheet = this.separateSheet.getSheetByName(this.getSheetName());
if (thisMonthSheet == null) {
// If not found, create a new month sheet
thisMonthSheet = this.makeMonthSheet();
}
return thisMonthSheet;
}
// Naming rule for month sheets
getSheetName() {
return Utilities.formatDate(this.date, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM");
}
// Create a new month sheet
makeMonthSheet() {
// Add the current month sheet and move it to the first position
var thisMonthSheet = this.separateSheet.insertSheet(this.getSheetName(), {index: 0});
thisMonthSheet.activate();
this.separateSheet.moveActiveSheet(1);
// Insert first column: field names, set pinned columns, width 200
thisMonthSheet.insertColumnsBefore(1, 1);
thisMonthSheet.setFrozenColumns(1);
thisMonthSheet.setColumnWidths(1, 1, 200);
// Fill in field names
for(const currentRow in this.sheetFields) {
const sheetField = this.sheetFields[currentRow];
const text = sheetField.name;
const style = sheetField.headerStyle;
const range = thisMonthSheet.getRange(parseInt(currentRow) + 1, 1);
this.setContent(range, text, style);
range.setHorizontalAlignment("left");
}
// Set row heights
thisMonthSheet.setRowHeights(1, Object.keys(this.sheetFields).length, 30);
// Set pinned first and second rows (Date, Day of Week)
thisMonthSheet.setFrozenRows(2);
// Add total column
thisMonthSheet.insertColumnsAfter(thisMonthSheet.getLastColumn(), 1); // Add one column after the last
const summaryColumnIndex = thisMonthSheet.getLastColumn() + 1;
// Fill total column
for(const currentRow in this.sheetFields) {
const sheetField = this.sheetFields[currentRow];
const summaryRowIndex = parseInt(currentRow) + 1;
const range = thisMonthSheet.getRange(summaryRowIndex, summaryColumnIndex);
const style = sheetField.contentStyle;
if (summaryRowIndex == 1) {
// Date...
this.setContent(range, "Total", style);
} else if (summaryRowIndex == 2) {
// Day of Week... merge...
const mergeRange = thisMonthSheet.getRange(1, summaryColumnIndex, summaryRowIndex, 1);
this.setContent(mergeRange, "Total", style);
mergeRange.merge();
} else {
this.setContent(range, '=IFERROR(SUM(INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, 1, 4), "1", "") & '+summaryRowIndex+'):INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, COLUMN() - 1, 4), "1", "") & '+summaryRowIndex+')), 0)', style);
// 1. IFERROR(value, [value_if_error]) checks for errors in the formula and returns the specified value if an error occurs. Here, it returns 0 if SUM causes an error.
// 2. SUM(range) calculates the total of all numbers in the range.
// 3. INDIRECT(ref_text, [is_A1_notation]) converts a string to a cell reference, used here to dynamically generate the range.
// 4. SUBSTITUTE(text, old_text, new_text, [instance_num]) replaces specified text in a string. Here, it removes "1" from the ADDRESS output.
// 5. ADDRESS(row, column, [abs_num], [a1], [sheet]) returns a cell address. ADDRESS(1, 1, 4) returns the cell at row 1, column 1 without $ or sheet name. ADDRESS(1, COLUMN() - 1, 4) returns the address for the first row and the column before the current one.
// 6. COLUMN() returns the current cell's column number.
// 7. summaryRowIndex = current row
}
}
return thisMonthSheet;
}
setContent(range, text, style) {
if (String(text) != "") {
range.setValue(text);
}
range.setBackgroundColor(style.backgroundColor);
range.setFontColor(style.color);
if (style.bold) {
range.setFontWeight("bold");
}
range.setHorizontalAlignment(style.horizontalAlignment);
range.setVerticalAlignment(style.verticalAlignment);
range.setFontSize(style.size);
range.setBorder(true, true, true, true, true, true, "black", SpreadsheetApp.BorderStyle.SOLID);
}
}
Main.gs serves as the main program entry point:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
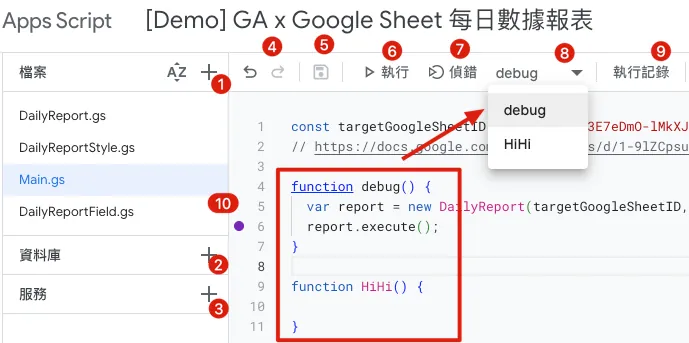
const targetGoogleSheetID = "1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE"
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit#gid=275710641
function debug() {
var report = new DailyReport(targetGoogleSheetID, new Date());
report.execute();
}
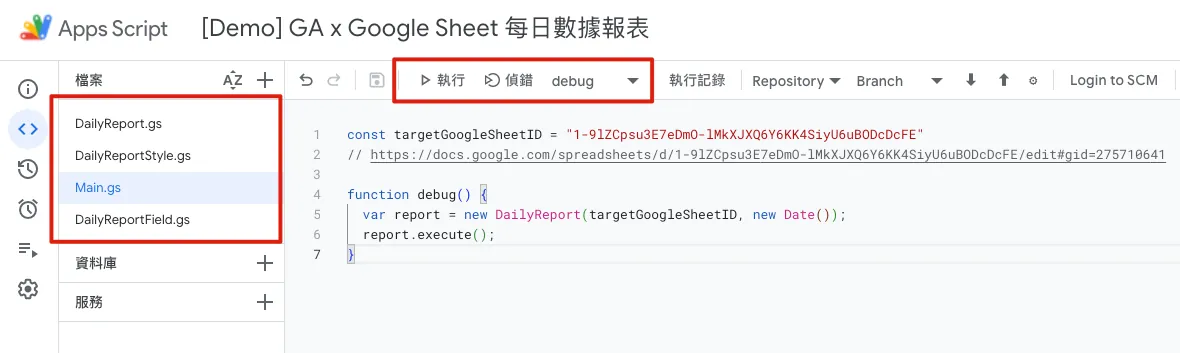
After finishing, return to Main.gs, select “debug,” and click debug to check if the execution results are correct and error-free.
Executing correctly returns to the report showing the current new month, including default fields and total fields. If it already exists, there will be no response.
3. Integrate Google Analytics to Fetch Data
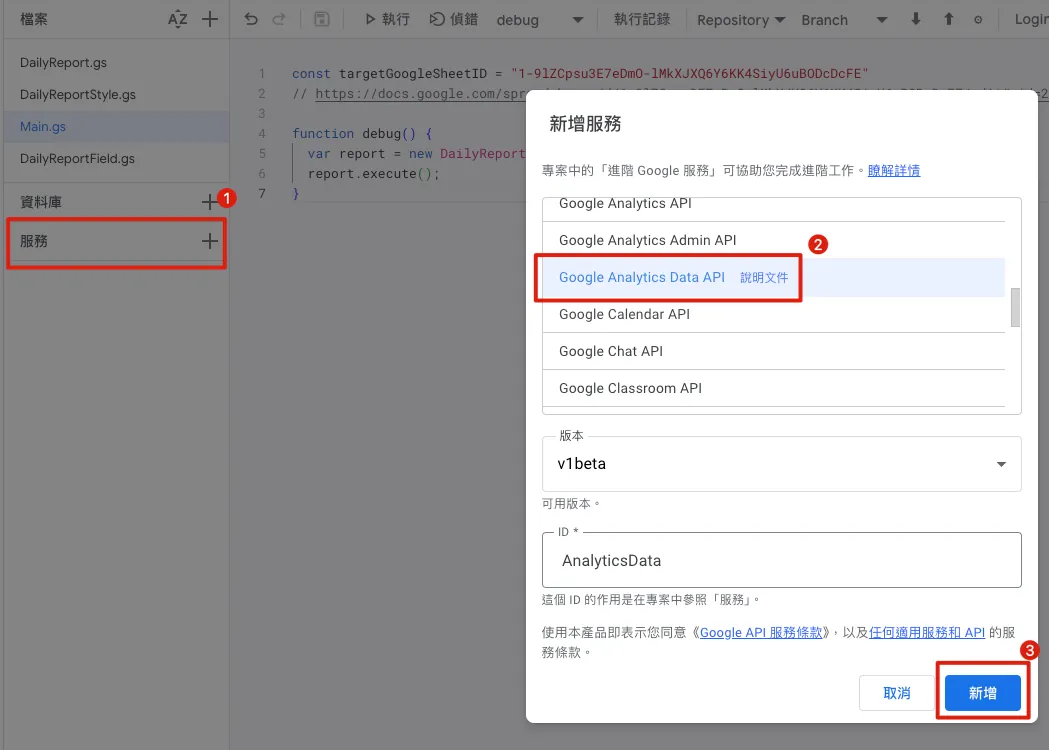
First, create the “AnalyticsData” service:
Build Query Conditions Using GA4 Debug Tool:
Can be compared when creating filter conditions in the GA4 backend
This article uses querying the number of Sessions as an example to distinguish device Grouping
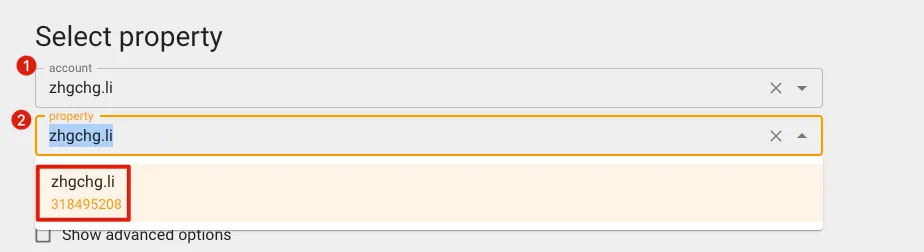
After logging in and authorizing, select the target resource:
Note down the number displayed under the property; this is the GA Property ID you need to query.
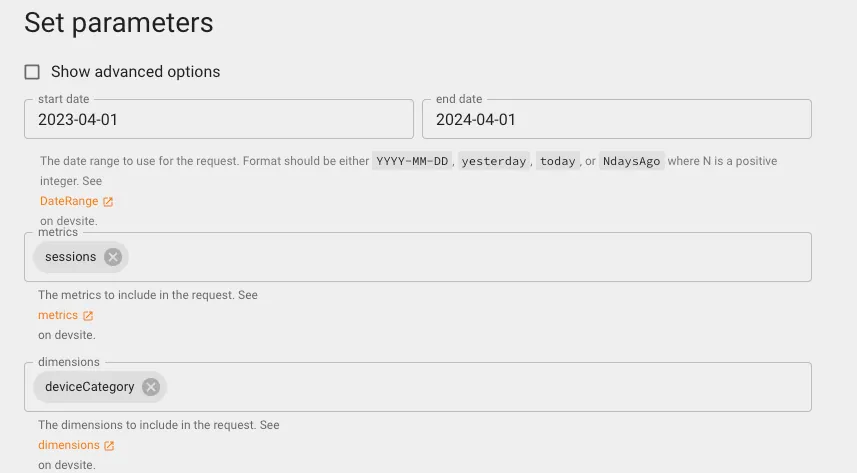
Set query parameters and filter conditions:
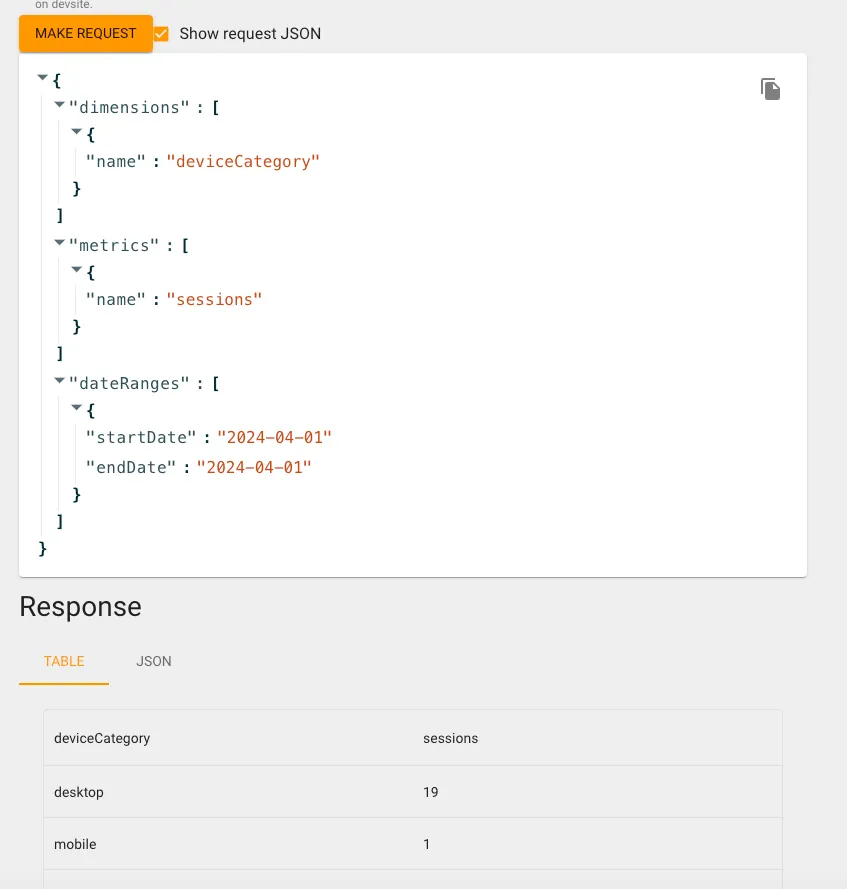
Press “Make Request” to get the Response result:
You can also compare the data under the same conditions in the GA4 backend to see if they match. If there is a large discrepancy, it might be due to missing Filter conditions, so you should check again.
Summary
Here is a small pitfall discovered by a marketing colleague: GA data can have delays, so the numbers you check today might differ from those checked yesterday (e.g., bounce rate). Therefore, it’s best to look back a few days to ensure the data reflects the final values.
Once the GA Debug Tool works properly, we can convert it into Google Apps Script.
Add a new file GAData.gs:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
// Remember to add Google Analytics Data API to Services, or you'll see this error: ReferenceError: AnalyticsData is not defined
// GA Debug Tool: https://ga-dev-tools.web.app/ga4/query-explorer/
class GAData {
constructor(date) {
this.date = date;
const traffic = this.fetchGADailyUsage();
this.pc_traffic = traffic["desktop"];
this.mobile_traffic = traffic["mobile"];
}
fetchGADailyUsage() {
const dimensionPlatform = AnalyticsData.newDimension();
dimensionPlatform.name = "deviceCategory";
const metric = AnalyticsData.newMetric();
metric.name = "sessions";
const dateRange = AnalyticsData.newDateRange();
// Default query for data within the given date range e.g. 2024-01-01 ~ 2024-01-01
dateRange.startDate = this.getDateString();
dateRange.endDate = this.getDateString();
// Filter Example:
// const filterExpression = AnalyticsData.newFilterExpression();
// const filter = AnalyticsData.newFilter();
// filter.fieldName = "landingPagePlusQueryString";
// const stringFilter = AnalyticsData.newStringFilter()
// stringFilter.value = "/life\|/article\|/chat\|/house\|/event/230502\|/event/230310";
// stringFilter.matchType = "PARTIAL_REGEXP";
// filter.stringFilter = stringFilter;
// filterExpression.filter = filter;
const request = AnalyticsData.newRunReportRequest();
request.dimensions = [dimensionPlatform];
request.metrics = [metric];
request.dateRanges = dateRange;
// Filter Example:
// const filterExpression = AnalyticsData.newFilterExpression();
// filterExpression.expression = filterExpression;
// request.dimensionFilter = filterExpression;
// or Not
// const notFilterExpression = AnalyticsData.newFilterExpression();
// notFilterExpression.notExpression = filterExpression;
// request.dimensionFilter = notFilterExpression;
const report = AnalyticsData.Properties.runReport(request, "properties/" + gaPropertyId).rows;
// No data
if (report == undefined) {
return {"desktop": 0, "mobile": 0};
}
// [{metricValues=[{value=4517}], dimensionValues=[{value=mobile}]}, {metricValues=[{value=3189}], dimensionValues=[{value=desktop}]}, {metricValues=[{value=63}], dimensionValues=[{value=tablet}]}]
var result = {};
report.forEach(function(element) {
result[element.dimensionValues[0].value] = element.metricValues[0].value;
});
return result;
}
getDateString() {
return Utilities.formatDate(this.date, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM-dd");
}
}
Main.gs Add test content:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
const targetGoogleSheetID = "1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE";
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit#gid=275710641
const gaPropertyId = "318495208";
function debug() {
var report = new DailyReport(targetGoogleSheetID, new Date());
report.execute();
//
var gaData = new GAData(new Date());
Logger.log(gaData);
}
Press Run or Debug to get the program fetch results:
OK! Match confirmed.
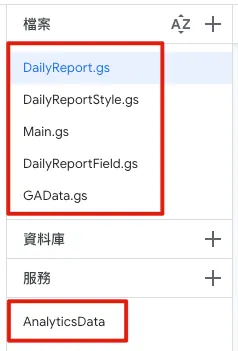
When this step is completed, the directory file structure will look like the image above.
4. Data Filling
After setting up the sheet and gathering the data, the next step is to fill the data into the fields.
Adjust DailyReport.gs to add a new column by date and include logic to fill data:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
class DailyReport {
constructor(sheetID, date, gaData, inHouseReportData) {
this.separateSheet = SpreadsheetApp.openById(sheetID);
this.date = date;
const dateString = Utilities.formatDate(date, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd");
const weekString = ["Sunday", "Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"][date.getDay()]; // Get the weekday, Sunday is 0, Monday is 1, etc.
this.sheetFields = [
new DailyReportField("Date", new HeaderDateStyle(), new HeaderDateStyle(), null, dateString),
new DailyReportField("Weekday", new HeaderDateStyle(), new HeaderDateStyle(), null, weekString),
new DailyReportField("Daily Traffic", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0", '=INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,COLUMN(),4),"1","")&4)+INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1,COLUMN(),4),"1","")&5)'), // =4(PC traffic) + 5(Mobile traffic)
new DailyReportField("PC Traffic", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0", gaData.pc_traffic),
new DailyReportField("Mobile Traffic", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0", gaData.mobile_traffic),
new DailyReportField("Registrations", new HeaderStyle(), new ContentStyle(), "#,##0", inHouseReportData.registers)
]
}
execute() {
const sheet = this.getSheet();
const dateColumnIndex = this.makeOrGetDateColumn(sheet); // Get existing or create new column
// Fill column content
for(const currentRow in this.sheetFields) {
const sheetField = this.sheetFields[currentRow];
const rowIndex = parseInt(currentRow) + 1;
if (rowIndex != null) {
const range = sheet.getRange(rowIndex, dateColumnIndex);
const text = sheetField.value;
const style = sheetField.contentStyle;
this.setContent(range, text, style);
this.setFormat(range, sheetField.format);
}
}
}
// Get the target sheet for the given date
getSheet() {
// Separate sheets by month, find sheet for current month
var thisMonthSheet = this.separateSheet.getSheetByName(this.getSheetName());
if (thisMonthSheet == null) {
// Create new month sheet if not found
thisMonthSheet = this.makeMonthSheet();
}
return thisMonthSheet;
}
// Month sheet naming
getSheetName() {
return Utilities.formatDate(this.date, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM");
}
// Create new month sheet
makeMonthSheet() {
// Add new sheet for current month, move to first position
var thisMonthSheet = this.separateSheet.insertSheet(this.getSheetName(), {index: 0});
thisMonthSheet.activate();
this.separateSheet.moveActiveSheet(1);
// Add first column, set header name, pin, width 200
thisMonthSheet.insertColumnsBefore(1, 1);
thisMonthSheet.setFrozenColumns(1);
thisMonthSheet.setColumnWidths(1, 1, 200);
// Fill column names
for(const currentRow in this.sheetFields) {
const sheetField = this.sheetFields[currentRow];
const text = sheetField.name;
const style = sheetField.headerStyle;
const range = thisMonthSheet.getRange(parseInt(currentRow) + 1, 1);
this.setContent(range, text, style);
range.setHorizontalAlignment("left");
}
// Set row heights
thisMonthSheet.setRowHeights(1, Object.keys(this.sheetFields).length, 30);
// Pin first and second rows (Date, Weekday)
thisMonthSheet.setFrozenRows(2);
// Add summary column
thisMonthSheet.insertColumnsAfter(thisMonthSheet.getLastColumn(), 1); // Add column after last column
const summaryColumnIndex = thisMonthSheet.getLastColumn() + 1;
// Fill summary column
for(const currentRow in this.sheetFields) {
const sheetField = this.sheetFields[currentRow];
const summaryRowIndex = parseInt(currentRow) + 1;
const range = thisMonthSheet.getRange(summaryRowIndex, summaryColumnIndex);
const style = sheetField.contentStyle;
if (summaryRowIndex == 1) {
// Date...
this.setContent(range, "Total", style);
} else if (summaryRowIndex == 2) {
// Weekday...merge...
const mergeRange = thisMonthSheet.getRange(1, summaryColumnIndex, summaryRowIndex, 1);
this.setContent(mergeRange, "Total", style);
mergeRange.merge();
} else {
this.setContent(range, '=IFERROR(SUM(INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, 1, 4), "1", "") & '+summaryRowIndex+'):INDIRECT(SUBSTITUTE(ADDRESS(1, COLUMN() - 1, 4), "1", "") & '+summaryRowIndex+')), 0)', style);
}
}
return thisMonthSheet;
}
// Create or get date column
// Add one column after the most recent date
makeOrGetDateColumn(sheet) {
const firstRowColumnsRange = sheet.getRange(1, 1, 1, sheet.getLastColumn()); // Get first row (date) range
const firstRowColumns = firstRowColumnsRange.getValues()[0]; // Get values of first row
var columnIndex = firstRowColumns.findIndex((date) => (date instanceof Date && Utilities.formatDate(date, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd") == Utilities.formatDate(this.date, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd"))); // Find column index for matching date
if (columnIndex < 0) {
// Not found, find previous date's position
var preDate = new Date(this.date);
preDate.setDate(preDate.getDate() - 1);
while(preDate.getMonth() == this.date.getMonth()) {
columnIndex = firstRowColumns.findIndex((date) => (date instanceof Date && Utilities.formatDate(date, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd") == Utilities.formatDate(preDate, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd")));
if (columnIndex >= 0) {
break;
}
preDate.setDate(preDate.getDate() - 1);
}
if (columnIndex >= 0) {
columnIndex += 1;
sheet.insertColumnsAfter(columnIndex, 1); // Insert new column after previous date column
columnIndex += 1;
}
} else {
columnIndex += 1;
}
if (columnIndex < 0) {
sheet.insertColumnsAfter(1, 1); // Default, insert new column after first column
columnIndex = 2;
}
// Set column width
sheet.setColumnWidths(columnIndex , 1, 100);
return columnIndex
}
// Set column format style
setFormat(range, format) {
if (format != null) {
range.setNumberFormat(format);
}
}
// Fill content into column
setContent(range, text, style) {
if (String(text) != "") {
range.setValue(text);
}
range.setBackgroundColor(style.backgroundColor);
range.setFontColor(style.color);
if (style.bold) {
range.setFontWeight("bold");
}
range.setHorizontalAlignment(style.horizontalAlignment);
range.setVerticalAlignment(style.verticalAlignment);
range.setFontSize(style.size);
range.setBorder(true, true, true, true, true, true, "black", SpreadsheetApp.BorderStyle.SOLID);
}
}
Adjust Main.gs to add data connection and assign values during the build phase:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
const targetGoogleSheetID = "1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE";
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit#gid=275710641
const gaPropertyId = "318495208";
function debug() {
const date = new Date();
const gaData = new GAData(date);
const inHouseReportData = fetchInHouseReportData(date);
const report = new DailyReport(targetGoogleSheetID, date, gaData, inHouseReportData);
report.execute();
}
// Simulate some data which might be fetched from other platform APIs.
function fetchInHouseReportData(date) {
// EXAMPLE REQUEST:
// var options = {
// 'method' : 'get',
// 'headers': {
// 'Authorization': 'Bearer XXX'
// }
// };
// OR
// var options = {
// 'method' : 'post',
// 'headers': {
// 'Authorization': 'Bearer XXX'
// },
// 'payload' : data
// };
// var res = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
// const result = JSON.parse(res.getContentText());
// REMEMBER, DUE TO SECURITY REASONS, we can't customize user-agent.
return {"registers": Math.floor(Math.random() * (180 - 30 + 1)) + 30} // MOCK DATA random 30~180
}
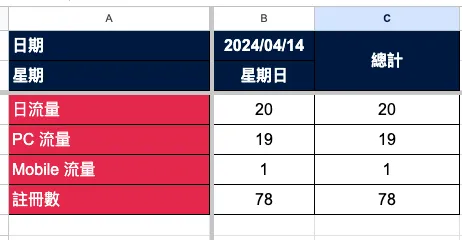
After finishing, go back to Main.gs, select “debug,” and click “Start Debugging” to check if the execution results are correct and error-free.
Back to Google Sheet! Success! We have successfully automated adding the data for that date.
5. Set a schedule to run automatically every day
After the script is completed, just set the automatic trigger condition, and it will run automatically every day.
Adjust Main.gs to add the cronjob() function:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
const targetGoogleSheetID = "1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE";
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit#gid=275710641
const gaPropertyId = "318495208";
function debug() {
cronjob();
}
// In reality, usually today's query is for yesterday's data to get complete information
function cronjob() {
const yesterday = new Date();
yesterday.setDate(yesterday.getDate() - 1);
const gaData = new GAData(yesterday);
const inHouseReportData = fetchInHouseReportData(yesterday);
const report = new DailyReport(targetGoogleSheetID, yesterday, gaData, inHouseReportData);
report.execute();
}
// Simulate that some data might be obtained from other platform APIs.
function fetchInHouseReportData(date) {
// EXAMPLE REQUEST:
// var options = {
// 'method' : 'get',
// 'headers': {
// 'Authorization': 'Bearer XXX'
// }
// };
// OR
// var options = {
// 'method' : 'post',
// 'headers': {
// 'Authorization': 'Bearer XXX'
// },
// 'payload' : data
// };
// var res = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
// const result = JSON.parse(res.getContentText());
// REMEMBER, DUE TO SECURITY REASONS, we can't customize user-agent.
return {"registers": Math.floor(Math.random() * (180 - 30 + 1)) + 30} // MOCK DATA random 30~180
}
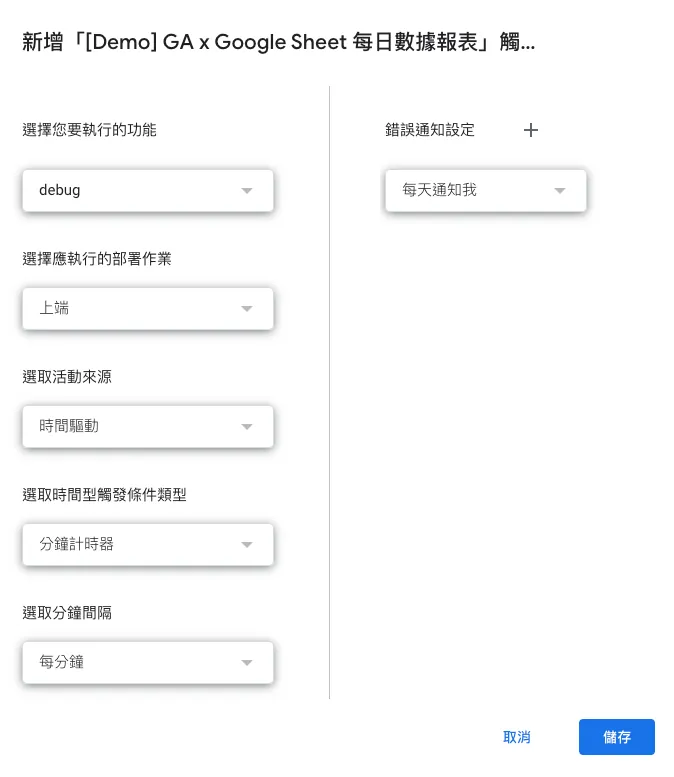
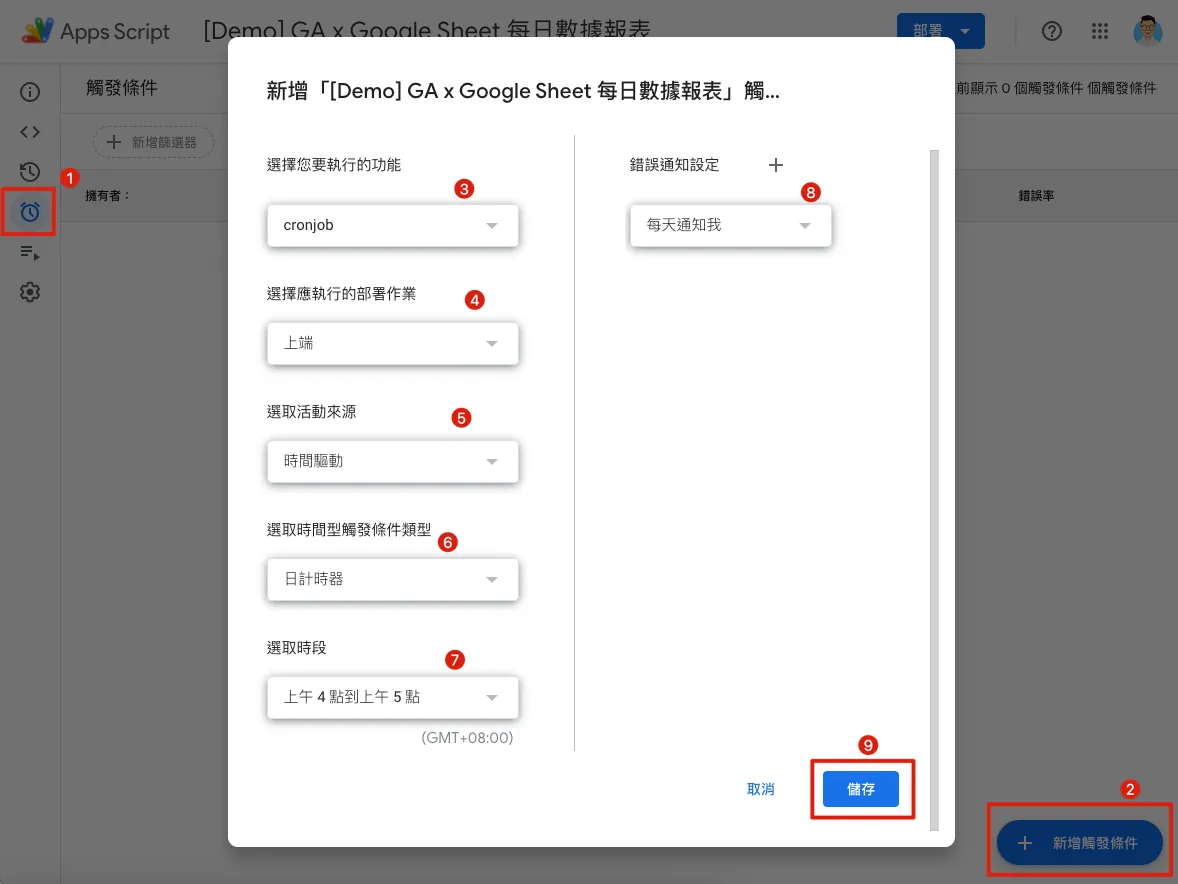
Switch to the “Trigger Conditions” tab in the editor, then select “Add Trigger Condition” at the bottom right:
Choose the function you want to execute: Newly added
Main.gsFunctioncronjobChoose the deployment operation to execute: Head (meaning the latest version)
Select Trigger Source: Time Driven
Select the time-based trigger type: Daily timer
Selected Time Slot: AM 4:00 — AM 5:00 (GMT+08:00)
Usually runs right at AM 4:00.Error Notification Settings: Should notifications be sent immediately when a script error occurs, or summarized once daily?
Settings saved, completed.
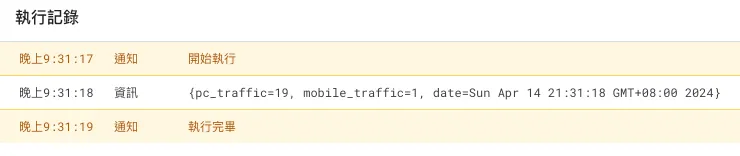
You can later check the execution records in the “Tasks” tab:
At this point, we have completed the RPA functions for automated query, data addition, and data entry in the report. 🎉🎉🎉
Building a Web GUI Dashboard
Next, there is a secondary requirement: we need to create a simple web display for daily data (similar to a command center concept) that will be shown directly on a large screen on the team’s back wall.
The effect is shown in the image below:
Add Web_DailyReport.gs to read Google Sheet and convert columns and styles into HTML format:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
class WebDailyReport {
constructor(sheetID, dayCount) {
this.separateSheet = SpreadsheetApp.openById(sheetID);
this.dayCount = dayCount;
this.sheetRows = [
"Date",
"Weekday",
"Daily Traffic",
"PC Traffic",
"Mobile Traffic",
"Registrations"
];
}
allData(startDate) {
var sheetRowsIndexs = {};
var count = this.dayCount;
var result = [];
while (count >= 0) {
const preDate = new Date(startDate);
preDate.setDate(preDate.getDate() - (this.dayCount - count));
const sheetName = Utilities.formatDate(preDate, "GMT+8", "yyyy-MM");
const targetSheet = this.separateSheet.getSheetByName(sheetName);
if (targetSheet != null) {
const firstRowColumnsRange = targetSheet.getRange(1, 1, 1, targetSheet.getLastColumn()); // Get first row (date) data range
const firstRowColumns = firstRowColumnsRange.getValues()[0]; // Get values of the data range, 0 = first row
var columnIndex = firstRowColumns.findIndex((date) => (date instanceof Date && Utilities.formatDate(date, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd") == Utilities.formatDate(preDate, "GMT+8", "yyyy/MM/dd"))); // Find column index for the date
if (columnIndex >= 0) {
columnIndex = parseInt(columnIndex) + 1;
if (sheetRowsIndexs[sheetName] == undefined \|\| sheetRowsIndexs[sheetName] == null) {
sheetRowsIndexs[sheetName] = this.sheetRows.map((sheetRow) => this.getFieldRow(targetSheet, sheetRow));
}
if (result.length == 0) {
// Add first column
const ranges = sheetRowsIndexs[sheetName].map((rowIndex) => (rowIndex != null) ? (targetSheet.getRange(rowIndex, 1)) : (null));
result.push(this.makeValues(ranges));
}
const ranges = sheetRowsIndexs[sheetName].map((rowIndex) => (rowIndex != null) ? (targetSheet.getRange(rowIndex, columnIndex)) : (null));
result.push(this.makeValues(ranges));
}
}
count -= 1;
}
var transformResult = {};
for (const columnIndex in result) {
for (const rowIndex in result[columnIndex]) {
if (transformResult[rowIndex] == undefined) {
transformResult[rowIndex] = [];
}
if (columnIndex == 0) {
transformResult[rowIndex].unshift(result[columnIndex][rowIndex]);
} else {
transformResult[rowIndex].splice(1, 0, result[columnIndex][rowIndex]);
}
}
}
return transformResult;
}
// Convert field attribute values into display objects
makeValues(ranges) {
const data = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getDisplayValues()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
const backgroundColors = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getBackgrounds()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
const colors = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getFontColorObjects()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
const sizes = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getFontSizes()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
const bolds = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getFontWeights()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
const horizontalAlignments = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getHorizontalAlignments()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
const verticalAlignments = ranges.map((range) => (range != null) ? (range.getVerticalAlignments()) : (null)).map((values) => (values != null) ? (values[0][0]) : (null));
var result = [];
for(const index in data) {
const row = data[index];
result.push({
"value": row,
"backgroundColor": backgroundColors[index],
"color": this.colorStripper(colors[index]?.asRgbColor()?.asHexString()),
"size": sizes[index],
"bold": bolds[index],
"horizontalAlignment": this.alignConventer(horizontalAlignments[index]),
"verticalAlignment": verticalAlignments[index]
});
}
return result;
}
colorStripper(colorString) {
if (colorString == undefined \|\| colorString == null) {
return null
}
if (colorString.length == 9) {
return "#"+colorString.substring(3, 9);
} else {
return colorString;
}
}
alignConventer(horizontalAlignment) {
if (horizontalAlignment == undefined \|\| horizontalAlignment == null) {
return null
}
return horizontalAlignment.replace('general-', '')
}
getFieldRow(sheet, name) {
const firstColumnRowsRange = sheet.getRange(1, 1, sheet.getLastRow(), 1); // Get first column (field) data range
const firstColumnRows = firstColumnRowsRange.getValues(); // Get values of the data range
const foundIndex = firstColumnRows.findIndex((firstColumnRow) => firstColumnRow[0] == name);
if (foundIndex < 0) {
return null;
} else {
return foundIndex + 1;
}
}
}
Main.gs Add Web Request Handler:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
const targetGoogleSheetID = "1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE";
// https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit#gid=275710641
const gaPropertyId = "318495208";
function debug() {
cronjob();
}
function cronjob() {
const yesterday = new Date();
yesterday.setDate(yesterday.getDate() - 1);
const gaData = new GAData(yesterday);
const inHouseReportData = fetchInHouseReportData(yesterday);
const report = new DailyReport(targetGoogleSheetID, yesterday, gaData, inHouseReportData);
report.execute();
}
function doGet(e) {
return HtmlService.createTemplateFromFile('Web_DailyReport_ Scaffolding').evaluate();
}
function getDailyReportBody() {
const html = HtmlService.createTemplateFromFile('Web_DailyReport_Body').evaluate().getContent();
return html;
}
// FOR POST
// function doPost(e) {
// ref: https://developers.google.com/apps-script/guides/web?hl=zh-tw
// }
// Simulate some data that might be obtained from other platform APIs.
function fetchInHouseReportData(date) {
// EXAMPLE REQUEST:
// var options = {
// 'method' : 'get',
// 'headers': {
// 'Authorization': 'Bearer XXX'
// }
// };
// OR
// var options = {
// 'method' : 'post',
// 'headers': {
// 'Authorization': 'Bearer XXX'
// },
// 'payload' : data
// };
// var res = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
// const result = JSON.parse(res.getContentText());
// REMEMBER, DUE TO SECURITY REASONS, we can't customize user-agent.
return {"registers": Math.floor(Math.random() * (180 - 30 + 1)) + 30} // MOCK DATA random 30~180
}
Added Web_DailyReport_ Scaffolding.html Web Dashboard framework. Since our command center screens need to update content automatically, we created a web scaffold that periodically fetches HTML content using Ajax:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<base target="_top">
<script>
function onSuccess(html) {
if (html != null) {
var div = document.getElementById('result');
div.innerHTML = html;
}
}
setInterval(()=>{
google.script.run.withSuccessHandler(onSuccess).getDailyReportBody()
}, 1000 * 60 * 60 * 1);
google.script.run.withSuccessHandler(onSuccess).getDailyReportBody();
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="result">Loading...</div>
</body>
</html>
Added Web_DailyReport_Body.html where data is actually rendered into HTML:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<base target="_top">
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid #000000;
padding: 8px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 36px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="text-align:center">ZHGCHG.LI</h1>
<table id="dataTable">
<tbody>
<?
// Display data for the past 7 days
const dashboard = new WebDailyReport(targetGoogleSheetID, 7);
// Start from yesterday
const yesterday = new Date();
yesterday.setDate(yesterday.getDate() - 1);
const data = dashboard.allData(yesterday);
for(const rowIndex in data) {
const row = data[rowIndex];
?>
<tr>
<?
for(const columnIndex in row) {
const column = row[columnIndex];
?>
<td style="background-color: <?=column["backgroundColor"]?>; color: <?=column["color"]?>; text-align: <?=column["horizontalAlignment"]?>;">
<?=column["value"]?>
</td>
<?
}
?>
</tr>
<?
}
?>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
</body>
</html>
Please note, we retrieve data from the past 7 days starting from yesterday, so today’s data will not be shown.
The project file directory after completing the above steps is as follows:
Test Deployment:
Click the project’s top right corner “Deploy” -> “Test Deployment Operation”
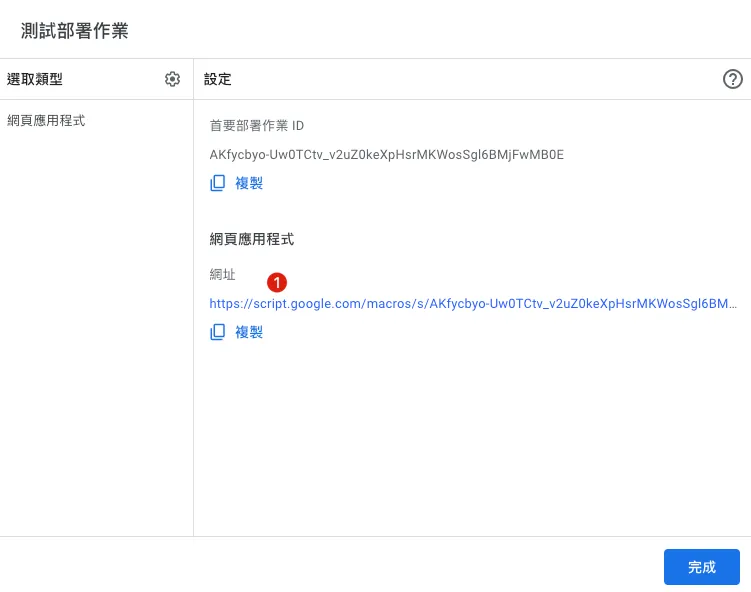
After deployment, click the link to view the test results.
Please note this URL is for one-time testing only. If the code is modified, you need to click the test deployment again.
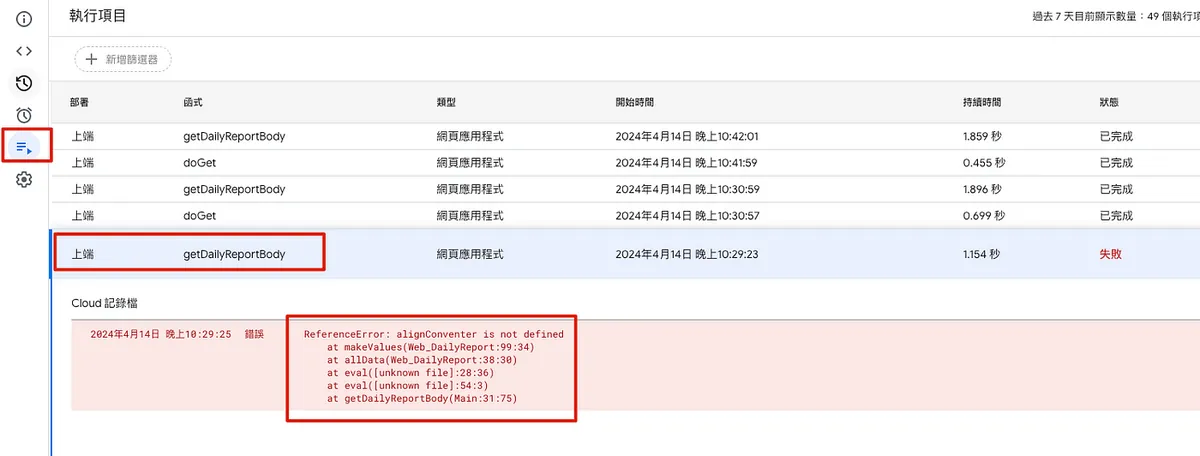
If stuck on Loading… with no content or a server error appears, you can go back to the editor’s “Run Items” tab to check the error messages:
Complete Formal Deployment:
If the testing is successful, the official deployment can be completed and the URL released.
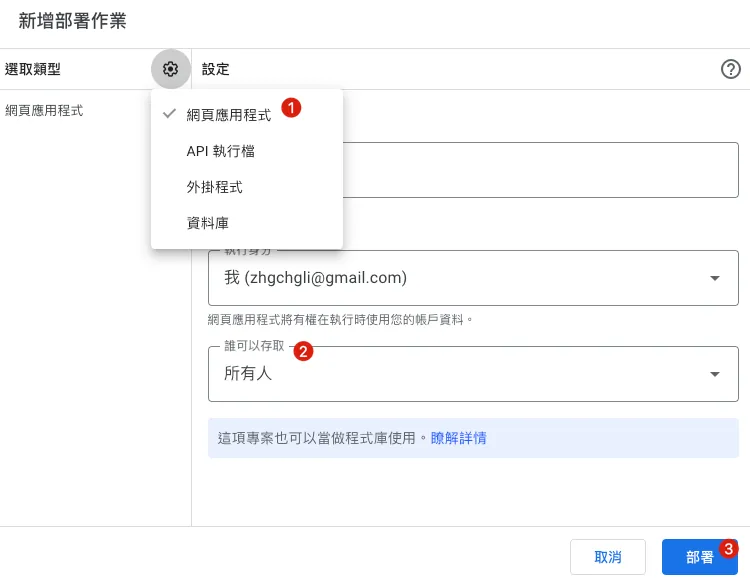
Click the project’s top right corner “Deploy” -> “New deployment” -> top left “Select type” -> “Web app”:
Execution identity: Default to the current account (same as the Google Apps Script user)
Who can access: Set to “Anyone with the link” so anyone who knows the URL can access, or set to “Organization only,” which requires Google sign-in to access.
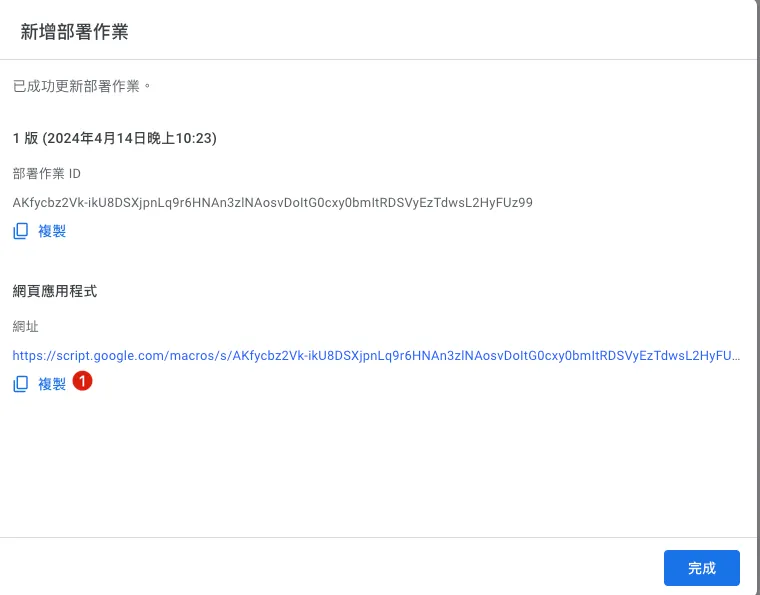
Deployment completed, URL obtained.
Code changes require redeployment to take effect:
Please note that when the code changes, redeployment is required (the URL will not change) for the changes to take effect; otherwise, the old version will persist.
Click the project’s top right corner “Deploy” -> “Manage Deployments”:
Click the top right “Pen 🖊️ ICON” -> “Versions” -> “Create New Version” -> “Deploy”.
After deployment, click the URL or refresh the original URL to see the updated changes.
🎉🎉Done! All our RPA requirements have been completed.🎉🎉
Final Result:
(Update the program to backfill this month’s data; otherwise, with fresh data, there will be only one record from yesterday)
Complete Google Sheet Demo:
Google Sheet:
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1-9lZCpsu3E7eDmO-lMkXJXQ6Y6KK4SiyU6uBODcDcFE/edit?usp=sharingWeb GUI URL:
https://script.google.com/macros/s/AKfycbz2Vk-ikU8DSXjpnLq9r6HNAn3zlNAosvDoItG0cxy0bmItRDSVyEzTdwsL2HyFUz99/execGoogle Apps Script:
https://script.google.com/home/projects/1vHgXPTV_q8MC75FVzAEtzD2JPVnPBpMfFXbjZR7SLMVjoEH1FcjKlo8l/edit
Other Daily Life Applications:
Robotic Process Automation with Google Apps Script — Github Repo Star Notifier to Line
Robotic Process Automation with Google Apps Script — Notion Database to Calendar
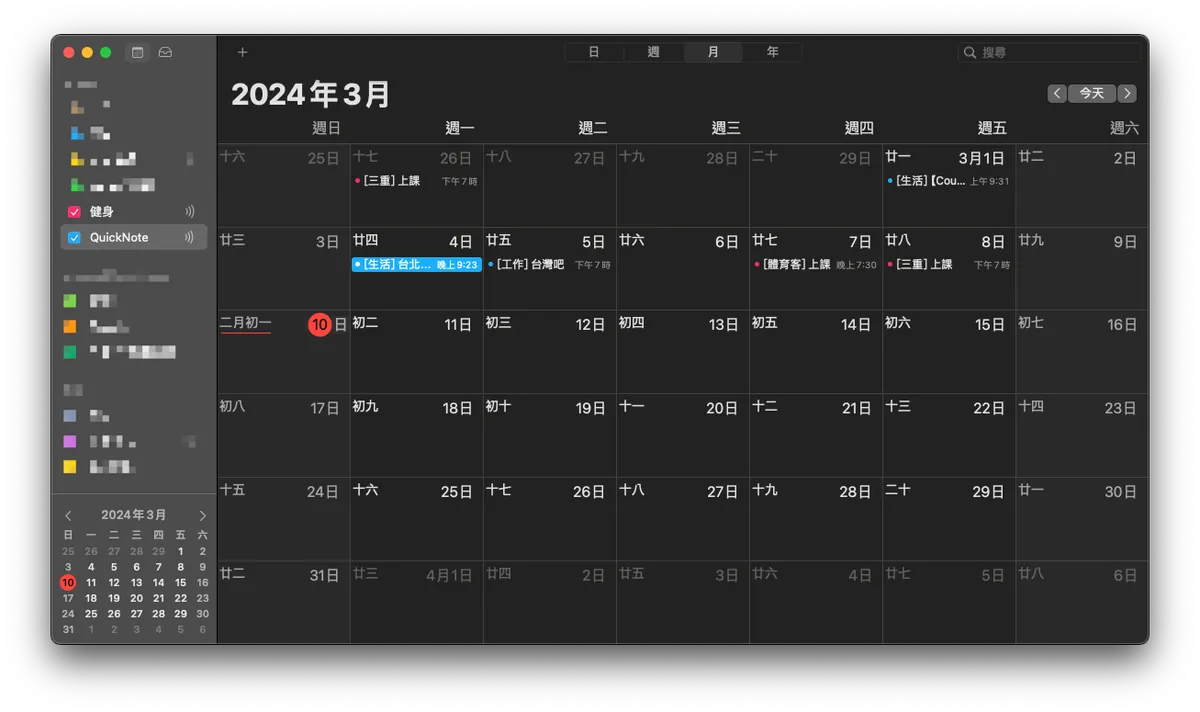
Previously implemented a simple Notion to Calendar feature.
The implementation connects to the Notion API to fetch database data and generate an ICS format webpage, then deploys it as a public webpage; just add this URL to Apple Calendar.
Main.gs :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
// Constant variables
const notionToken = "XXXXX";
const safeToken = "XXXXX";
function doGet(e) {
const ics = HtmlService.createTemplateFromFile('ics');
if (e.parameter.token != safeToken) {
return ContentService.createTextOutput("Access Denied!");
}
ics.events = getQuickNote();
return ContentService.createTextOutput(ics.evaluate().getContent()).setMimeType(ContentService.MimeType.ICAL);
}
function debug() {
const ics = HtmlService.createTemplateFromFile('ics');
ics.events = getQuickNote();
Logger.log(ics.evaluate().getContent());
}
function getQuickNote() {
// YOUR FILTER Condition:
const payload = {
"filter": {
"and": [
{
"property": "Date",
"date": {
"is_not_empty": true
}
}
,
{
"property": "Name",
"title": {
"is_not_empty": true
}
}
]
}
};
const result = getDatabase(YOUR_DATABASE_ID, payload);
var events = [];
for (const index in result.results) {
const item = result.results[index]
const properties = item.properties;
const id = item['id'];
const create = toICSDate(item["created_time"]);
const edit = toICSDate(item["last_edited_time"]);
const startDate = properties['Date']['date']['start'];
const start = toICSDate(startDate);
var endDate = properties['Date']?.['date']?.['end'];
if (endDate == null) {
endDate = startDate;
}
const end = toICSDate(endDate);
const type = properties['Type']?.['multi_select']?.[0]?.['name'];
const title = "["+type+"] "+properties?.['Name']?.['title']?.[0]?.['plain_text'];
const description = item['url'];
events.push(
{
"id":id,
"create":create,
"edit":edit,
"start":start,
"end":end,
"title":title,
"description":description
}
)
}
return events;
}
// TO UTC Date
function toICSDate(date) {
const icsDate = new Date(date);
icsDate.setHours(icsDate.getHours() - 8);
return Utilities.formatDate(icsDate, "GMT+8", "yyyyMMdd'T'HHmmss'Z'");// 20240304T132300Z
}
// Notion
function getDatabase(id, payload) {
const url = 'https://api.notion.com/v1/databases/'+id+'/query/';
const options = {
method: 'post',
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer '+notionToken,
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Notion-Version': '2022-06-28'
},
payload: JSON.stringify(payload)
};
const result = UrlFetchApp.fetch(url, options);
return JSON.parse(result.getContentText());
}
ics.html :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
BEGIN:VCALENDAR
PRODID:-//Google Inc//Google Calendar 70.9054//EN
VERSION:2.0
CALSCALE:GREGORIAN
METHOD:PUBLISH
X-WR-CALNAME:NotionCalendar
X-WR-TIMEZONE:Asia/Taipei
BEGIN:VTIMEZONE
TZID:Asia/Taipei
X-LIC-LOCATION:Asia/Taipei
BEGIN:STANDARD
TZOFFSETFROM:+0800
TZOFFSETTO:+0800
TZNAME:CST
DTSTART:19700101T000000
END:STANDARD
END:VTIMEZONE
<?
for(const eventIndex in events) {
const event = events[eventIndex];
?>
BEGIN:VEVENT
DTSTART:<?=event["start"]?>
DTEND:<?=event["end"]?>
DTSTAMP:<?=event["edit"]?>
UID:<?=event["id"]?>
CREATED:<?=event["create"]?>
LAST-MODIFIED:<?=event["edit"]?>
SEQUENCE:0
STATUS:CONFIRMED
SUMMARY:<?=event["title"]?>
DESCRIPTION:<?=event["description"]?>
TRANSP:OPAQUE
END:VEVENT
<?
}
?>
END:VCALENDAR
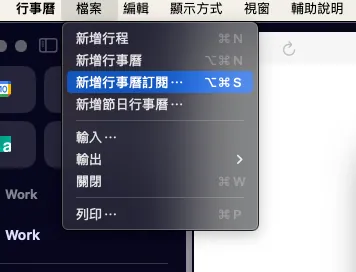
As before, deploy as a web service by clicking “Deploy” at the top right of the project -> “New Deployment” -> top left “Select Type” -> “Web App”:
- Who can access should be set to Everyone, because Google login verification cannot be completed when adding the Calendar.
Add the URL to your calendar subscription, done 🎉🎉🎉🎉 !
Business Time
If you and your team need automation tools or process integration, whether it’s Slack App development, Notion, Asana, Google Sheets, Google Forms, GA data, or any other integration, feel free to contact me for development.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to contact me.
This post was originally published on Medium (View original post), and automatically converted and synced by ZMediumToMarkdown.

](/assets/f6713ba3fee3/1*U6bzH6b5-PRxFBktvkOa2Q.webp)